![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which is more stable, cis-2-butene or trans-2-butene? Why?
|
trans-2-butene is more stable. This is because cis- alkenes undergo more steric strain between the two large constituents on the same side of the double bond.
|
|
|
What does Pd stand for?
|
Palladium, a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal
|
|
|
What does Pt stand for?
|
Platinum; a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal.
|
|
|
nucleophile
|
a Lewis base
|
|
|
The carbon-carbon double bond of an alkene is electron rich and can donate a pair of electrons to an ____________
|
electrophile (Lewis acid)
|
|
|
regiospecific
|
a chemical reaction in which one structural isomer is produced exclusively when other isomers are also theoretically possible
|
|
|
Markovnikov's rule
|
In the addition of HX to an alkene, the H attaches to the carbon with fewer alkyl substituents and the X attaches to the carbon with more alkyl substituents
|
|
|
What's the formula for phosphoric acid?
|
H3PO4
|
|
|
What is KI called?
|
potassium iodide
|
|
|
A more highly substituted carbocation forms _______ than a less highly substituted one
|
faster
|
|
|
A more highly substituted carbocation is ______ stable than a less highly substituted one
|
more
|
|
|
Draw the symbol for activation energy
|
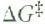
|
|
|
Hammond postulate
|
transition states represent energy maxima
THe structure of a transition state resembles the structure of the nearest stable species. Transition states for endergonic steps structurally resemble products, and transition states for exergonic steps structurally resemble reactants. |
|
|
George Simms Hammond
|
taught at UCSC
|
|
|
The fragrance of California by trees come from:
|
myrcene, a simple terpene
|

