![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What's the name for Viagra?
|
sildenafil
|
|
|
Draw cholesterol
|
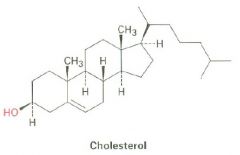
|
|
|
When did organic chemistry originate?
|
Mid-1700s
|
|
|
Who was the first chemist to distinguish between organic and inorganic?
|
Torbern Bergman in 1770
|
|
|
vitalistic theory
|
An incorrect idea that organic substances contained a "vital force" that resulted from their living origins. It was thus believed that organic compounds could not be synthesized
|
|
|
Draw the structure for urea:
|
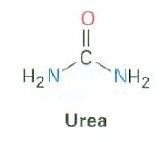
|
|
|
What is the distinguishing feature of organic chemistry?
|
That organic chemicals all contain carbon.
|
|
|
Of the ~ 30 million known compounds, how many of them contain carbon?
|
~99%
|
|
|
picometer (pm)
|
1×10^−12 m
|
|
|
angstrom (Å)
|
Often used in expressions of atomic distance; internationally recognized unit of length equal to 0.1 nanometre or 1×10^−10 metres
|
|
|
atomic number
|
number of protons in an atom
|
|
|
mass number
|
protons + neutrons
|
|
|
isotope
|
atoms with the same atomic number but a differing mass number
|
|
|
amu
|
atomic mass units; used to express atomic and molecular masses.
|
|
|
atomic mass/weight
|
the weighted average mass in amu of an element's naturally occurring isotopes
|
|
|
What's the atomic mass of hydrogen?
|
1.008
|
|
|
What's the atomic mass of carbon?
|
12.011
|
|
|
What's the atomic mass of phosphorous?
|
30.974
|
|
|
ψ
|
psi
|
|
|
Draw an s orbital
|

|
|
|
Draw a p orbital
|
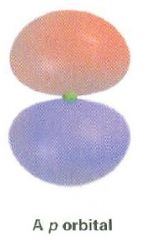
|
|
|
Draw a d orbital
|
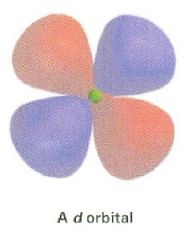
|
|
|
electron shells
|
orbital layers of successively larger size and energy
|
|
|
What's the capacity of the first electron shell?
|
2 electrons
1s |
|
|
What's the capacity of the second electron shell?
|
8 electrons
1s2s2p |
|
|
What's the capacity of the third electron shell?
|
18 electrons
1s2s2p3s3p3d |
|
|
How are the electrons of each orbital represented?
|
Up and down arrows
|
|
|
How are the three different p orbitals written?
|
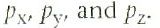
|
|
|
node
|
the area between orbitals containing zero electron density
|
|
|
Draw a 2px orbital
|
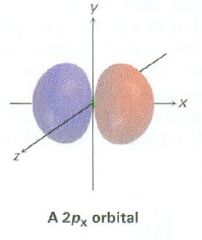
|
|
|
Draw a 2py orbital
|
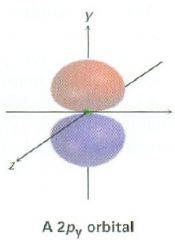
|
|
|
Draw a 2pz orbital
|
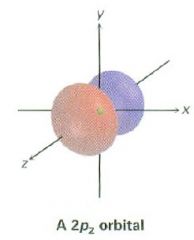
|
|
|
ground-state electron configuration
|
the lowest energy arrangement of an atom
|
|
|
aufbau principle
|
lowest energy orbitals fill up first
1s --> 2s --> 2p --> 3s --> 3p --> 4s --> 3d |
|
|
Pauli exclusion principle
|
Only two electrons can occupy an orbital
|
|
|
Hund's rule
|
If two or more empty orbitals of equal energy are available, one electron occupies each with spins parallel until all orbitals are half-full
|
|
|
What is carbon's ground state configuration?
|
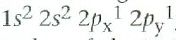
|
|
|
Draw out the ground state configuration of phosphorous
|
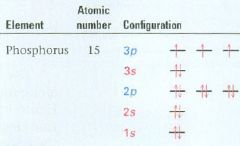
|
|
|
tetravalent
|
forms four bonds (e.g., carbon)
|
|
|
Does making bonds release or absorb energy?
|
release
|
|
|
Does breaking bonds release or absorb energy?
|
absorbs
|
|
|
valence shell
|
the outermost shell
|
|
|
ionic bonds are caused by?
|
electrostatic attraction
|
|
|
molecule
|
the neutral collection of atoms held together by covalent bonds
|
|
|
Lewis structure
|
electron-dot structure
|
|
|
Kekule structures
|
line-bond structure
|
|
|
What's the formula for ammonia?
|
NH3
|
|
|
What's the formula for methanol?
|
CH3OH
|
|
|
lone pair electrons
|
valence electrons not used for bonding
|
|
|
What's the formula for chloroform?
|
CHCl3
|
|
|
valence bond theory
|
covalent bond forms when two atoms approach each other closely and a singly occupied orbital on one atom overlaps a singly occupied orbital on the other atom
|
|
|
σ
|
sigma
|
|
|
sigma (σ) bond
|
bond formed by the head-on overlap of two atomic orbitals
|
|
|
bond length
|
the optimum distance between nuclei, where atoms are neither repelled due to proximity or are too far apart to bond
|
|
|
Draw four sp^3 orbitals
|
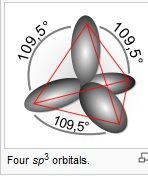
|
|
|
Draw an sp^3-sp^3 alpha bond
|

|
|
|
What's the formula for ethylene?
|
C2H4
|
|
|
pi bond
|
covalent chemical bonds where two lobes of one involved electron orbital overlap two lobes of the other involved electron orbital.
|
|
|
What's the formula for formaldehyde?
|
CH2O
|
|
|
organophosphate
|
compound that contains a phosphorous atom bonded to four oxygens, with one of the oxygens also bonded to a carbon
|
|
|
sulfide
|
compounds which have a sulfur atom bonded to two carbons
|
|
|
thiol
|
sulfur atom bonded to one hydrogen and one carbon
|
|
|
condensed structures
|
structures drawn where the bonds aren't shown.
e.g. CH3CH2CH3 |
|
|
skeletal structures
|
where carbon and hydrogen symbols are omitted and bonds are drawn as lines
|
|
|
hyponatremia
|
an electrolyte disturbance in which the sodium concentration in the serum is lower than normal
can be lethal |
|
|
sp^3 is caused by ______ bonds
|
single
|
|
|
sp^2 is caused by ______ bonds
|
double
|
|
|
sp is caused by ______ bonds
|
triple
|
|
|
Vitamin C is also called:
|
ascorbic acid
|
|
|
Are vitamin C and citric acid the same thing?
|
No@
|
|
|
NutraSweet is?
|
aspartame
|
|
|
How many valence electrons in iron?
|
2 (in 4s subshell), 6 (in 3d subshell)
|
|
|
At what angles are the bonded carbons of a benzene ring?
|
120 degree
|
|
|
Advil is made from?
|
ibuprofen
|
|
|
Tylenol is made from?
|
acetaminophen
|
|
|
Aleve is made from?
|
naproxen
|
|
|
In a solid line structure, a dashed bond represents:
|
The bond pointing towards the viewer.
|
|
|
In a solid line structure, a wedged bond represents:
|
The bond pointing away toward the viewer.
|
|
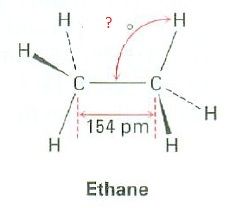
What's the bond angle?
|
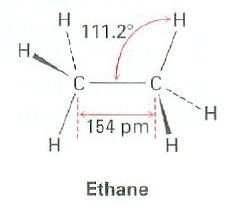
|
|
|
How will a carbon structure with a triple bond orient itself?
|
In a straight line
-C:::C- |
|
|
carbocation
|
an ion with a positively-charged carbon atom
|
|
|
A positively charged carbon is ____ hybridized
|
sp2
|
|
|
carbanion
|
an anion in which carbon has an unshared pair of electrons and bears a negative charge usually with three substituents for a total of eight valence electrons
|
|
|
isoelectric
|
having the same number of electrons
|
|
|
carbene
|
a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is RR'C:
|
|
|
A carbanion is _______ hybridized
|
sp3
|
|
|
Draw a single and a triple methylene.
|
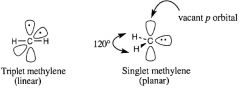
|

