![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The octet rule applies to which elements? |
All main group elements except hydrogen, lithium, boron and aluminum |
|
|
What is the octet rule? |
Stable electron configuration consists of 8 electrons in valence shell |
|
|
Hydrogen and lithium need how many valence electrons to be stable? |
2 |
|
|
When drawing Lewis structures for Ionic compounds, which ions are inside brackets? |
The anions |
|
|
Electron geometry |
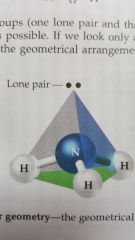
The geometry of a molecule including the bonds and lone pairs around the central atom. |
|
|
Molecular geometry |
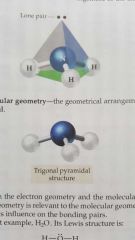
The geometry of a molecule including electron groups and EXLUDING lone pairs around central atoms. |
|
|
Molecular geometry and bond angle of molecule with 2 EG (electron groups) and zero lone pairs around central atom? |
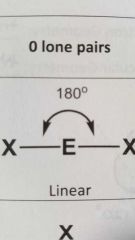
Linear 180° |
|
|
Molecular geometry and bond angle of a moleule with 2 EGs and 1 lone pair around central atom? |
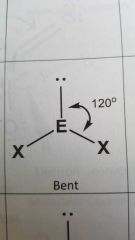
Bent 120° |
|
|
Molecular geometry and bond angles of molecule with 3 EGs and zero lone pairs around central atom? |
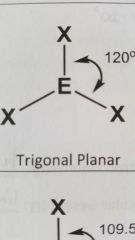
Trigonal Planar 120° |
|
|
Molecular geometry and bond angle of molecule with 4 E.G.s and zero lone pairs around central angal? |
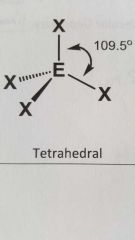
Tetrahedral 109.5° |
|
|
Molecular geometry and angle of molecule with 3 EGs and 1 lone pair around central atom? |

Trigonal Pyramidal <109.5° |
|
|
Molecular geometry and bond angle of molecule with 2 EGs and 2 lone pairs around central atom? |
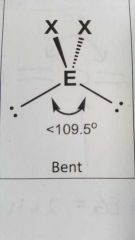
Bent <109.5° |
|
|
Why can VSEPR predictions of bond angles slightly deviate from the actual angles? |
Because lone pairs occupy more space th and atoms |
|
|
Electronegativity |
Measure of how much an atom "takes/wants" shared electrons in a covalent bond |
|
|
What does it mean for one atom to be more electronegative than another? |
Shared electrons are more likely to be found near the more electronegative atom |
|
|
How and in which directions on the periodic table does electronegativity change? |
Electronegativity INCREASES from bottom up and left to right (excluding noble gases) |
|
|
The most electronegative element? |
Flourine |
|
|
The bigger the difference in electronegativity between the 2 atoms involved in a bond... |
the more polar the bond is |
|
|
Dr Dong's bond polarity scale by change in elecronegativity between TWO atoms |
Between 0 to .4 = Non-polar Covalent Between .4 to 2 = Polar Covalent Greater than 2.0 = Ionic |
|
|
Net dipole |
The sum of all individual dipoles in a molecule |
|
|
When drawing a Lewis Structure, which atom is the central atom? |
The least electronegative |
|
|
How does polarity relate to solubility? |
The more polar a substance, the more soluble it is |
|
|
Do lone pairs count as an Electron Group? |
Yes |
|
|
How many electron groups is a triple bond? |
One |
|
|
Which elements are exceptions to the octet rule? |
Hydrogen Lithium Aluminum Boron |
|
|
How many electrons does Boron and Aluminum need to be stable in a bond? |
6 (Sextet Rule) |

