![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Excited state (of an electron) |
Highest energy level |
|
|
Ground state (pertaining to an electron) |
Lowest energy level |
|
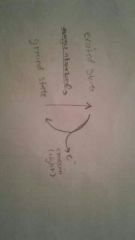
|
When an e- is excited, it absorbs energy (photons). As is it falls back from the excited state to ground state, it releases the energy in the form of light. |
|
|
E=hv |
V=frequency H=planck's constant (6.626×10^ -34) E=energy |
|
|
Frequency |
The higher the frequency, the higher the energy. |
|
|
deBroglie |
E- have dual waves and particle natjre E=hv -to determine energy from the wavelength E- are considered waves around nucleus |
|
|
R O Y G B I V |
- visible light spectrum - red= longest wavelength, lowest frequency - violet= shortest wavelength, highest frequency |
|
|
Hund's Rule |
Fill all orbitals with ONE e- before you double them up |
|
|
Pauli Expulsion Principle |
No two e- can have the same four quantum numbers |
|
|
Auffbau Principle |
An e- will occupy the lowest orbital that can receive it |
|
|
Eisenburg |
You CANNOT detect the location or velocity of an e- |
|
|
Chromim Copper Tungsten |
Don't follow the rules because they are more stable in a lower configuration |
|
|
2n^2= |
Number of electrons *n=energy level |
|
|
Speed of light |
3×10^8 |
|
|
Quantum Numbers |
Principle Quantum Number: n, energy level, 1- 7 Angular Momentum Number: l, shape, s=○, p=dumbell Magnetic Number: orientation of orbital around 0 Spin: opposite spins, +1/2 - 1/2 |
|
|
Bohr Model |
E- travel in orbitals around the nucleus- WRONG!!! |
|
|
Always a Noble Gas if... |
8 e- in highest energy level (1,2,3,4,5...) All sublevels are full--> NONREACTIVE |
|
|
Photoectric effect |
When you shine light on metal, it releases e- |
|
|
Quantum |
Minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom |
|
|
Photon |
Particle of electromagnetic radiation that has 0 mass and carries quantum energy |
|
|
Electromagnetic radiation |
Form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior |
|
|
Electron configuration |
Arrangement of e- Ground state e- co figuration Lowest energy arrangement |

