![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Personal Risk management checklist |
P - Pilot health (IMSAFE checklist) A - aircraft airfworthy (ARROW checklist) V - enVironment E - external pressures |
PAVE |
|
|
I M S A F E |
I - current/recent illness M - taking medications S - stress psychological/anxiety A. -, Alcohol in last 8hrs F - Fatigue E - emotionally upset? |
IMSAFE |
|
|
Aircraft inspections |
A -, Airworthiness Directives V - VOR check 30days/IFR I - inspections annual/100hr A - Altimeter 24 calendar Mo./IFR T - Transponder 24 calendar months E - E.L.T. 12 calendar 1hr use or 1/2 battery life S - static system 24 Months IFR |
|
|
|
Private pilot license requirements |
•Be at least 17 years old to receive a Private Pilot certificate •read speak write and understand English •obtain at least a third class medical certificate •pass a knowledge test with a 70% or better •logbook endorsements certifying aeronautical knowledge and flight proficiency |
|
|
|
Prognostic charts |
Issued four times daily, Valid for the time specified, usually 12, 24, 36, 48 hours |
|
|
|
Surface analysis charts |
Computer generated charts with frontal and pressure analysis. Issued every 3 hours, lower left corresponds the time of observation Informations about 2 to 3 hours old It's all observed data |
|
|
|
What is trough |
It's a elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure often associated with fronts. Most bring clouds showers and wind shift. |
|
|
|
What is TAF |
Terminal aerodrome forecast Normally valid for 24 hours |
|
|
|
What is a METAR |
Meteorological terminal air report Usually issued 55 minutes after the hour |
|
|
|
What do you need to form a thunderstorm, and it's stages |
Moisture, unstable air, and lift
The cumulus stage Mature stage Dissipating stage |
|
|
|
Supplement oxygen requirements |
Above 12500 feet flight crew must use oxygen longer than 30 minutes Altitudes above 14000 feet crew members must use oxygen Altitudes above 15000 feet each occupant must be provided with oxygen |
|
|
|
PreFlight planning acronym |
N - Notams W - Weather K - Known ATC Delays R - Runway lengths A - Alternates F - Fuel Requirements T - Takeoff/Landing Distance |
|
|
|
Special use airspace are |
M – Military Operations Area (MOA) C – Controlled Firing Area P – Prohibited Area R – Restricted Area A – Alert Area W – Warning Area N – National Security TFR
Prohibited airspace •depicted as a p + # Restricted airspace •picked it as a r + # Usually has altitude use Military operations area •M.O.A. establish to separate IFR from Military training activities Dipicted in magenta Warning areas • similar to MOA Alert areas •high volumes of pilot training Parachute jumping glider towing Non-regulatory in nature Temporary flight restrictions • if a type of notam restricting Air travel due to a hazard, special Event, or general warning National security areas •depicted inside a magenta dash Similar to class echo but larger Controlled firing areas • they are not depicted on maps. When radar or a spotter sees a plane activities are stopped. |
|
|
|
Effects of a forward CG |
Increased longitudinal stability Lower Cruise speed (higher AOA =lift, more drag) Higher stall speed |
|
|
|
Effects of a aft CG |
Decreased longitudinal stability Higher Cruise speed Lower stall speed Poor stall / spin recovery |
|
|
|
What is maneuvering speed
|
V.a speed (as weight increases VA increases)
It is the speed at which full deflection of a single flight control should not cause damage to the plane. For 172 Cessna 2550lb = 105kias 2200lb = 98kias 1900lb = 90kias |
|
|
|
Cessna 172 load factor limits |
Normal category 2550 lb Flaps up +3.8 g or -1.52 g Flaps down +3.0g Utility category 2000lbs Flaps up +4.4 g, -1.76 g Flaps down +3.0 g
|
|
|
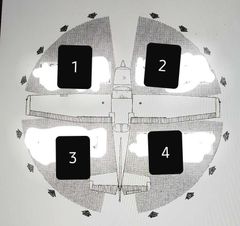
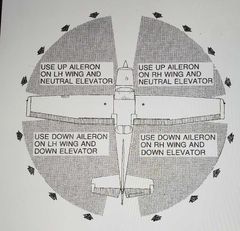
Wind direction during taxi |
|
|
|
|
Bus 2 Cessna 172 |
Electrical 2 Instrument & ignition fuel landing beacon flaps
Avionics 2 Avionics fan GPS Nav / com 1 Headset, speaker Autopilot, ADF |
|
|
|
Bus 1 Cessna 172 |
Electrical Turn coordinator Control wheel Map lights Strobe lights Taxi lights Pitot heat
Avionics HSI and Gyro Autopilot Transponder ADF Nav / com2 Speaker power Receiver |
|
|
|
Cabin heating and ventilation and defrosting system |
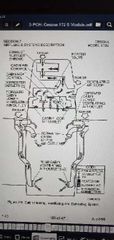
For heating, Ram air over exhaust muffler shroud, through heater valve, (controlled by cabin air control), to cabin floor, and defroster outlets.
For ventilation system, Ram air, right side through cabin floor, and defroster outlets.
Ram air, 1 on each front of the wing, through lower ventilation air outlet, forward cabin upper air outlets, and rear cabin, ventilating are outlets |
|
|
|
Vacuum system |
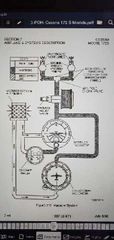
Through vacuum system air filter, Into attitude indicator and vacuums,/ amp gauge. Then through directional indicator.
Then through vacuum relief valve, through manifold check valve, through low vacuum switches, sucked through engine driven vacuum pump, out overboard Vent lines. |
|
|
|
V speeds Va VFe vne V.s Vno so Vso vx vy
|
VA is maneuvering speed 2550 lb 105 indicated2200 lb 98 indicated1900 lb 90 indicated Vfe is maximum flap extended speed 110 indicated at 10% 85 indicated 10 to 30% Vno is Max structural Cruise speed 129 indicated Vne is never exceed speed 163 indicated Vs is stalling speed or the minimum steady flight speed in cruise 48 indicated Vso is the stalling speed in the landing configuration 40 indicated Vx is the best angle of climb speed Vy best rate of climb speed |
|
|
|
ATC light signals Steady green air/ ground Flashing green air / ground Steady red air / ground Flashing red Flashing white Red green alternating |
Steady green, cleared for takeoff on ground, clear to land, during flight. Flashing green, cleared to taxi, on ground, return for landing, in air. Steady red, stop on ground, give-way or continue circling in air. Flashing red, taxi clear of runway, on ground, airport unsafe, do not Land, in air. Flashing white, return to starting point, on airport ground, not applicable in air. Alternating red and green, exercise extreme caution, both ground and air. |
|
|
|
Pilotage vs. Dead reckoning |
Pilotage is the art of knowing where you are by reading a map and comparing it with surrounding terrain and landmarks. dead reckoning is the art knowing where you currently are by using a compass your ground speed a clock and an initial note position |
|
|
|
5 C's for lost procedures |
Confess Conserve Climb Communicate Comply |
|
|
|
Recover from a spin acronym |
P -power retard throttle to idle A -aileron's neutral R- full apposite rudder E- forward elevator D- recover from dive |
|
|
|
A,B,C,D,E ,checklist aviation emergency landing |
A, airspeed B, best place to land C, checklist D, declare emergency E, execute emergency landing |
|
|
|
How long are first, second, and third class medicals good for? |
3rd class Medical under 40, 60 months. Third class Medical over 40, 24 months. First class Medical 12 months under 40. First class Medical 6 months over 40. 2nd class Medical 12 months regardless of age. |
|
|
|
Low pressure versus high pressure direction |
Low pressure is counterclockwise, high pressure is clockwise |
|
|
|
Airmets and what types |
Type S, mountain obscuration, ceilings are less than a 1000'. Type T, light to moderate turbulence or substantial surface winds of 30 knots. Type Z, moderate icing and freezing levels.
Airmets are normally for general aviation. Valid for 6 hours at a time |
|
|
|
Sigmets |
Sigmets last for 2 hours Can be issued for actual or forecasted weather Classified as either convective or non convective Non convective for severe or greater turbulence or dust / Ash Convective are for thunderstorms • 3/4 lnch hail • rain covering 40% or more of a 3000 square miles. • surface winds greater than or equal to 50 knots Tornadoes Embedded thunderstorms or a line of thunderstorms |
|
|
|
Types of air speeds |
Indicated airspeed is read right off of your airspeed indicator
Calibrated airspeedit is the indicated AirSpeed corrected for instrument and positional errors
true AirSpeed is a speed of your aircraft relative to the air it is flying through. Example: at 10000 feet true AirSpeed is roughly 20% faster than what you would read off of your airspeed indicator
Ground speed the movement of your airplane relative to the ground is called ground speed
|
|
|
|
Illusions of flight
I C E F L A G G S |
I - Inversion illusion C - Coriolis illusion E - Elevator illusion F - False horizon L - leans A - Autokinesis G - Graveyard spin G - Graveyard spiral S - Somatogravic illusion |
|
|
|
Coriolis illusion |
Caused by making quick head movements during a constant rate turn. most common of this is during a 180 degree turn, pilot drop something, picks it up, and believes they are in straight and level flight. |
|
|
|
Graveyard spin |
the pilot recovering from a spin, that was stopped, the fluid in the inner ear, can create the illusion that he or she has entered a spin in the other direction, there by possibly entering the original spin. |
|
|
|
Graveyard spiral |
As your plane banks, if you don't increase back pressure on the yoke, it starts descending as well. This becomes a problem in a big hurry. As your plane starts descending faster and faster, you realize what you 'think' is happening, which is a wings-level descent. But in reality, you're in a banked descent. You correct by pulling back on the yoke, but you don't level the wings. |
|
|
|
Somatogravic illusion |
this is caused usually during takeoff, the rapid acceleration pushes the pilot back in his or her seat, giving them the sensation of a nose up attitude, to correct the pilot noses the plane over towards the Earth, a rapid deceleration has the opposite effect. |
|
|
|
Inversion illusion |
a quick change from a climb to level flight makes a pilot feel as though he, or she is stumbling backwards, the natural tendency is to nose the aircraft over which actually intensifies illusion. |
|
|
|
Elevator illusion |
on a turbulent day, an up draft could cause extreme vertical acceleration, the pilot then proceeds to nose over the aircraft. This illusion also has the opposite effect with downdrafts. although intense this illusion presents the least of troubles considering that usually happens at higher altitudes |
|
|
|
False horizon |
a false horizon can be caused by City lights, clouds, Stars, or darkness. it causes the pilot to believe that he,/she is not level to the horizon, the pilot falsely corrects , and places the aircraft in this dangerous attitude. |
|
|
|
Autokinesis |
at night when a light is stared at for a long time, it begins to move. while flying at night pilots should not stare at stationary lights for long periods of time, to avoid this sensation. |
|
|
|
Types of structural icing |
Clear, Mixed, Rime,
Clear ice typically forms when temperatures are around 2 ° C. to -10° C. and with the presence of large water droplets freezing drizzle, or freezing rain. Clear ice is the most dangerous type of structural ice not only because it is hard to see, but also because it can change the shape of the airfoil. In addition, clear ice often forms well beyond the ice-protected areas of the aircraft. Rime ice forms when small droplets freeze immediately on contact with the aircraft surface. It typically occurs with temperatures between -15° C. and -20 ° C. Rime ice has a milky, opaque appearance resulting from air trapped when it strikes the leading edge of an airfoil and freezes. It is less dense, and usually easier to remove than clear ice. Rime ice tends to form wedge-shaped accretions that do not disturb airflow as much as clear ice.
Mixed ice, a combination of clear ice and rime ice that has the worst characteristics of both, can form rapidly when ice particles become embedded in clear ice and build a very rough accumulation. Mixed ice is most likely to form at temperatures between -10° C to -15° C.
|
|
|
|
Acronym for the Cessna 172 |
L - lycoming IO 360 - L2A H - horizontally opposed A - air-cooled N - normally aspirated D - direct drive IO = injected opposed 360 = displacement in cubic centimeters L2A = model number |
|
|
|
Right of way |
1 Aircraft in distress 2 Balloons 3 Gliders 4 aerial refueling and towing 5 Airships 6 Everyone else
Plane on the right has right off way, Aircraft being overtaken has right off way, Head on, both turn right, Lower aircraft has right off way, Landing aircraft has the right is way over aircraft, or vehicles on the ground,
Pilot may not use these rules to cut anyone off. |
|
|
|
Types of fog |

|
|
|
|
What is a Notam |
Notice To Airmen or NOTAM is a notice containing information concerning the establishment, condition, or change in any component. the timely knowledge of which is essential to personnel concerned with flight operations. This could be a closed taxiway, a notification about construction cranes or maintenance on a navigation aid. |
|
|
|
Types of Notams |
CLASS I CLASS II INTERNATIONAL DOMESTIC CIVIL MILITARY PUBLISHED FDC CENTER AREA NOTAM (D)S INCLUDING (U) AND (O)
|
|
|
|
During pre-flight an instrument or equipment item is inoperative. Describe how you will determine if the aircraft is still airworthy for flight. |
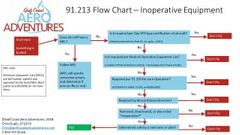
Does the aircraft have a MEL? Yes : use MELNo: is it required for day VFR (ATOMATOFLAMES) yes- don't fly.No: Is it required or kinds of operation equipment list. yes - don't fly No: required for 91.205 for your operation? Yes -don't fly No: is it required by airworthiness directive (A.D.). Yes - don't fly No - remove deactivate or placard inoperative. No - don't fly Yes - determine safe by mechanic or Pilot? Yes - fly No - don't fly. |

