![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
203 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Elements combine with each other to form _____________. |
compounds |
|
|
Describe the proportions that occur when mixing a Hydrogen-Oxygen mixture. |
A H-O mixture can have any proportions of H and O gas. |
|
|
Describe H-O proportions of H-O compounds. |
Definite proportions |
|

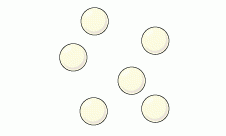
Name this picture |
Mixture |
|

Name this picture |
Compound |
|
|
How are compounds held together? |
With chemical bonds |
|
|
How do chemical bonds form? |
From attractions between the charged particles (the electrons and protons) that compose atoms. |
|
|
Two types of chemical bonds: |
1. Ionic 2. Covalent |
|
|
Ionic bonds occur between what? |
Metals and Nonmetals |
|
|
When a metal interacts with a nonmetal, it does what?
The metal atom becomes what? The nonmetal? |
It can transfer one or more of its electrons to the nonmetal
The metal atom becomes a cation and the nonmetal atom becomes an anion. |
|
|
How do oppositely charged attract one another? What do they form? |
electrostatic forces
ionic bond |
|
|
Describe an ionic compound. |
in the solid phase its composed of a crytalline lattice - a regular 3D array - of alternating cations and anions |
|
|
Covalent bonds occur between what? |
two or more nonmetals |
|
|
What do covalent bonds involve? |
The sharing of electrons between two atoms |
|
|
What happens when a nonmetal bonds with another nonmetal? |
Neither atom transfers its electron to the other. Instead, the bonding atoms share some of their electrons. |
|
|
What do the covalently bound atoms compose? |
A molecule; hence, we call covalently bonded compounds molecular compounds |
|
|
What does a chemical formula indicate? |
Indicates the elements present in the compound and the relative number of atoms or ions in each |
|
|
Chemical formulas can generally be categorized into three different types: |
1. Empirical Formula 2. Molecular Formula 3. Empirical Formula |
|
|
Define empirical formula |
gives the relative number of atoms of each element in a compound |
|
|
Define molecular formula |
gives the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule of a compound |
|
|
Give the empirical formula for the following: 1. C4H8 2. B2H6 3. CCl4 |
1. CH2 2. BH3 3. the EF and the MF are identical |
|
|
Define structural formula |
uses lines to represent covalent bonds and shows how atoms in a molecule are connected or bonded to each other |
|
|
What is the this an example of?
H - O - O - H |
The structural formula for H2O |
|
|
Out of the three possible chemical formulas, which one communicates the most information? The least information? |
The structural formula
The empirical formula |
|
|
What is a more accurate and and complete way to specify a compound? |
A molecular model |
|
|
Define a ball-and-stick molecular model |
represents atoms as balls and chemical bonds as sticks; and how the two connect reflects a molecule's shape; balls are typically color-coded to specific elements |
|
|
Define a space-filling molecular model |
atoms fill space between each other to more closely represent our best estimates for how a molecule might appear if scaled to visible size |
|
|
Name the two molecule models: |
1. Ball and stick 2. Space filling |
|
|
Elements may either be _________ or ___________. |
atomic or molecular |
|
|
Compounds may either be __________ or _________. |
Molecular or ionic |
|

Name this picture |
Molecular elements |
|
Name this picture |
Atomic element |
|
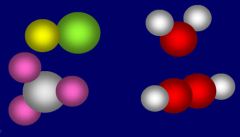
Name this picture |
Molecular compounds |
|
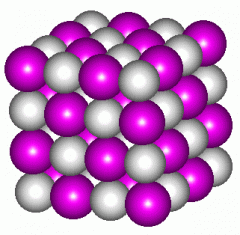
Name this picture |
Ionic Compound |
|
|
Define atomic elements |
exist in nature with single atoms as their basic units
*most elements fall into this category |
|
|
Define molecular elements |
do not normally exist in nature with single atoms as their basic units; instead, they exist as molecules - two or more atoms of the element bonded together |
|
|
Name the 7 diatomic elements. |
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, and I2 |
|
|
Name the two polyatomic elements. |
P4, S8, Se |
|
|
Define molecular compounds |
usually composed of two or more covalently bonded nonmetals; the basic units are molecules composed of constituent atoms |
|
|
Define ionic compounds |
Composed of cations (usually a metal) and anions (usually one or more nonmetals) bound together by ionic bonds; the basic unit is the formula unit, the smallest, electrically neutral collection of ions |
|
|
Most common ionic compounds contain ions that are themselves composed of a group of covalently bonded atoms with an overall charge. What is this group of charges species called? |
Polyatomic ions |
|
|
Ionic compounds always contain _______ and _______ ions. |
positive
negative |
|
|
In a chemical formula, the sum of the charges of the _________ ions must equal the sum of the charges of the ___________ ions. |
positive
negative |
|
|
The formula of an ionic compound reflects the __________ whole-number ratio of ions. |
smallest |
|
|
How are charges of representative elements predicted? |
From their group numbers |
|
|
Anytime you see a ______ and one or more __________ together in a chemical formula, assume that you have an ionic compound. |
metal, nonmetals |
|
|
Ionic compounds can be categorized into two types, depending on what? |
On the metal in the compound |
|
|
The first type of ionic compound: |
contains a metal whose charge is invariant from one compound to another
whenever the metal forms an ion, the ion always has the same charge |
|
|
The second type of ionic compound: |
contains a metal with a charge that can differ in different compounds
the metals can form more than one kind of cation (depending on the compound)
*often transition metals |
|
|
Define binary compounds; type 2 binary ionic compounds take what form? |
contain only two different elements; [Name of cation (metal)][base name of anion (nonmetal) + -ide] |
|
|
Name for KCl. |
Potassium Chlorideq |
|
|
Name for CaO. |
Calcium Oxide |
|
|
How do you name Type 2 binary ionic compounds? What does the form look like? |
The name of the cation is followed by a roman numeral (in parentheses) that indicates the charge of the metal in that particular compound
[Name of cation (metal)][charge of cation in roman numerals][base name of anion (nonmetal) + -ide] |
|
|
Determine the charge of Cr in CrBr3 then write out the name. |
Br has a charge of -1. x + 3(-1) = 0 x = +3 meaning the charge for chromium is +3
Name: Chromium(III) bromide |
|
|
How do you name ionic compounds that contain a polyatomic ion? |
In the same way as other ionic compounds, except that we use the name of the polyatomic ion whenever it occurs. |
|
|
Name NaNO2 |
Sodium Nitrite |
|
|
Name C2H3O2 with a 1- charge |
Acetate |
|
|
Name CO3 with a 2- charge |
Carbonate |
|
|
Name HCO3 with a 1- charge |
Hydrogen carbonate or bicarnonate |
|
|
Name OH 1- charge |
Hydroxide |
|
|
Name NO2 1- charge |
Nitrite |
|
|
Name NO3 1- charge |
Nitrate |
|
|
Name CrO2 2- charge |
Chromate |
|
|
Name Cr2O7 2- charge |
Dichromate |
|
|
Name PO2 3- charge |
Phosphate |
|
|
Name H2PO4 1- charge |
Dihydrogen phosphate |
|
|
Name HPO4 2- charge |
Hydrogen phosphate |
|
|
Name NH4 1+ charge |
Ammonium |
|
|
Name ClO 1- charge |
Hypochlorite |
|
|
ClO2 1- charge |
Chlorite |
|
|
ClO3 1- charge |
Chlorate |
|
|
ClO4 1- charge |
Perchlorate |
|
|
MnO4 1- charge |
Permanganate |
|
|
SO3 2- charge |
Sulfite |
|
|
HSO3 1- charge |
Hydrogen sulfite or bisulfite |
|
|
SO4 2- charge |
Sulfate |
|
|
HSO4 1- charge |
Hydrogen sulfate or bisulfate |
|
|
CN 1- charge |
Cyanide |
|
|
O2 2- charge |
Peroxide |
|
|
Most polyatomic ions are ____________. |
oxyanions |
|
|
Define oxyanions |
anions containing oxygen and another element |
|
|
When a series of oxyanions contains a different number of oxygen atoms, how are they named? |
According to the number of oxygen atoms in the ion |
|
|
If there are two ions in the series, the one with more oxygen atoms has the ending ______ and the one with fewer has the ending ______. |
-ate -ite |
|
|
If there are more than two ions in the series then the prefixes _____, meaning less than, and ____, meaning more than, are used. |
Hypo- per- |
|
|
Define Hydrates |
ionic compounds containing a specific number of water molecules associated with each formula unit |
|
|
What is this an example of? MgSO4 * 7H2O |
A Hydrated ionic compound by the name of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate |
|
|
Hydrate prefixes: 1. hemi = ? 2. mono = ? 3. di = ? 4. tri = ? 5. tetra = ? 6. penta = ? 7. hexa = ? 8. hepta = ? 9. octa = ? 10. nona = ? 11. deca = ? |
1. 1/2 2. 1 3. 2 4. 3 5. 4 6. 5 7. 6 8. 7 9. 8 10. 9 11. 10 |
|
|
How do you name molecular compounds? What does the the form look like? |
generally write the name of the element with the smallest group number first; if they lie in the same group, then write the element with the greatest row number first [prefix][name of first element][prefix][base name of 2nd element + -ide] |
|
|
Define acids |
molecular compounds that release Hydrogen ions when dissolved in water |
|
|
How are acids named? |
composed of hydrogen, usually written first in their formula, and one or more nonmetals, written second |
|
|
HCl is a molecular compound that, when dissolved in water, forms H (aq) and Cl (aq) ions where aqueous means what? |
dissolved in water |
|
|
True or False: A compound is not considered an acid if it does not dissolve in water. |
True |
|
|
Acids can be broken down into two types: |
1. Binary acids which contain only two elements 2. Oxyacids which contain oxygen |
|
|
Define binary acids |
Have H cation and nonmetal anion |
|
|
Define oxyacids |
Have H cation and polyatomic anion |
|
|
How do you name binary acids? What does the form look like? |
Write hydro- as prefix, follow with the nonmetal name, change the ending of the nonmetal to -ic, then write the word acid at the end [hydro][base name of nonmetal + -ic][acid] |
|
|
How do you name Oxyacids? |
If polyatomic ion name ends in -ate, then change ending to -ic suffix. If polyatomic ion name ends in -ite, then change ending to -ous suffix. Write word acid at the end of all names. |
|
|
Name H2S |
Hydrosulfuric acid |
|
|
Name HClO3 |
Chloric acid |
|
|
Name HC2H3O2 |
Acetic acid |
|
|
When name ends in _____, formulas start with H. |
acid |
|
|
_______ prefix means it is binary acid; no prefix means it is an oxyacid. |
Hydro- |
|
|
How is acid rain formed? |
Certain pollutants - such as NO, NO2, SO2, SO3 - form acids when mixed with water |
|
|
Define formula mass |
The mass of an individual molecule or formula unit The sume of the masses of the atoms in a single molecule or formula unit |
|
|
Define the molar mass |
the mass in grams of 1 mol of its molecules or formula units - is numerically equivalent to its formula mass |
|
|
How to find the empirical formula: |
1. Convert % to grams (assume you start with 100 g of the compound and skip if already in grams) 2. Convert grams to moles (use molar mass of each elemetn) 3. Write pseudoformula using moles as subscripts 4. Divide by the smallest # of moles 5. Multiply all mole rations by a # to make all whole numbers |
|
|
Describe combustion analysis |
A common technique for analyzing compounds is to burn a known mass of compound and weigh the amounts of product made. By knowing the mass of the product and composition of constituent element in the product, the original amount of constituent element can be determined. Once the masses of all the constituent elements in the original compound have been determined, the EF can be found. |
|
|
How does one show that a reaction obeys the Law of Conservation of Mass? |
The equation must be balanced |
|
|
Two types of compounds: |
1. Organic 2. Inorganic |
|
|
Define organic compounds |
Compounds from living things that are easily decomposed but used to not be be made in labs Today however, they are commonly made in labs. |
|
|
Define inorganic compounds |
Compounds from nonliving things that are very difficult to decompose but are able to be synthesized |
|
|
What is the main element that is the focus of organic chemistry? |
Carbon |
|
|
Carbon atoms bond almost exclusively __________. |
covalently |
|
|
When C bonds, how many covalent bonds does it have? |
4 |
|
|
Organic compounds can be categorized into two types: |
1. Hydrocarbons 2. Functionalized hydrocarbons |
|
|
Define hydrocarbons |
organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen compose common fuels such as oil and gas |
|
|
Hydrocarbons containing only single bonds are called what? |
Alkanes |
|
|
Hydrocarbons containing double or triple bonds are called what? |
Alkenes and alkynes |
|
|
How do you name hydrocarbons? |
Base name and suffix |
|
|
Base names for # of hydrocarbons? (1 to 10) |
1 = meth 2 = eth 3 = prop 4 = but 5 = pent 6 = hex 7 = hept 8 = oct 9 = non 10 = dec |
|
|
Define functionalized hydrocarbons |
The term function group derives from the functionality or chemical character that a specific atom or group of atoms imparts to an organic compound A group of organic compounds with the same functional group forms a family |
|
|
Familes in organic compounds? |
Alcohols, Ethers, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic acids, esters, amines |
|
|
What do the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere do? |
1. allow sunlight to enter the atmosphere 2. warm Earth's surface 3. prevent some of the heat generated by the sunlight from escaping |
|
|
Scientists have measured an avg _____ degrees Celsius rise in atmospheric temp since 1860. |
0.6 |
|
|
Atmospheric CO2 levels have risen ___% since 1860. |
25% |
|
|
What are two sources of increased CO2? |
1. the combustion reactions of fossil fuels we use to get energy 2. volcanic action |
|
|
Define stoichiometry |
The study of the numerical relationship between chemical quantities in a chemical reaction |
|
|
The coefficients in a chemical reaction specify the relative amounts in what? |
moles of each of the substances involved in the reaction |
|
|
Suppose that we burn 22.0 moles of C8H18; how many moles of CO2 form? |
22.0 mol C8H18 * 16 mol CO2/2 mol C8H18 = 176 mol CO2 |
|
|
The limiting reactant is? |
The reactant that will produce the smallest amount of product This reactant gets completely consumed |
|
|
The theoretical yield is? |
The maximum number of product that can be made due to the limiting reactant |
|
|
Reactants that are not completely consumed are called what? |
Excess reactants |
|
|
Define the actual yield |
The actual amound of product made in a chemical reaction |
|
|
How can you calculate the percent yield? |
Actual yield / Theoretical Yield *100 |
|
|
Homogeneous mixtures are also called ____________. |
solutions |
|
|
What is the name of the component of the solution that changes state? |
the solute |
|
|
What is the name of the component that keeps its state? |
solvent |
|
|
What happens if both components start in the same state? |
The major component is the solvent |
|
|
How are solutions often described? |
Quantitatively, as dilute or concentrated |
|
|
Define dilute solutions |
have a small amount of a solute compared to solvent |
|
|
Define concentrated solutions |
have a large amount of solute compared to solvent |
|
|
What is a common way to express solution concentration? |
Molarity (M) |
|
|
What is the equation for Molarity? |
M = amount of solute (in mol) ------------------------------------- volume of solution (in L) |
|
|
Often, solutions are stored as concentrated ________ ______________. |
stock solutions |
|
|
How do you make solutions of lower concentrations from stock solutions? Does the amount of solute change? |
add more solvent the amount of solute doesnt change, just the volume of solution |
|
|
The concentrations and volumes of the stock and new solutions are inversely proportional. What is the equation for this? |
M1*V1 = M2*V2 |
|
|
What happens when a solute dissolves? |
There are attractive forces b/w the solute particles holding them together. There are also attractive forces between the solvent molecules. When we mix the solute with the solvent, there are attractive forces b/w the solute particles and the solvent molecules. If the attractions b/w solute and solvent are strong enough, the solute will dissolve. |
|
|
What is the result when there is an uneven distribution of electrons within a water molecule? |
Causes the oxygen side of the molecule to have a partial negative charge and the hydrogen side to have a partial positive charge. |
|
|
Define strong electrolytes |
Ionic substances that completely dissociate into ions when they dissolve in water |
|
|
What is an example of a strong electrolyte? |
NaCl |
|
|
Most ____________________ dissolve in water as intact molecules. |
Molecular compounds |
|
|
Do acids dissolve in water as intact molecules? |
No |
|
|
What are acids? |
Molecular compounds that ionize when they dissolve in water. The molecules are pulled apart by their attraction for the water. |
|
|
What happens when acids ionize? |
They form H+ cations and also anions |
|
|
Acids that ionize almost 100% are called ______ _____. |
strong acids |
|
|
Acids that only ionize a small percentage are called _____ _____. |
weak acids |
|
|
Ionic compounds and strong acids are examples of what? |
Strong electrolytes |
|
|
Define weak electrolytes |
materials that dissolve mostly as molecules, but partially as ions |
|
|
Weak acids are an example of what? |
weak electrolytes |
|
|
When compounds containing a polyatomic ion dissolve, what happens to the polyatomic ion? |
the polyatomic ion stays together |
|
|
Define dissociation |
When ionic compounds dissolve in water, the anions and cations are separated from each other. |
|
|
What is this an example of?
Na2SO4 (aq) --> 2Na (aq) + S2 (aq) |
dissociation |
|
|
When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, what happens to the polyatomic group? |
the group stays together as one ion |
|
|
When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule __________ into H+ and anions. |
ionizes |
|
|
H2SO4 (aq) ---> 2H (aq) + SO4 (aq) |
Ionization |
|
|
Name the compounds that are always soluble. |
Li+, Na+, K+, and NH4+ NO3- and C2H302- |
|
|
Cl-, Br-, and I- Are they always insoluble or soluble? Do they exceptions? |
Soluble Except when these ions pair with Ag+, Hg2 2+ or Pb 2+ |
|
|
SO4 2- Always soluble or insoluble? Have any exceptions? |
Soluble Except when it pairs with Sr 2+, Ba 2+, Pb 2+, Ag+, or Ca 2+ |
|
|
OH- and S 2- Always soluble or insoluble? Any exceptions? |
Insoluble Except when they pair with Li, Na, K, or NH4. When S 2- pairs with Ca 2+, Sr 2+, or Ba 2+. When OH- pairs with Ca 2+, Sr 2+,or Ba 2+, the resulting compound is slightly soluble |
|
|
CO3 2- and PO4 3- Always soluble or insoluble? Any exceptions? |
Insoluble Except when these ions pair with Li, Na, K, or NH4 |
|
|
Define precipitation reactions |
reactions in which a solid forms when we mix two solutions |
|
|
Reactions between aqueous solutions of ionic compounds produce what? |
An ionic compound that is insoluble in water. This insoluble product is called a precipitate |
|
|
What does it mean if no precipitation occurs when two aqueous solutions are mixed? |
There was no reaction |
|
|
Define molecular equation |
An equation showing complete neutral formulas for each compound in the aqueous reaction as if they existed as molecules |
|
|
Define complete ionic equations |
In actual solutions of soluble ionic compounds, dissolved substances are present as ions. Equations that describe the material's structure when dissolved |
|
|
What are the rules of writing the complete ionic equation? |
Aqueous strong electrolytes are written as ions Insoluble substances, weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes are written in molecule form |
|
|
In complete ionic equations, sometimes some of the ions in the solution appear to be unchanged on both sides of the equation. What are these ions called and why? |
Spectator ions because they do not participate in the reaction |
|
|
Define net ionic equation |
An ionic equation in which the spectator ions are removed |
|
|
Two other important classes of reactions that occur in aqueous solution are: |
1. acid-base reactions 2. gas-evolution reactions |
|
|
Describe an acid-base reaction |
It is also called a neutralization reaction because the acid and base neutralize each other's properties. An acid reacts with a base and the two neutralize each other, producing water (or in some cases a weak electrolyte) |
|
|
Describe gas-evolutions |
a gas forms, resulting in bubbling |
|
|
In both acid-base and gas-evolution reactions, as in precipitation reactions, when do the reactions occur? |
when the anion from one reactant combines with the cation of the other -Many gas-evolution reactions are also acid-base reactions |
|
|
What are Arrhenius definitions of acid and base? |
Acid: substance that produces H+ - some acids are called polyprotic acids Base: substance that produces OH ins in aqueous solution |
|
|
Describe polyprotic acids |
These acids contain more than one ionizable proton and release them sequentially.
Ex: sulfuric acid, H2SO4 is a diprotic acid |
|
|
Describe acid-base titrations |
a substance in a solution of known concentration is reacted with another substance in a solution of unknown concentration at this point, called the endpoint, the reactants are in their stoichiometric ratio |
|
|
What is added to change the color when the solution undergoes large changes in acidity/alkalinity? |
an indicator |
|
|
At the endpoint of an acid-base titration, the number of moles of H+ equals the number of moles of OH-. This is also known as _______________. |
Equivalence point |
|
|
Define oxidation reactions |
the reactions in which electrons are transferred from one reactant to the other also called redox reactions many involve the reaction of substance with oxygen |
|
|
Losing an electron: oxidation or reduction? |
oxidation |
|
|
Gaining an electron: oxidation or reduction? |
reduction |
|
|
Describe oxidation states |
allows chemists to determine the electron flow in the reaction; imaginary charges assigned based on a set of rules |
|
|
What are rules for oxidation states? |
1. Free elements have an ox state equal to zero 2. Monatomic ions have an ox state equal to their charge 3. (a) the sum of the ox states of all the atoms in a compound is zero (b) the sum of the ox states of all the atoms in a polyatomic ion equals the charge on the ion 4. (a) Group 1 metals have an ox state of +1 in all their compounds (b) Group 2 metals have an ox state of +2 in all their compounds 5. In their compounds, nonmetals have ox states according to the table |
|
|
Fluorine has an ox state of what? |
-1 |
|
|
Hydrogen has an ox state of what? |
+1 |
|
|
Oxygen has an ox state of what? |
-2 |
|
|
Group 7A has an ox state of what? |
-1 |
|
|
Group 6A has an ox state of what? |
-2 |
|
|
Group 5A has an ox state of what? |
-3 |
|
|
Oxidation and reduction must occur _______________. What does this mean exacly? |
simultaneously If an atom loses electrons, another atom must take them. |
|
|
The reactant that reduces an element in another reactant is called the ___________ _________. |
reducing agent which contains the element that is oxidized |
|
|
The reactant that oxidized an element in another reactant is called the __________ ______. |
oxidized agent which contains the element that is reduced |
|
|
Combustion reactions are characterized by what? |
the reaction of a substance with to form one or more oxygen-containing compounds, often including water they also emit heat |
|
|
CH4 and ethanol both react with oxygen and form what? |
CO2 and water |

