![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A Mw 7.2 magnitude earthquake would release ____ times the energy of a 4.2 quake. |
... would release approximately 33,000 times the energy of a 4.2 quake. There’s a three-step difference between a 4.2 and 7.2 quake. The difference in ground shaking (amplitude) for this would be 10 x 10 x 10 = 1,000. The energy difference would be approximately 32 x 32 x 32, which is almost 33,000. |
|
|
A tsunami... |
May be just a low and very broad wave at sea but both slows in speed and grows in height as it approaches a shallowing shore. |
|
|
Earthquakes are commonly caused by the brittle fracture of rock due to accumulated tectonic stresses. There are other causes. Which of the following processes could not cause an earthquake? |
thelithification of sediment |
|
|
Earthquake prediction is not highly reliable, but geologists do know that |
more earthquakes happen along plate boundaries than at intraplate locations |
|
|
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the 2010 Haiti earthquake? |
The earthquake generated a tsunami that was responsible for the majority of the lives lost. |
|
|
Which statement is TRUE? Liquefaction… a) can cause clay-rich sediment to turn into an unstable slurry of clay and water b) caused great damage in the Alaska quake of 1964 c) is the sudden loss of strength of some soils that happens because of earthquake shaking d) can affect sand layers below ground surface and cause them to erupt as sand volcanoes or sand boils e) All the possible answers are correct |
All the possible answers are correct |
|
|
The displacement of a fault is the distance between twofeatures along it that a geologist believes were once located directly next toone another. T/F? |
True |
|
|
Which statement is TRUE? a) R- and L-waves are surface seismic waves b) S-waves are compressional body waves; P-waves are shear body waves c) Surface waves are the first to show up on a seismogram recording of a quake d) Shallow-focus quakes do less damage than deep-focus quakes e) All the possible answers are correct. |
R- and L-waves are surface seismic waves |
|
|
Most major earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur... |
alongdivergent and convergent plates |
|
|
Which statement concerning tsunami events is FALSE? a) The velocity of a tsunami wave increases when the wave moves from open ocean into shallower water b) Tsunamis may be generated by underwater earthquakes, landslides in coastal mountain ranges, or submarine landslides c) The interval between waves varies from about 15 minutes to an hour, and wave action may continue for several hours d) Upthrust of the sea floor along a fault can displace huge amounts of water and result in giant tsunami waves e) Tsunamis can travel as fast as jet planes (several hundred mph). |
Thevelocity of a tsunami wave increases when the wave moves from openocean into shallower water. |
|
|
Identify the FALSE statement. The Richter scale... a) measures the size of a quake in terms of the damage it does (its intensity) b) measures the amplitude of the largest deflection on a seismogram in response to specifically defined seismic waves at a specifically defined distance and depth c) is today termed a local magnitude reading (Mz) d) works well only for shallow, nearby earthquakes e) requires use of a particular design of seismograph. |
Measures the size of a quake in terms of the damage it does (its intensity) |
|
|
The primary reason that earthquake aftershocks occur is... |
stress that has not been fully released and/or was created by a main shock. |
|
|
Identify the FALSE statement. Seismographs... a) may be of the mechanical type, consisting of a weight, spring, frame, pen, and revolving cylinder b) may be electronic, consisting of a heavy cylindrical magnet, coil of wire, spring, and computer readout of the voltage generated c) are sensitive enough to record ground movements down to only about one millimeter d) located throughout the world contribute to a seismic network whose data is available worldwide e) operate because of inertia; one part of the instrument remains motionless while the recording device moves in response to seismic waves. |
aresensitive enough to record ground movements down to only about one millimeter. |
|
|
Identify the FALSE statement. a) Normal faults result from stretching the Earth’s crust, thrust faults from squeezing it horizontally b) The modern description of earthquake size is complex; it includes surface-wave magnitude, body-wave magnitude, local magnitude, and moment magnitude measurements c) Moment magnitude (Mw) rating is the number now used for the official (archival) record d) All earthquake magnitude scales are logarithmic, which means a difference of one unit in magnitude reading represents a ten-fold difference in ground motion e) The energy released from a magnitude 6.6 earthquake is 10 times greater than the energy released from a magnitude 5.6 earthquake. |
The energy released from a magnitude 6.6 earthquake is 10 times greater than the energy released from a magnitude 5.6 earthquake. |
|
|
Identify the FALSE statement. a) Seismic waves become smaller in amplitude with increasing distance from the epicente b) Earthquake magnitude is based on ground motion recorded by a seismograph; intensity is based on the amount of damage produced c) Contour lines representing Mercalli values are used to delimit zones of quake intensity; the greater the quake the higher the intensity values and the wider the zones d) The moment magnitude scale takes into account the size of the affected area and characteristics of the rock affected e) Earthquakes do not occur at depths greater than about 100 km (60 miles). |
Earthquakes do not occur at depths greater than about 100 km (60 miles). |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a good technique for building earthquake-resistant structures? |
Usenon-steel reinforced concrete-block rather than wood-frame construction. |
|
|
Identify the FALSE statement. Long-termearthquake predictions... a) are statements of the likelihood of an earthquake happening in some particular area within the next thousand years b) are based on the identification of seismic zones c) are based on the study of historic recurrence intervals d) involve looking for sand volcanoes and disrupted bedding in the area e) involve looking for young fault scarps in the area. |
are statements of the likelihood of an earthquake happening in some particular area within the next thousand years |
|
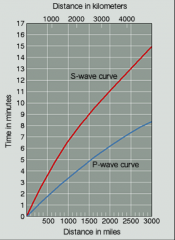
If a P-wave arrives 3 minutes 19 seconds (3'19") before an S-wave, how far away is the epicenter from the point where the time-difference in wave arrival was measured? |
Answer: 2,000 km If 3 minutes and 19 seconds elapses from the first “shake” of a P-wave until the first “shake” of an S-wave, the estimated distance that the waves have traveled from the epicenter is 2,000 km, based on average velocities for these types of waves. |
|
|
The Richter scale of magnitude is more accurate and has replaced the moment magnitude scale of magnitude. T/F? |
False |
|
|
Which of the following earthquake phenomena has killed the fewest number of humans? |
ground shaking with people in open areas |
|
|
Identify the FALSE statement. The tsunami event of December 26, 2004... a) involved a monstrous magnitude 9.3 earthquake that lasted 9 minutes b) was first noticed as a withdrawal of the sea along the beachfront c) consisted of local tsunamis that affected the island of Sumatra and later tsunamis that struck all along the Indian Ocean coast d) created a wide swath of elevated water that moved inland and submerged broad areas e) was caused by a massive earthquake along a transform fault. |
was caused by a massive earthquake along a transform fault |
|
|
The reading XIX is logical for a moderate-sized quake on the Mercalli intensity scale, which runs from X to XXX. T/F? |
False |
|
|
Plotting the hypocenters (foci) of earthquakes, showingtheir progression from shallow to intermediate to deep as you move eastwardacross South America, is really drawing the profile of a subducting oceanplate. T/F? |
True |
|
|
Major weather events such as hurricanes and tornadoes release as much energy as the great earthquakes (Mw > 8.5). T/F? |
False |
|
|
Roughly 80% of the earthquake energy released on Earth comes in the continental collision zone where the Himalayas are still growing; the remaining 20% is scattered at random locations worldwide. |
False |
|
|
Although the risk is small, disastrous earthquakes canhappen in regions that are not usually regarded as seismic zones. T/F? |
True |
|
|
It takes less energy to activate an old fault than tocreate a comparably sized new one, so old faults must still be treated as areasof weakness vulnerable to earthquakes. T/F? |
True |
|
|
If a rock undergoes stress producing elastic strain, anearthquake always happens. T/F? |
False |
|
|
The New Madrid, Missouri, quakes of 1811–1812 and theCharleston, South Carolina, quake of 1886 were both large intraplate quakes. |
True |
|
|
Rayleigh seismic waves cause the Earth’s surface to movevertically; Love seismic waves cause the ground to ripple back and forthlaterally, creating a snakelike movement of the surface. |
True |

