![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
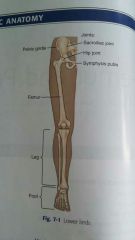
Femur |
Is the longest and strongest bone in the body. |
|
|
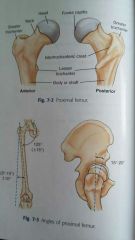
proximal femur |
Head Neck Greater and lesser trochanters |
|
|
Head |
Of the femur is rounded and smooth for articulation with the hip bones |
|
|
Doves capitis |
Is a depression on the head of the femur wherein a major ligament called ligament of the head of the femur is attached |
|
|
Neck |
Of the femur is a strong pyramidal process of bone that connects the head with the body or shaft in the region of trochanters |
|
|
Greater trochanters |
Is a large prominence that is located superiorly and laterally to the femoral shaft and is probable as a bony landmark. |
|
|
Lesser trochanters |
Is a smaller blunt conical eminence that projects medially and posteriorly from the junction of the neck and shaft of the femur |
|
|
Intertrochanteric crest |
Joins the trochanter posteriorly by a thick Ridge |
|
|
15 to 20 degrees internally |
The femur and leg must be rotated internally 15 to 20 degrees to place the femoral neck parallel to the IR |
|
|
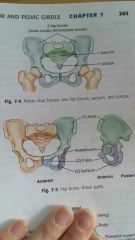
The complete pelvis |
Serves as the base of the trunk and forms the connection between the vertebral column and lower limbs |
|
|
Pelvic girdle |
Consist only of the two hip bones |
|
|
Pelvis |
Includes the right and left hip bones the sacrum and coccyx |
|
|
Hip bone |
Ilium Ischium Pubis |
|
|
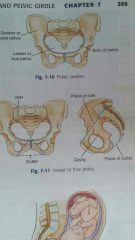
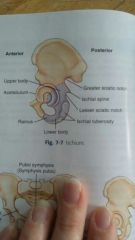
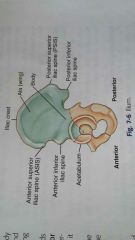
Acetabulum |
Is a deep cup shaped cavity that accepts the head of the femur to form the hip joint |
|
|
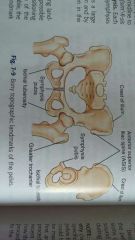
Ilium |
The largest of the three divisions is located superior to the acetabulum |
|
|
Ischium |
Is inferior and posterior to the acetabulum |
|
|
Pubis |
Is inferior and anterior to the acetabulum |
|
|
Ilium |
Consists body & ala The body of the ileum is the more inferior portion near the acetabulum and includes the superior two fifths of the acetabulum. the ala is the thin and flared superior part of the ilium |
|
|
Ilium crest |
Is the superior margin of the ALA it extends from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) to the posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) |
|
|
Ischium |
Is a part of the hip bone that lies inferior and posterior to the acetabulum |
|
|
Ischium |
The superior portion of the body of the ischium makes up the posteroinferior two fifths of the acetabulum |
|
|
Ischia tuberosity |
The rounded roughened area near the junction of the lower body and the inferior Rami |
|
|
Ramus |
Projecting anteriorly from the ischial tuberosity is the |
|
|
Ischial spine |
Posterior to the acetabulum is a bony projection |
|
|
Greater sciatic notch |
Directly superior to the ischial spine is a deep notch |
|
|
Lesser sciatic notch |
Inferior to the ischial spine is a smaller notch |
|
|
Pubis |
The body of the pubis is anterior and inferior to the acetabulum and includes the anteroinferior one fifth of the acetabulum |
|
|
Superior ramus |
Is extending andteriorly and medially from the body of each pubis |
|
|
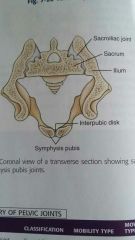
Symphysis pubis |
The to superior Rami meet in the midline to form the amphiarthrodial joint called |
|
|
Each inferior ramus |
Passes down and posterior from the symphysis pubis to join the ramus of the respective ischium |
|
|
The obturator foramen |
Is a large opening formed by the Ramos and body of each ischium and by the pubis. The obturator foramen is the larger foramen in human skeletal system. |
|
|
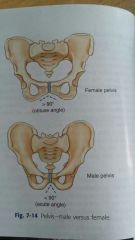
Female pelvis |
Is wider with the ilia more flared and more shallow from front to back. Angle greater than 90 Usually larger and more round |
|
|
Male pelvis |
Is narrower and deeper and less flared Angle less than 90 Usually narrower and more oval or heart shaped |
|
|
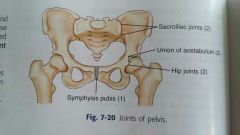
Sacroiliac joint |
Joints between the sacrum and each ilium |
|
|
Symphysis pubis |
Structure between the right and left pubis bones |
|
|
Union of acetabulum |
Temporary growth joint of each acetabulum that solidifies in the mid teen years |
|
|
Hip joints |
Joints between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis |
|
|
Sacroiliac |
Synovial joint |
|
|
Symphysis pubis |
Cartilaginious joint Symphysis subtype |
|
|
Union of acetabulum |
Cartilaginious type Synchondrosis subtype, which is immovable or synarthrodial |
|
|
Hip joint |
Synovial type Freely movable |
|
|
Label |
|
|
|
Label |
|
|
|
Label |
|
|
|
Label |
|
|
|
Label |
|
|
|
Label |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

