![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
128 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The ______ system and the ______ system, coordinate and control functions in the body. They are very closey related by functionally and anatomically. |
Nervous and Endocrine |
|
|
What are the 3 general functions of the nervous system? |
Sensory, integrative (analysis), motor (action) |
|
|
The basic functional unit of the nervous system |
Neurons |
|
|
The cell body is where the nucleus and most cytoplasm is located. It is also called the _______. |
Perikaryon |
|
|
multiple and conduct impulses toward the body (recieves the stimuli). They can serve as a sensory receptors. |
Dendrites |
|
|
Single and conduct impulses away from the cell body toward another neuron or effector cell. |
Axons |
|
|
Acts like "insulation" around an axon to increase the efficency of nerve impulse conduction. ( cell membrane of glial cells tightly wrapped around axon). |
Myelin sheath |
|
|
Supporting and protecting cells in the central nervous system |
Glial Cells (Neuroglia) |
|
|
The central nervous system contains the ... |
Brain and spinal cord |
|
|
The peripheral nervous system contains... |
cord-like "nerves" (bundles of axons) outside the central nervous system. |
|
|
All sensory information is relayed to the CNS before it is ______ and _______ upon. |
Interpreted and acted |
|
|
The _ _ _ is anatomically composed of the cranial nerves and spinal nerves. |
PNS |
|
|
Impulses are conducted to the central nervous system |
Afferent (sensory) |
|
|
Impulses conducted away from the central nervous system. |
Efferent (motor) |
|
|
Voluntary actions are controlled by |
Somatic functions |
|
|
Somatic functions consist of efferent nerves that carry impulses from the CNS to _____ muscle tissue. |
Skeletal |
|
|
Self-regulating involuntary actions ( does NOT have voluntary control). |
Autonomic Function |
|
|
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system are subdivisions of the |
Autonomic Nervous System |
|
|
When a neuron is not being stimulated it is considered to be in _______ ______. |
Resting State |
|
|
When the cell membrane is polarized at rest. Resting fibers have + charges lined up on the outside of the cell membrane and - charges on the inside. |
Resting membrane potential |
|
|
Pumps sodium and potassium ions to the interior and exterior of the cell membrane to establish the polarized resting membrane potential. ( it has a relative negative charge during a resting state). |
Sodium-potassium pump |
|
|
The firing of a neuron (change reversal) |
Depolarization |
|
|
Depolarization creates a large change in electrical charge from negative to positive on the inside of the cell. TRUE OR FALSE? |
True |
|
|
Neurons have a high requirement for _______ and _________. |
Oxygen and Glucose |
|
|
Neurons can not reproduce but they can _________. |
Regenerate |
|
|
Tissue containing myelinated axons |
White Matter |
|
|
May be short or long , and they terminate in nerve endings |
Telodendra |
|
|
The ________ ____ _________ of the telodendra pass nerve impulses to an adjacent structure. (acetylcholine). |
Synaptic end bulbs |
|
|
Myelinated axons conduct impulses _______ than unmyelinated ones. |
Faster |
|
|
Oligodendrocytes are located in the |
brain and spinal cord |
|
|
Schawnn Cells are located in the |
Nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
Gaps between adjacent myelin sheaths that are responsible for Saltatory conduction. |
Nodes of Raniver |
|
|
What are the Nodes of Ranvier responsible for? |
Saltatory conduction |
|
|
Transmission of impulses occurs via ____ ______. Waves of change reversal moving along the cell membrane. |
action potentials |
|
|
What are the 3 factors that cause the resting membrane potential? |
Sodium Potassium Pump, Differential permeability of the membrane to the diffusion of ions, negatively charged anions trapped in the cell |
|
|
A stimulus must be of at least a minimum strength in order for depolarization to occur at all. TRUE OR FALSE? |
True |
|
|
No amount of stimulus can cause another action potential. |
Absolute refractory period |
|
|
During end of the repolarization period |
Relative refactory period |
|
|
Begins a fraction of a second after depolarization. (the return to resting membrane potential. Resting state is restored. (+ outside, - inside). |
Repolarization |
|
|
Neuron depolarizes to its maximum strength or not at all. |
All or nothing principle |
|
|
What is the major neurotransmitter in the parasympethic nervous system? |
Acetylcholine |
|
|
Insensitive to additional stimuli |
Refactory period |
|
|
In myelinated axons, cell membrane depolarization only occurs at the Nodes of Ranvier. True or False. |
True |
|
|
Saltatory conduction has a ____ means of conducting an action potential. |
Rapid |
|
|
______ neurotransmitters generally stimulate the postsynaptic cell membrane moves toward the threshold to produce an impulse. |
Excitatory |
|
|
________ neurotransmitters generally inhibit the postsynaptic cell farther away from the threshhold from producing a nerve. |
Inhibitory |
|
|
Gray matter is found in the |
Cerebral cortex: outerlayer of the brain |
|
|
White Matter contains fibers beneath the cortex and the corpus callosum. Fibers that connect the 2 halves of the cerebral cortex. True or False? |
True |
|
|
Junction between 2 neurons or a neuron and a target cell. |
Synapse |
|
|
Gap between adjaccent neurons |
synaptic cleft |
|
|
Neuron bringing the depolarizaton wave to the synapse. Releases a neurotransmitter. |
presynaptic neuron |
|
|
Contains receptors for the neurotransmitter |
Postsynaptic Neuron |
|
|
Branched structure on presynaptic neuron |
Telodendron |
|
|
Slightly enlarged bulb on each end of telodendron (synaptic end bulb, synaptic knob). |
Terminal Buton |
|
|
When depolarization waves reach synaptic knob, vesicles fuse with the knobs cellular membrane and dump neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. True or false? |
True |
|
|
The cellmembrane of the presynaptic neuron where the neurotransmitter is released. |
Presynaptic Membrane |
|
|
The cell membrane of the neuron or structure where the neurotransmitter binds to its receptors. |
Postsynaptic membrane |
|
|
Can be excitatory or inhibitory depending on its location in the body. Found in the parasypeticnerves system. |
acetylcholine |
|
|
Sympethic nerve system contains |
Catecholamines |
|
|
What are the two neurotransmitetrs associated with fight or flight? |
Norepinephrine and epinephrine |
|
|
Dopamine is involved in |
autonomic functions and muscle control. |
|
|
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)and glycine are |
inhibtory neurotransmitters |
|
|
Found on the post synaptic membrane that breaks down acetylcholine is called |
acetylcholinesterase (AChE) |
|
|
What breaks down norepinephrine |
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) |
|
|
What breaks down norepinephrine |
Catechol-o-methyl transferase (COMT |
|
|
What part of the part brain is responsible for communication,expression of emotional responses,learing,memmory and recall, and any other behavior associated with conscious activity. |
Cerebrum |
|
|
Folds in cerebral hemispheres |
Gyri (gyrus) |
|
|
Deep grooves seperating the gyri |
Fissures |
|
|
Shallow grooves seperating the gyri |
Sulci (sulcus) |
|
|
Prominent groove that divides the cerebrum into right and left cerebral hemispheres |
Longitudinal Fissure |
|
|
What acts as the relay station in the diencephalon? |
Thalamus |
|
|
In the diencephalon what is the interface between nervous system and endocrine system? |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
What controls temperature regulation, hunger, thirst, componets of anger / rage behaviors? It exerts effects on the pituitary gland. |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
What is considered the exocrine "master gland"? |
Pituitary |
|
|
Cats infected with Feline Panleukopenia (distemper) virus (FIV) can develop cerebellar hypoplasia which results in intention tremors which interfers with motor skills. True or False? |
True |
|
|
What is the largest most rostral part of the mammalian brain? |
Cerebrum |
|
|
THis part of the brain is responsible for higher order functions - consciousness, learning, reasoning, intelligence, awareness, and thinking? |
Cerebrum |
|
|
This paart of the brain smooths out and coordinates movements, and influences balance, posture and complex reflexes. If movements are not being carried out accurately, this will stimulate or inhibit muscles to fien tune the movement. |
Cerebellum |
|
|
Lack of normal cerebellar activity causes |
hypermetria |
|
|
The passage between the brain stem and cerebrum |
Diencephalon |
|
|
The most primative part of the brain is |
the brainstem |
|
|
The brainstem maintains |
basic functions of the body |
|
|
Composed of medulla oblongata, the pons and midbrain |
Brainstem |
|
|
_____supplies nutrients and oxygen to the superficial tissues of the brain and spinal cord. |
Meninges |
|
|
What provides cushioning function? |
Cerebrospinal fluid |
|
|
This protects the brain from some toxins,but also prevetns some drugs from penetrating into the brain. Also prevents protiens, ions and other molecules.Capillary walls in the brain have no fenestrations. |
Blood-brain barrier |
|
|
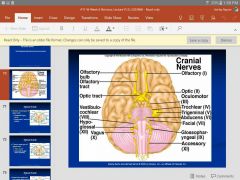
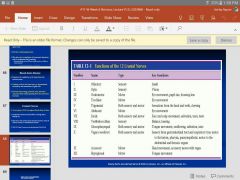
12 nerve pairs PNS that originate directly form the brain |
Crainial nerves |
|
|
Tough mother consists of tough fibrous it is also called |
Dura mater |
|
|
Delicate and spiderlike |
arachnoid |
|
|
Very thin, lies on the surface of the brain and spinal cord |
Pia mater |
|
|
What are the 3 layers of the meninges? |
Dura matter(tough mother), arachnoid, pia mater |
|
|
Cortex is the ________ matter |
White |
|
|
Medulla is the ____matter. |
Gray |
|
|
The central part of spinal cord is called the |
Medulla |
|
|
The ___ is the outer part of the spinal cord. |
Cortex |
|
|
Neurons in the gray matter that foward sensory (afferent) nerve impulses to brain and other parts of the spinal cord. |
Dorsal Horns |
|
|
Neurons in gray matter that foward motor (efferent) nerves impulses to the spinal nerves. |
Ventral Horns |
|
|
Arises from the thoracolumbar spinal cord. It has short preganglionic and long postganglionic axons. it is found in the |
Sympathetic Nervous System |
|
|
Arises from the Brainstem and spinal cord. It has long preganglionic and short postganglionic axons. |
parasympathetic Nervous system |
|
|
Most autonomic neurons secrete either acetylcholine (ACH) or norepinephrine (NE) as a neutotransmitter. (all preganglionic neurons secrete Ach). Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons secret Ach. (Ach- releasing synapses are called cholinergic.) Most symathetic postganglionic neurons secrete norepinephrine (NE). True or false? |
True |
|
|
Cholinergic are |
Ach releasing synapses |
|
|
what are the 2 different types of receptors that ach stimulates? (chollnergic receptors) |
Muscarinic and Nicotinic |
|
|
Wahat are the two receptors that are stimulated by NE? (adrenergic receptors) |
Aplpha and Beta |
|
|
Alpha 1 is responsible for |
vasoconstriction of skin, GI tract and kidneys |
|
|
Beta 1 is responisble for |
Increased heart rate and force of contraction |
|
|
Beta 2 is responsible for |
Bronchodilation |
|
|
Nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine are two types of |
receptors |
|
|
Dorsal spinal nerve roots bring ______ information in. |
sensory (afferent) |
|
|
Ventral spinal nerve roots carry ________ information out. |
motor (Efferent) |
|
|
What part of the nervous system regulates blood pressure, heart rate, intestinal motility and diameter of the pupils. It is always not under conscious control. |
Automonic nervous system |
|
|
Fight or flight |
Sympathetic nervous system |
|
|
rest and restore. increased gastrointestinal motility and decreased heart rate and diameter of bronchioles |
Parasympathetic nervous system |
|
|
Consists mainly of norepinephrine |
sympathetic nervous system |
|
|
The cell body is in a peripheral structure called |
Ganglion |
|
|
1. It innervates smooth muscle,cardiac muscle, some glands. (innervates skeletal muscle). 2. Number of nerves in the peripheral nervous system. |
2 ways the somatic nervous system is different |
|
|
Monosynaptic reflex there are no interneurons involved. EXample. patellar reflex |
Stretch reflex |
|
|
Flexor reflex- several interneuron synapses |
Withdrawl reflex |
|
|
Contralateral reflex |
Crossed extensor relex |
|
|
The role of the upper CNS in moderating reflexes produces an inhibitory effect. True or False? |
True |
|
|
Eyelids snap shut when medial canthus is touched. It is often used to acess the depth of an animials anesthesia. |
Palpebral reflex |
|
|
When a bright light is shone in to the eye, the pupils of both eyes will normally constrict- often used to acess central nervous system function in cases of tramua and disease. ( direct and consensual response) |
Pupillary light refelx |
|
|
Involves skeletal muscle |
Somatic reflex |
|
|
REgulates smooth muscle,cardiac muscle and endocrine glands |
Autonomic reflexs |
|
|
Starts on one side of body and travels to opposite side of body |
Contralateral reflex |
|
|
Stimulus and response are on the same side of the body |
Ipsilateral reflex |
|
|
With injury intact reflex arcs caudal to the spinal cord traauma |
Hyper-reflexive |
|
|
TRamua where feflex arcs enters or leaves the spinal cord, or damage to the sensory nerve or motor nerve of the reflexs results in either |
Hypo-reflexive or absent reflex arcs. |
|
|
|

