![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cellular reproduction |
production of new cells by splitting the parent cell into 2 daughter cells |
|
|
daughter cells |
are identical to the original parent cell |
|
|
2 important processes of cellular reproduction |
growth cell division |
|
|
how do daughter cells at the end of mitosis and cytokinesis compare to the parent cell |
they have the same number of chromosomes and the same amount of DNA ( identical ) |
|
|
how is DNA packaged so it can be passed to the daughter cells |
chromatin condenses into a set of chromosomes |
|
|
histones |
are protein molecules |
|
|
nucleosomes |
a set of 8 histones chromatin wraps itself around |
|
|
why do cells need histones and nucleosomes |
with them chromatin fit better inside the nucleus |
|
|
when are chromosomes easily visible |
during mitosis using a light microscope |
|
|
sister chromatids |
duplicated chromosomes compared of 2 identical halves |
|
|
Centromere |
holds together sister chromatids |
|
|
3 phases of cell cycle |
interphase mitosis cytokinesis |
|
|
what phase last the longest |
interphase |
|
|
3 stages of interphase |
G1 S G2 |
|
|
G1 |
DNA synthesis |
|
|
S |
DNA is replicated |
|
|
G2 |
cell synthesizes proteins needed for cell division |
|
|
G0 |
some cells will not undergo cell division. nerve cells divide and muscle cells ell only divide to repair damage |
|
|
4 phases of mitosis |
prophase metaphase anaphase telophase |
|
|
spindle |
part of the cyroskelton made of microtubules, pulls apart chromatids |
|
|
plant cells |
have centrosomes but lack centrioles |
|
|
animal cells |
each centrosomes has 2 centrioles and an aster |
|
|
aster |
array of microtubules |
|
|
what happens if mitosis occurs but cytokinesis doesn't |
the cells will have multi nuclei |
|
|
cell cycle is controlled by ____ |
internal and external signals |
|
|
internal signals |
control g1 and g2 |
|
|
external signals |
stimulate cell to go through the cell cycle |
|
|
G1 checkpoint |
cells are committed to divide |
|
|
G2 checkpoint |
cell verified duplication of DNA |
|
|
Mitosis stage checkpoint |
checks to make sure chromosomes are correctly attached to spindle |
|
|
cyclins |
internal signals that control passage from g1 to see and g2 to mitosis |
|
|
kinases |
enzymes that remove a phosphate from ATP and add it to another molecule on/off switch |
|
|
apotipsis |
programmed cell death |
|
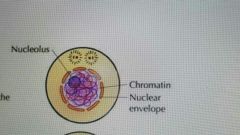
the necleolus and the nuclear envelope are distinct and the chromosomes are in the form of threadlike chromatin |
interphase |
|
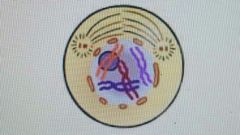
chromosomes appear condensed, and the nuclear envelope is not apparent |
prophase |
|
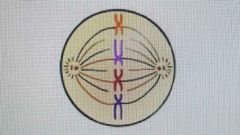
thick , coiled chromosomes, each with two chromatids, lined up on the _____ plate |
metaphase |
|
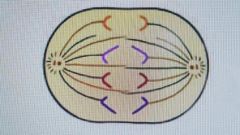
chromatids of each chromosome have separated and are moving toward poles |
anaphase |
|

chromosomes at poles and are becoming more diffuse. nuclear envelope is reforming, cytoplasm may be dividing |
telophase |
|

division into 2 daughter cells is complete |
cytokinesis |

