![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Amenorhhea |
The absence or cessation of the menstrual period. Normally occurs before puberty, during pregnancy,and after menopause. |
|
|
Cervix |
The lower narrow end of the uterus that opens into the vagina |
|
|
Colposcopy |
Examination of the cervix using a colposcope (a lighted instrument with a magnifying lens) |
|
|
Dysmenorrhea |
Pain associated with the menstrual period. |
|
|
Dyspareunia |
Pain in the vagina or pelvis experienced by a woman during sexual intercourse. |
|
|
Dysplasia |
The growth of abnormal cells. It is a precancerous condition that may or may not develop into cancer. |
|
|
Effacement |
The thinning and shortening of the cervical canal from its normal length of 1 to 2 cm to a structure with paper thin edges in which there is no canal at all. |
|
|
Embryo |
The child in utero from the time of conception to the beginning of the first trimester |
|
|
Fetus |
The child in utero from the third month after conception to birth |
|
|
Fundus |
The dome-shaped upper portion of the uterus between the fallopian tubes. |
|
|
Gestation |
The period of intrauterine development from conception to birth |
|
|
Gravidity |
The total number of pregnancies a woman has had regardless of duration. |
|
|
Metorrhagia |
Bleeding between menstrual periods |
|
|
Multigravida |
A woman who has been pregnant more than once |
|
|
Parity |
The condition of having borne offspring regardless of the outcome |
|
|
Perimenopause |
Before the onset menopause, the phase during which the woman with regular periods changes to irregular cycles and increased periods of amenorrhea. |
|
|
Perimenopause |
Before the onset of menopause, the phase during which the woman with regular periods changes to irregular cycles and increased periods of amenorrhea. |
|
|
Preeclampsia |
A major complication of pregnancy the cause of which is unknown characterized by increasing hypertension, albuminuria, and edema. If this condition is neglected or is not treated properly it may develop into ecclampsia... |
|
|
Primigravida |
A woman who is pregnant for the first time |
|
|
Trimester |
Three months or one third of the gestational period of pregnancy |
|
|
Colp/o |
Vagina |
|
|
Scopy |
Visual examination |
|
|
Dys |
Painful abnormal difficult |
|
|
Orrhea |
Flow, excessive discharge |
|
|
Ecto |
Outside outer |
|
|
Endo |
Within |
|
|
Gravid/o |
Pregnancy |
|
|
Gynec/o |
Woman |
|
|
Ology |
Study of |
|
|
Men/o |
Menstruation |
|
|
Nat/o |
Birth |
|
|
The pelvic exam consists of.. |
Inspection of the internal genitalia, vagina, and cervix; collection of a specimen for a pap; bimanual pelvic exam; rectal vaginal exam |
|
|
Function of the speculum |
To hold the walls of the vagina apart to allow visual inspection of the vagina and cervix |
|
|
Pap is used for |
Early detection of cervical cancer which are caused by the human papillomavirus (hpv) |
|
|
Cervical specimen is collected by |
Placing the s shaped end of the plastic spatula just inside the cervical canal at the external os and rotating the blade 360 degrees |
|
|
The ectocervix |
Is the part of the cervix that projects into the vagina and is lined with stratified squamous epithelium. |
|
|
Liquid based prep |
Improves the quality of the specimen resulting in fewer slides that are unsatisfactorily for evaulation. A better quality specimen also reduces the occurrence of false-negative test results. |
|
|
Liquid based steps |
First it separates the cells from debris present in the specimen and then it disperses a representative cell sample onto a slide in a thin uniform layer. The slide is next immersed in a fixative to maintain the normal appearance of the cells. |
|
|
Direct smear method |
A vial of liquid preserves all or most of the specimens |
|
|
When a pap specimen is collected, it includes unnecessary... |
Debris such as blood and mucus |
|
|
With the liquid based method, the automated processor.. |
Removes a large portion of the debris from the specimen |
|
|
With the liquid based method.. |
The automated processor disperses the cells onto the slide in a thin, even layer. |
|
|
Maturation index |
Provides the physician with an endocrine evaluation of the patient, which can assist in evaluating the cause of infertility, menopausal or postmenopausal bleeding, or amenorrhea and can help assess the results of treatment with hormones. |
|
|
TBS |
The bethesda system |
|
|
The bethesda system (tbs) does what |
Provides a detailed cytologic description,rather than a numerical result. |
|
|
Specimen adequacy in the bethesda system |
The category refers to the quality of the specimen collected by the physician |
|
|
General categorization in the bethesda system |
Category provides the medical office with a quick review of the report. |
|
|
Interpretive results in the bethesda system |
This part of the report provides the physician with a detailed description of findings. Includes any significant benign changes and any abnormal changes in the epithelial cells. |
|
|
Trich |
Pear shaped , flagella(motility) |
|
|
Symptoms of trich |
Profuse,frothy vaginal discharge that is usually yellowish green and has an unpleasant odor, itching. And irritation. |
|
|
Strawberry cervix |
Cervix may exhibit small red spots |
|
|
How to identify trich in the office |
Wet prep, involving placing a small amount of the discharge on a slide using a sterile swab adding a drop of isotonic solution and placing the coverslip over it to protect it. Slide is examined under the microscope and observed for moving flagella. |
|
|
Trich is treated with |
Metronidazole (flagyl) |
|
|
Conditons thats can cause a candidal infection(yeast infection) |
Pregnancy, diabetes mellitus, and prolonged antibiotic therapy |
|
|
Symptoms of candidiasis(yeast infection) |
White patches on the mucous membranes of the vagina, A thick odorless cottage cheese like discharge , extremely irritating and results in burning and intense itching |
|
|
koh dissolves celluar debris present in the smear and allows better visualization of.. |
Yeast buds, spores, or hyphae. |
|
|
Chlamydia symptoms |
Dysuria,itching and irritation..and a yellowish odorless vaginal discharge. Appear 1 to 3 weeks after infection. If not treated can lead to PID. |
|
|
Gonorrhea |
An infection of the genitourinary tract that is transmitted through sexual intercourse. |
|
|
Men have more gonorhhea symptoms..they include |
Dysuria, and a whiteish discharge from the penis which may progress to a thick creamy discharge |
|
|
How is gonorrhea diagnosed |
Dna probe test or a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) |
|
|
What does the NAAT test do? |
Detects the presence of the genes of the gonorrhea bacterium |
|
|
3 diseases that could affect mother and fetus(oast medical history) |
Diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. |
|
|
Gravidity (G) |
Recorded using one digit, indicates number of times a women has been pregnant including current pregnancy |
|
|
Parity |
Refers to the condition of having borne offspring regardless of the outcome. |
|
|
Term birth (T) |
Delivery after 37 weeks whether child is alive or stillborne |
|
|
Preterm birth (P) |
Delivery between 27 and 30 weeks regardless if child is alive or stillborne |
|
|
Abortion(A) |
Termination of a pregnancy before 20 weeks |
|
|
Living children (L) |
Number of living children |
|
|
Expected date of delivery formula |
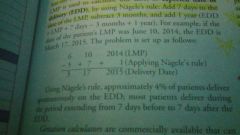
Add 7days, subtract 3 months and add 1 year from the last menstrual period |
|
|
Purpose of initial prenatal exam |
To confirm pregnancy and establishes a baseline. Includes gynecologic exam and a general physical exam |
|
|
Warning signs during pregnancy |
Signs of spontaneous abortion: Abdominal pain and cramping Signs of placental or fetal problems: vaginal spotting or bleeding |
|
|
If gonorrhea is present at delivery and not treated... |
Could lead to blindness. |
|
|
When is a woman tested for group b strep |
Between 35 and 37 weeks |
|
|
Rubella antibody titer |
Assesses the level of antibody against rubella |
|
|
Rh antibody titer |
Detects the quantity of circulating Rh antibodies against red blood cells |
|
|
0 to 28 weeks return prenatal visits |
Every 4 weeks |
|
|
Positive reaction to glucose may indicate |
The development of gestational diabetes mellitus or a prediabetic condition, |
|
|
Positive reaction to protein |
May indicate a UTI or preeclampsia |
|
|
Most common medical disorder of pregnancy |
Hypertension |
|
|
Normal fetal heart rate |
Between 120 and 160 beats per minute |
|
|
Lcd screen on the doppler purpose |
To display the fetal pulse rate |
|
|
Purpose of gel applied during doppler |
To increase conductivity of the sound waves between the abdomen and the transducer |
|
|
Mulitple marker test |
To screen for the presence of certain fetal abnormalities which include neural tube defects, down syndrome, trisomy 18,and ventral wall defect |
|
|
Primary purpose of ultrasound scan |
To evaluate the health of the fetus and to determine gestational age |
|
|
Transabdominal ultrasound scan |
Patient must have a full bladder..32 ounces of water approximately between 1 hour before the procedure. A full bladder acts as an acoustic window through which the sound wave scan travel to provide a clear visualization of the uterus |
|
|
The non stress test(NST) |
Monitors changes in the fetal heart rate in response to the fetus' spontaneous movements. |
|
|
The puerperium |
Includes the time in which the body systems are returning to their pre pregnant or nearly pre pregnant state, usually 4 to 6 weeks after delivery |
|
|
Color of the lochia after birth |
First 2 days: mostly blood by 4 days:becomes pink or brownish. By 10 days: yellowish white. Becomes paler until the 3rd week after delivery |
|
|
When to call office with discharge after delivery |
If the amount increases instead of decreases, if it is absent with 2 weeks of delivery, if it changes to red after having been yellowish white, or if it takes a foul odor indicating infection. |
|
|
6 week check up |
Evaluation of the general mental status and physical appearance, breast and pelvic examination and checks to see is the muscle tone has returned to the abdominal wall. NO PAP |

