![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Genetics is the science of __________.
|
__________ is the science of heredity.
|
Genetics is the science of heredity.
|
|
|
The genome of a cell is the __________ information in a cell.
|
The __________ of a cell is the genetic information in a cell.
|
The genome of a cell is the genetic information in a cell.
|
|
|
Constitutive enzymes are those that are constantly produced at a __________ rate.
|
__________ enzymes are enzymes that are constantly produced at a fixed rate.
|
Constitutive enzymes are enzymes that are constantly produced at a fixed rate.
|
|
|
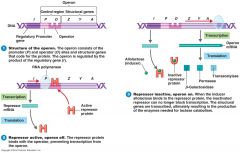
Inducible enzymes are enzymes that are not made until __________, with a default position of off.
|
__________ enzymes are enzymes that are not made until needed, with a default position of __________.
|
Inducible enzymes are enzymes that are not made until needed, with a default position of off.
|
|
|
Repressible __________are enzymes that are made until __________ needed, with a default position of on.
|
__________ enzymes are enzymes that are made until no longer needed, with a default position of __________.
|
Repressible enzymes are enzymes that are made until no longer needed, with a default position of on.
|
|
|
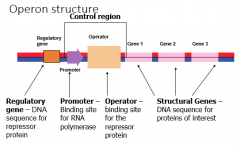
Three regions of the __________
regulatory gene control region structural genes |
Three regions of the operon.
__________ __________ __________ |
Three regions of the operon.
regulatory gene control region structural genes |
|
|
Regulatory gene codes for the __________ protein, it acts as "on/off" switch and can act as repressor or __________.
|
__________ gene codes for the regulatory protein, it acts as __________ switch and can act as a __________ or inducer.
|
Regulatory gene codes for the regulatory protein, it acts as "on/off" switch and can act as repressor or inducer.
|
|
|
Two areas of the __________ region
promoter operator |
Two areas of the control region.
__________ __________ |
Two areas of the control region
promoter operator |
|
|
The promoter is the __________ site for __________ polymerase.
|
The __________ is the binding site for RNA __________.
|
The promoter is the binding site for RNA polymerase.
|
|
|
The operator is the __________ site for the __________ protein.
|
The __________ is the binding site for the repressor __________.
|
The operator is the binding site for the repressor protein.
|
|
|
Structural __________ are genes being __________ on the operon.
|
__________ genes are genes being transcribed on the __________.
|
Structural genes are genes being transcribed on the operon.
|
|
|
Catabolite __________ happens when glucose represses enzymes for __________ degradation.
Alarmone is _________________ binding to catabolite activating protein (CAP). _________________ binds to the promoter and induces RNA _________________ to bind. |
__________ repression happens when __________ represses enzymes for lactose degradation.
_________________ is cAMP binding to catabolite activating protein (CAP). CAP binds to the _________________ and induces RNA polymerase to bind. |
Catabolite repression happens when glucose represses enzymes for lactose degradation.
Alarmone is cAMP binding to catabolite activating protein (CAP). CAP binds to the promoter and induces RNA polymerase to bind. |
|
|
Operons are rare in __________, they utilize transcription factors or __________ splicing of exons.
_________________ may be regulated at translation level. __________ of expression in archaea is unsure and may be more similar to eukaryotes than bacteria. |
__________ are rare in eukaryotes, they utilize __________ factors or alternate splicing of __________.
Expression may be regulated at _________________ level. Regulation of expression in __________ is unsure and may be more similar to eukaryotes than bacteria. |
Operons are rare in eukaryotes, they utilize transcription factors or alternate splicing of exons.
Expression may be regulated at translation level. Regulation of expression in archaea is unsure and may be more similar to eukaryotes than bacteria. |
|
|
__________ use global regulatory systems to adapt to changing __________ by altering levels of gene __________.
|
Microbes use __________ __________ __________ to adapt to changing environments by altering levels of gene expression.
|
Microbes use global regulatory systems to adapt to changing environments by altering levels of gene expression.
|
|
|
Signal transduction is __________ of information from external environments to inside the cell and allows the cell to respond to __________ changes.
|
__________ __________ is transmission of information from __________ environments to inside the cell and allows the cell to respond to environmental changes.
|
Signal transduction is transmission of information from external environments to inside the cell and allows the cell to respond to environmental changes.
|
|
|
Quorum sensing is based on the __________ of cell __________ and activation of genes is beneficial only when produced by multiple cells.
bio-luminescence |
__________ __________ is based on the density of cell population and activation of genes is beneficial only when produced by __________ cells.
bio-luminescence |
Quorum sensing is based on the density of cell population and activation of genes is beneficial only when produced by multiple cells.
bio-luminescence |
|
|
__________ that may occur at the translation level.
Riboswitches Antisense RNA |
Regulation that may occur at the translation level.
__________ __________ |
Regulation that may occur at the translation level.
Riboswitches Antisense RNA |
|
|
Riboswitches are __________ that will fold on itself and can't bind on __________.
|
__________ are mRNA that will fold on itself and can't bind on ribosomes.
|
Riboswitches are mRNA that will fold on itself and can't bind on ribosomes.
|
|
|
__________ mechanisms for genetic diversity.
mutation gene transfer |
Bacterial mechanisms for genetic diversity.
__________ __________ |
Bacterial mechanisms for genetic diversity.
mutation gene transfer |
|
|
__________ are changes in genotype, may or may not cause phenotypic __________, passed vertically to all __________.
|
Mutations are changes in __________, may or may not cause __________ changes, passed __________ to all offspring.
|
Mutations are changes in genotype, may or may not cause phenotypic changes, passed vertically to all offspring.
|
|
|
Point mutations are a change in one base __________.
|
__________ mutations are a change in one base substitution.
|
Point mutations are a change in one base substitution.
|
|
|
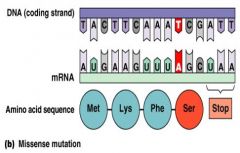
Missense mutations results in change of __________ __________.
|
__________ mutation results in change of amino acid.
|
Missense mutation results in change of amino acid.
|
|
|
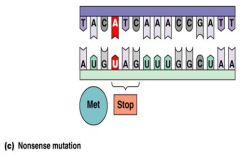
Nonsence mutations results in a __________ __________.
|
__________ mutation results in a stop codon.
|
Nonsence mutation results in a stop codon.
|
|
|
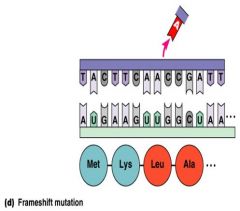
Frame-shift mutation results in __________ or __________ of one or more bases.
|
__________ mutation results in insertion or deletion of one or more bases.
|
Frame-shift mutation results in insertion or deletion of one or more bases.
|
|
|
Mutagens are __________ or __________ agents that induce mutations.
|
__________ are physical or chemical agents that induce mutations.
|
Mutagens are physical or chemical agents that induce mutations.
|
|
|
Spontaneous mutations occur in the absence of a __________, may be due to error or __________.
|
__________ mutations occur in the absence of a mutagen, may be due to error or transposons.
|
Spontaneous mutations occur in the absence of a mutagen, may be due to error or transposons.
|
|
|
Transposable elements (__________), may disrupt proper gene __________, contain insertion sequences (transposase), complex __________ carry other genes.
|
__________ elements (transposons), may disrupt proper gene function, contain insertion sequences (__________), complex transposons carry other __________.
|
Transposable elements (transposons), may disrupt proper gene function, contain insertion sequences (transposase), complex transposons carry other genes.
|
|
|
Nuceleotide excision repair uses the __________ enzyme to cut damaged DNA, then uses DNA __________ to put in new DNA, then uses DNA __________ to seal DNA fragments together.
|
__________ __________ repair uses the endonuclease enzyme to cut damaged DNA, then uses DNA polymerase to put in new DNA, then uses DNA ligase to seal DNA fragments together.
|
Nuceleotide excision repair uses the endonuclease enzyme to cut damaged DNA, then uses DNA polymerase to put in new DNA, then uses DNA ligase to seal DNA fragments together.
|
|
|
Light repair is the direct repair of damaged DNA by photoactivation with the enzyme __________.
|
__________ repair is the direct repair of damaged DNA by photoactivation with the enzyme photolayse.
|
Light repair is the direct repair of damaged DNA by photoactivation with the enzyme photolayse.
|
|
|
Induced mutations are __________ produced to demonstrate function of a particular gene or set of genes.
|
__________ mutations are intentionally produced to demonstrate function of a particular gene or set of genes.
|
Induced mutations are intentionally produced to demonstrate function of a particular gene or set of genes.
|
|
|
Ways to __________ mutations.
chemical mutagens transposition radiation |
Ways to induce mutations.
__________ __________ __________ |
Ways to induce mutations.
chemical mutagens transposition radiation |
|
|
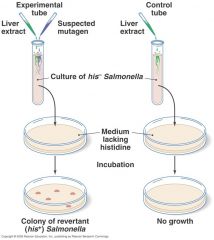
Ames Test uses a mutational reversion assay to test __________ of compounds by utilizing a histidine __________.
|
__________ __________ uses a mutational reversion assay to test mutagenicity of compounds by utilizing a __________ auxotroph.
|
Ames Test uses a mutational reversion assay to test mutagenicity of compounds by utilizing a histidine auxotroph.
|
|
|
Positive selection detects mutant cells because they grow or appear different, __________ selection.
|
__________ selection detects mutant cells because they grow or appear different, direct selection.
|
Positive selection detects mutant cells because they grow or appear different, direct selection.
|
|
|
Negative selection detects mutant cells because they do not grow, __________ selection.
|
__________ selection detects mutant cells because they do not grow, indirect selection.
|
Negative selection detects mutant cells because they do not grow, indirect selection.
|
|
|
Genetic recombination is the __________ of genes between two DNA molecules that forms new __________ of genes on a chromosome.
|
__________ __________ is the exchange of genes between two DNA molecules that forms new combinations of genes on a __________.
|
Genetic recombination is the exchange of genes between two DNA molecules that forms new combinations of genes on a chromosome.
|
|
|
Vertical gene transfer occurs during reproduction, between __________ generations of cells.
|
__________ gene transfer occurs during reproduction, between different generations of cells.
|
Vertical gene transfer occurs during reproduction, between different generations of cells.
|
|
|
Horizontal gene transfer occurs between cells of the __________ generation.
|
__________ gene transfer occurs between cells of the same generation.
|
Horizontal gene transfer occurs between cells of the same generation.
|
|
|
Mechanisms of __________ transfer, that result in recombination.
transformation transduction conjugation |
Mechanisms of horizontal transfer, that result in recombination.
__________ __________ __________ |
Mechanisms of horizontal transfer, that result in recombination.
transformation transduction conjugation |
|
|
Transformation is picking up __________ DNA from the environment. Discovered by __________ __________ in 1928.
|
__________ is picking up naked DNA from the environment. Discovered by Fredrick Griffith in __________.
|
Transformation is picking up naked DNA from the environment. Discovered by Fredrick Griffith in 1928.
|
|
|
Showed DNA was a __________ agent when __________ cells pick up DNA and integrate it into a chromosome.
Avery MacLeod McCarty |
Showed DNA was a transforming agent when competent cells pick up DNA and integrate it into a chromosome.
__________ __________ __________ |
Showed DNA was a transforming agent when competent cells pick up DNA and integrate it into a chromosome.
Avery MacLeod McCarty |
|
|
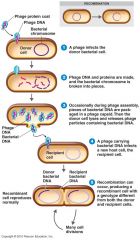
Transduction happens when __________ DNA transferred from a donor to recipient via __________.
|
__________ happens when bacterial DNA transferred from a donor to recipient via bacteriophage.
|
Transduction happens when bacterial DNA transferred from a donor to recipient via bacteriophage.
|
|
|
Generalized __________ happens when any DNA could be picked up.
|
__________ transduction happens when any DNA could be picked up.
|
Generalized transduction happens when any DNA could be picked up.
|
|
|
Specialized __________ happens when a specific gene is picked up.
|
__________ transduction happens when a specific gene is picked up.
|
Specialized transduction happens when a specific gene is picked up.
|
|
|
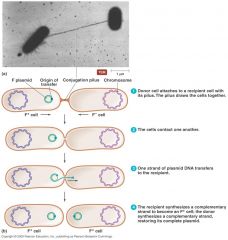
Conjugation requires __________ contact between cells using a __________ and is the only form of gene exchange in which the donor survives.
|
__________ requires direct contact between cells using a pili and is the only form of gene exchange in which the donor __________.
|
Conjugation requires direct contact between cells using a pili and is the only form of gene exchange in which the donor survives.
|
|
|
Fertility factors are a plasmid type that contain genes to perform __________.
|
__________ factors are a plasmid type that contain genes to perform conjugation.
|
Fertility factors are a plasmid type that contain genes to perform conjugation.
|
|
|
Dissimilation plasmids contain genes for using usual __________ for energy.
|
__________ plasmids contain genes for using usual substrates for energy.
|
Dissimilation plasmids contain genes for using usual substrates for energy.
|
|
|
Resistance factors are plasmids with genes that resist __________ compounds.
|
__________ factors are plasmids with genes that resist damaging compounds.
|
Resistance factors are plasmids with genes that resist damaging compounds.
|
|
|
Bacteriocin factors are plasmids that code for bacterial __________.
|
__________ factors are plasmids that code for bacterial exotoxins.
|
Bacteriocin factors are plasmids that code for bacterial exotoxins.
|
|
|
Virulence plasmids are genes containing __________ __________.
|
__________ plasmids are genes containing virulence factors.
|
Virulence plasmids are genes containing virulence factors.
|
|
|
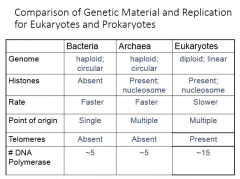
Comparison of Genetic Material and Replication for Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
---------------------------Bacteria Archaea Eukaryotes Genome Histones Rate Point of origin Telomers # DNA polymerase |
|
|
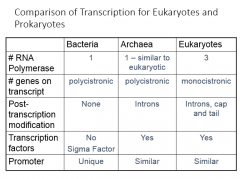
Comparison of Transcription for Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
|
Comparison of Transcription for Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
----------------------------------------Bacteria Archaea Eukaryotes #RNA polymerase # genes on transcript Post-Transcript modification Transcription factors Promoter |
|
|
|
Operon structure
|
|
|
|
|
Inducible enzyme
|
|
|
|
|
Catabolite repression
(know this slide) |
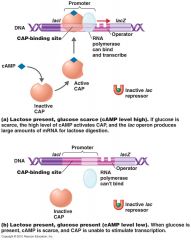
|
|
|
|
2 step diauxic growth
|
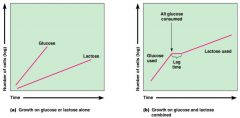
|
|
|
|
Repressible enzyme
|
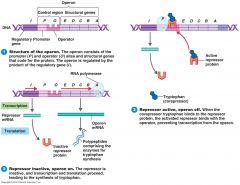
|
|
|
|
Nucleotide excision repair
|
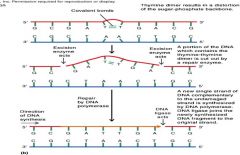
|
|
|
|
Light repair
|

|
|
|
|
Ames Test
|
|
|
|
|
Positive selection test
|
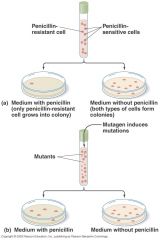
|
|
|
|
Replica plating
Negative selection |
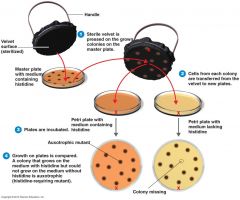
|
|
|
|
Griffith experiment
Transformation |
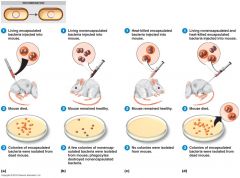
|
|
|
|
Transduction
|
|
|
|
|
Conjugation
|
|
|
|
|
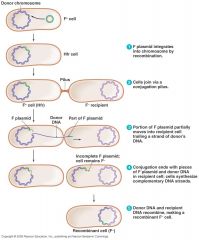
Conjugation
inserting plasmid DNA into primary chromosome |
|
|
|
|
image
|
|
|
|
|
Missense mutation
Results in change of amino acid |
|
|
|
|
Nonsense mutation
Results in a stop codon |
|
|
|
|
Frame-shift mutation
Insertion or deletion of one or more bases |
|
|

