![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definite genetics |
Study of inheritance and inheritable traits as expressed in an organisms genetic material |
|
|
Define genome |
The entire genetic compliment of an organism Includes it’s genes and nucleotide sequence |
|
|
What is the structure of nucleic acids? |
Polymers of nucleotides (Building blocks of dna and rna) |
|
|
What are nucleotides made up of? |
Phosphate Pentose sugar Nitrogenous base (nucleoside) |
|
|
What are the base pairs? |
A-T C-G A-U (rna only) |
|
|
How does the sequence communicate? |
5’-3’ |
|
|
(The structure of prokaryotic genomes) How are prokaryotic genomes packaged? Describe their structure. |
Made up of Chromosomes and plasmids - main portion of dna along with associated proteins and rna is packaged as a single chromosome - prokaryotic cells are HAPLOID (single chromosome copy) - typical chromosome is a circular molecule of dna in the nucleoid |
|
|
What are plasmids in prokaryotic genome? |
Small molecules of dna that replicates independently |
|
|
Describe plasmids (fun facts) |
- They aren’t essential for normal metabolism growth of reproduction - they can confer survival advantages |
|
|
What are the types of plasmids? |
- fertility factors (f factors/plasmids) - resistance factors (r plasmids) - bacteriocin factors - virulence plasmids |
|
|
What do fertility factors do? |
Carry instructions for conjugation - process of dna transfer between cells |
|
|
What do resistance plasmids do? |
Carry genes for resistance to one or more antimicrobial drugs |
|
|
What do bacteriocin plasmids do? |
Carry genes for proteinaceous toxins called bacteriocins * kills bacterial cells of the same or similar species that lacks a plasmid |
|
|
What do virulence plasmids do? |
Carry genes for structures enzymes or toxins that enable bacterium to become pathogenic |
|
|
Structure of Eukaryotic genomes |
Nuclear chromosomes typically have more than one chromosome per cell - nuclear chromosomes are linear and sequestered within the nucleus |
|
|
What are eukaryotic chromosomes composed of ? Are they did diploid or haploid? |
Composed of DNA and histones (proteins) * diploid! (Two chromosome copies) /not all! |
|
|
What are extranuclear chromosomes of eukaryotes? |
- dna molecules of mitochondria and chloroplasts - resembles chromosomes of prokaryotes - only code for about 5% of rna and proteins (Some fungi, algae and Protozoa carry plasmids) |
|
|
Characteristics of microbial genomes Bacteria? |
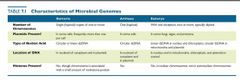
# of chromosomes: 1! Haploid Plasmids?: in some, usually more than one per cell Type of nucleic acid: circular or linear dsDNA Location of dna: nucleoid of cytoplasm and in plasmids Histones?? No! |
|
|
Characteristics: Archaea? |
# of chromosome? Haploid 1 Plasmids? In some Type of nucleic acid: circular dsDNA Location of dna: in nucleoid of cytoplasm and plasmids Histones? Yes! |
|
|
Characteristics of genomes: Eukarya?? |
# of chromosomes: with one exception. It’s two or more! Diploid Plasmids? In some fungi algae and Protozoa Type of nucleic acid? Linear dsDNA in nucleus and chloroplasts &&&& circular dsDNA in mitochondria and plasmids Histones?? Yes I’m nuclear chromosomes Nottt in extranuclear chromosomes |
|
|
Who proposed the central dogma of molecular biology?? |
Francis crick! |
|
|
What pertains to dna replication?? |
Key to replication is the complementary structure of the two strands *replication is semiconservative* |
|
|
What does semiconservative mean?? |
New dna composed of one original and one daughter strand |
|
|
Anabolic polymerization processes is a part of dna replication. What does it require and what does it do? |
Monomers and energy - triphosphate deoxyribonucleotides serve both functions (it has the energy needed for the process of replication) |

