![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cellular Respiration |

|
|
|
aerobic respiration |

|
|
|
Adenosine triphosphate |
A primary aim of cellular respiration is to make... |
|
|
Glycolysis |
During this process, glucose is broken down to two pyruvate molecules (with 3 carbons each), producing a net energy yield of two ATP molecules and two NDAH molecules. |
|
|
Substrate-level phosphorylation |

|
|
|
1. glycolysis 2. The breakdown of pyruvate (shuttle step) 3. The citric acid cycle 4. Oxidative phosphorylation |
What are the four metabolic pathways involved in the oxidation of glucose? |
|
|
Breakdown of pyruvate- shuttle step |
Second step of the oxidation process of glucose where the two pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria matrix, where each one is broken down via oxidation, one NADH molecule is made by the reduction of NAD+. Pyruvate is converted to AcCoA (Acetyl Coenzyme A). |
|
|
Citric acid cycle- krebs cycle |
Third step in the oxidation of glucose process where each acetyl group is incorporated into an organic molecule, which is later oxidized to liberate two CO2 molecules. Here is where one ATP, three NADH, and one FADH2 are made in this process. One ATP is formed via substrate level phosphorylation. |
|
|
Oxidative phosphorylation |
The fourth step in the oxidation process of glucose where the nadh and fadh2 made in the three previous stages contain high energy electrons that can be readily transferred to a redox reaction to other molecules. Once removed from nadh or fadh2, these high-energy electrons release some energy, and through an electron transport chain, that energy is harnessed to produce an H+ electrochemical gradient that produces 3 ATP for each nadh and 2 ATP for each FADH2. |
|
|
Chemiosmosis |

Is also the synthesis of ATP that occurs as a result of pushing H+ across a membrane |
|
|
30-34 ATP max of 36-38 |
How many ATP molecules are made via oxidative phosphorylation? |
|
|
Cristae |

Also where oxidation phosphorylation happens. Increases surface area of the inner membrane and thereby increasing the amount of ATP that can be made. |
|
|
Biochemistry |
The study of the chemistry of living organisms. |
|
|
First phase of glycolysis |
Two ATP molecules are hydrolyzed, and the phosphates from those ATP molecules are attached to glucose, which is converted to fructose - 1, 6-bisphophate. The energy investment phase raises the free energy of glucose, thereby allowing later reactions to be exergonic. |
|
|
Cleavage phase of glycolysis (2nd phase) |
This phase of glycolysis breaks this 6 carbon molecule into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. |
|
|
Energy liberation phase (3rd phase) |
This phase of glycolysis produces 4 ATP, 2 nadh, and two molecules of pyruvate. Because two molecules of ATP are used in this face, the net yield is two molecules of ATP. |
|
|
The net reaction of glycolysis |
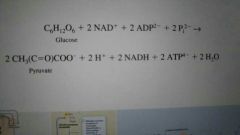
|
|
|
Cancer cells |
Certain _________ cells preferentially use glycolysis for ATP production, and contrast two healthy cells, which mainly generate ATP from oxidative phosphorylation. |
|
|
Mitochondria |
In eukaryotes, glycolysis produces pyruvate in the cytosol, which is then transported into the _______. |
|
|
Pyruvate dehydrogenase |
Once in the mitochondrial Matrix, pyruvate molecules are broken down (oxidized) by an enzyme complex called __________. |
|
|
Coenzyme A (CoA) |
Once a molecule of CO2 is removed from pyruvate, the remaining acetyl group is attached to an organic molecule called __________. |
|
|
The net reaction of pyruvate |
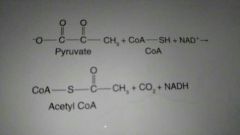
|
|
|
Sulfur |
The acetyl group is attached to CoA via a covalent bond to a _______ atom. The hydrolysis of this Bond releases a large amount of free energy, making it possible for the acetyl group to be transferred to other organic molecules. |
|
|
The citric cycle |
|
|
|
Oxidative phosphorylation |

|
|
|
Electron transport chain (ETC) |

|
|
|
Oxygen |
At the end of the chain is _______, which is the most electronegative component and the final electron acceptor. |
|
|
Respiratory change |
The ETC, or electron transport chain, is also called this, because the oxygen we breathe is used in this process. |
|
|
H+ electrochemical gradient |
A transmembrane gradient for H+ composed of both a membrane potential and a concentration difference for H+ across a membrane. This is established during the active transport of H+ across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space. An excess a positive charge exists outside of the Matrix because of this. |
|
|
ATP synthase |
An enzyme that utilizes the energy stored in a H+ electrochemical gradient For the synthesis of ATP by chemiosmosis. |
|
|
-25 kcal/mol |
The total energy released by single electron is approximately this. |
|
|
ATP synthase |
Is a rotary machine that makes ATP as it spins |
|
|
A, b, and c |
The region embedded in the membrane for ATP synthase is composed of three types of subunits called ____, _____, ______ ________. |
|
|
10-14 |
Approximately this many C subunits form a ring in the membrane of ATP synthase |
|
|
1 a 2 b |
This many a subunits are bound to this ring in the membrane of ATP synthase, and this many B subunits are attached to the A subunit and protrude from the membrane. |
|
|
Anaerobic |
Refers to a process that occurs in the absence of oxygen; a form of metabolism that does not require oxygen |
|
|
Anaerobic respiration |
The breakdown of organic molecules in the absence of oxygen |
|
|
Fermentation |
The breakdown of organic molecules to produce energy without any net oxidation of an organic molecule. |
|
|
Anaerobic respiration and fermentation |
Two different strategies that may be used by cells to metabolize organic molecules in the absence of oxygen |
|
|
O2 |
Many organisms, including animals and yeast, use only this as the final electron acceptor of their ETCs. |
|
|
Lactate, or lactic acid |
When a muscle is working strenuously and becomes anaerobic, as in high intensity exercise, the pyruvate from glycolysis is reduced to make this. |
|
|
Fermentation |
The pathways of breaking down glucose to lactate or ethanol are examples of this. |
|
|
Autotrophs- producers |
Photosynthetic and other organisms that can capture energy from inorganic sources and converted to organic chemical energy |
|
|
Heterotrophs- consumers |
Cannot directly capture energy from inorganic sources, rely on consuming organic |
|
|
Chemothrophs |
Obtain energy from chemicals. Can be organic chemicals or inorganic chemicals |
|
|
Phototrophs |
Obtain energy from light. Use that energy to build organic molecules |
|
|
1. Substrate level phosphorylation 2. Oxidative phosphorilation |
Two ways ATP is made |
|
|
Cytosol |
Where glycolysis occurs |
|
|
Primary metabolism |
Any process involving building or breaking down the 4 main organic molecules: carbohydrate, protein, fat, nucleic acid |
|
|
Secondary metabolism |
Building or breaking down molecules NOT in the 4 main organic groups, but they can use one of the four as precursors. |
|
|
Molecules for communication and defense |
2 main categories for secondary metabolites. |

