![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Impingement syndrome
|
Entrapment of soft tissue structures under coracoacromial arch of the shoulder
treatment: NSAIDs; rest until symptoms decrease and then gradual ROM and strengthening exercises |
NSAIDs; rest until symptoms decrease and then gradual ROM and strengthening exercises
|
|
|
Rotator cuff tear
|
Tear within muscle or tendinoligamentous structures about the shoulder
Treatment: If minor tear, rest shoulder, NSAIDs, and gradual mobilization with ROM and strengthening exercises If major tear, surgical repair |
If minor tear, rest shoulder, NSAIDs, and gradual mobilization with ROM and strengthening exercises
If major tear, surgical repair |
|
|
Shin splints
|
Inflammation along anterior aspect of calf from periostitis caused by improper shoes, overuse, or running on hard pavement
Treatment: Rest, ice, NSAIDs, proper shoes; gradual increase in activity; if pain persists, x-ray should be done to rule out stress fracture of tibia |
Rest, ice, NSAIDs, proper shoes; gradual increase in activity; if pain persists, x-ray should be done to rule out stress fracture of tibia
|
|
|
Tendinitis
|
Inflammation of tendon as a result of overuse or incorrect use
Treatment: Rest, ice, NSAIDs; gradual return to sport activity; protective brace (orthosis) may be necessary if symptoms recur |
Rest, ice, NSAIDs; gradual return to sport activity; protective brace (orthosis) may be necessary if symptoms recur
|
|
|
Ligament injury
|
Tearing or stretching of ligament; usually occurs as a result of inversion, eversion, shearing, or torque applied to a joint; characterized by sudden pain, swelling, and instability
Treatment: Rest, ice, NSAIDs; protection of affected extremity by use of brace; if symptoms persist, surgical repair may be necessary |
Rest, ice, NSAIDs; protection of affected extremity by use of brace; if symptoms persist, surgical repair may be necessary
|
|
|
Meniscal injury
|
Injury to fibrocartilage of the knee characterized by popping, clicking, or tearing sensation, effusion, and swelling
Treatment: Rest, ice, NSAIDs; gradual return to regular activities; if symptoms persist, surgical arthroscopy to diagnose and repair meniscal injury may be necessary |
Rest, ice, NSAIDs; gradual return to regular activities; if symptoms persist, surgical arthroscopy to diagnose and repair meniscal injury may be necessary
|
|
|
Soft tissue injuries include
|
sprains, strains, dislocations, and subluxations.
|
|
|
|
sprain
|
an injury to tendinoligamentous structures surrounding a joint, usually caused by a wrenching or twisting motion.
|
|
|
|
first-degree (mild) sprain
|
involves tears of only a few fibers resulting in mild tenderness and minimal swelling.
|
|
|
|
second-degree (moderate) sprain
|
partial disruption of the involved tissue with more swelling and tenderness.
|
|
|
|
third-degree (severe) sprain
|
a complete tearing of the ligament in association with moderate to severe swelling.
|
|
|
|
strain
|
an excessive stretching of a muscle and its fascial sheath. It often involves the tendon.
|
|
|
|
first degree strain
|
mild or slightly pulled muscle
|
|
|
|
second degree strain
|
moderate or moderately torn muscle
|
|
|
|
third degree Strain
|
severely ruptured or torn muscle
|
|
|
|
hemarthrosis
|
bleeding into a joint space or cavity
|
|
|
|
If an injury occurs, the immediate care focuses on
|
(1) stopping the activity and limitation of movement
(2) applying ice compresses to the injured area (3) compressing the involved extremity (4) elevating the extremity (5) providing analgesia as necessary. RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation) has been found to decrease local inflammation and pain for most musculoskeletal injuries. |
|
|
|
dislocation
|
a severe injury of the ligamentous structures that surround a joint. Dislocation results in the complete displacement or separation of the articular surfaces of the joint.
|
|
|
|
subluxation
|
a partial or incomplete displacement of the joint surface.
|
|
|
|
avascular necrosis
|
bone cell death as a result of inadequate blood supply
|
|
|
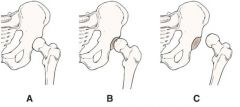
|
Soft tissue injury of the hip. A, Normal. B, Subluxation (partial dislocation). C, Dislocation.
|
|
|
|
Repetitive strain injury (RSI)
|
a cumulative traumatic disorder resulting from prolonged, forceful, or awkward movements.
|
|
|
|
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)
|
a condition caused by compression of the median nerve, which enters the hand through the narrow confines of the carpal tunnel
|
|
|
|
causalagia
|
burning pain
|
|
|
|
Phalen's test
|
Holding the wrists for 60 seconds produces tingling and numbness over the distribution of the median nerve: the palmar surface of the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and part of the ring finger
|
a positive test
|
|
|
Tinel's sign
|
Tapping gently over the volar aspect of the wrist (area of the inflamed median nerve) may reproduce paresthesia.
|
a positive test
|
|
|
drop arm test
|
the arm falls suddenly after the patient is asked to slowly lower the arm to the side after it has been abducted 90 degrees, is another sign of rotator cuff injury.
|
|
|
|
acromioplasty
|
surgical removal of part of the acromion to relieve compression of rotator cuff during movement
|
|
|
|
fracture
|
a disruption or break in the continuity of the structure of bone
|
|
|
|
stable fracture
|
occurs when a piece of the periosteum is intact across the fracture and either external or internal fixation has rendered the fragments stationary. Stable fractures are usually transverse, spiral, or greenstick.
|
|
|
|
unstable fracture
|
grossly displaced during injury and is a site of poor fixation. Unstable fractures are usually comminuted or oblique.
|
|

