![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Efficiency |
Process of comparing the amount of the energy we can actually use from the process to the original amount of the energy that went into the process |
Light bulbs |
|
|
Law of Conservation of energy |
A fundamental natural conservation law. The total amount of energy entering a process equals the sum of all forces of energy that exist at the end of the process |
|
|
|
P=M x V |
P = momentum M = mass of system measured in kilos V = velocity of magnitude [speed] of a system [m/s] |
|
|
|
Momentum |
Moving objects have a property that determines how much force is needed to change its motion |
|
|
|
Conservation of momentum |
System of colliding objects. sum of the momentum before collision is equal to sum of momentum after collision with no external force |
|
|
|
Elastic collision |
Two objects collide and rebound so that the sum of their momentum and kinetic energies are the same before and after the collision |
|
|
|
Partially elastic collision |
After the collision, the rebounding objects are temporarily or permanently deformed |
|
|
|
Inelastic collision |
Object stick together after collision |
|
|
|
Pendulum |
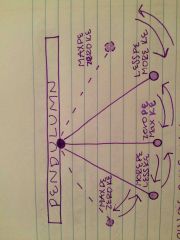
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
First law of thermodynamics |
Energy and matter can only change forms they cannot be created nor destroyed |
|

