![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Characteristics of Karst Topography |
caves, springs, natural bridges, sinkholes, tower karst, disappearing streams |
|
|
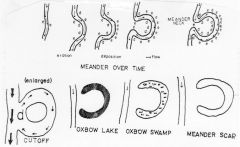
Oxbow Lake |

caused by sediment being carried |
|
|
Point Bar |

caused by deposition |
|
|
Meander |

developed on flood plain of stream near base level, then change in base level caused stream to downcut either base level dropped or land on which river was flowing was uplifted |
|
|
Old Stream |
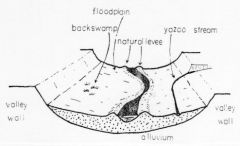
low gradient means broad flat floodplain meandering becomes significant not near valley walls most load in suspension |
|
|
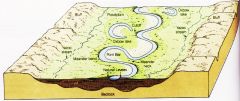
Mature Stream |
no rapids or waterfalls down-cutting has stopped gradient is less floodplain begins to develop, valley widening |
|
|
Young Stream |

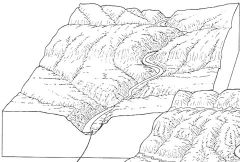
v-shaped steep valley walls occurs where stream is above base level and gradient is steep narrow channel, no meanders down-cutting is taking place faster than widening rapids and waterfalls |
|
|
Yazoo Tributaries |
flows roughly parallel to main stream cannot enter river because of levees |
|
|
Back Swamps |
poorly drained behind levee marshees |
|
|
Natural Levees |
parallel to river created by floods gentle slope |
|
|
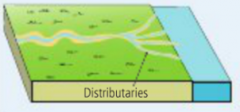
Distributaries |
distribute water from the main channel across the delta |
|
|
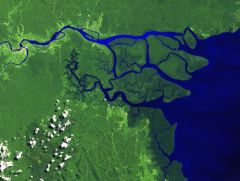
Delta |
deposited at mouth of a stream as it enters a lake or ocean velocity is reduced splits into smaller streams (distributaries) |
|
|
Alluvial Fan |

fan/cone shaped gathering of alluvium deposited where gradient is reduced. Emerges from a mountainous, narrow valley onto flatter terrain. |
|
|
Braided Stream |
Channels with interwoven appearance consists of sand/gravel wide and shallow if stream load is greater than its capacity... |
|
|
Alluvium |
term that describes all the sediment deposited by a stream |
|
|
Capacity |
maximum load transported depends on the steam's discharge |
|
|
Competence |
maximum size particles transported depends on stream's velocity K.E.=1/2mv^2 |
|
|
Bed Load |
particles that are too heavy to be carried in suspension and that roll or bounce along the bottom |
|
|
Suspended Load |
fine sand, silt, clay particles in suspension |
|
|
Dissolved Load |
most dissolved minerals come from ground water |
|
|
Transportation |
dissolved load suspended load bed load-determined by capacity and competence |
|
|
Deposition |
occurs when stream's velocity is reduced heavier particles settle out first-sorting of transported material |
|
|
3 "Works" of Streams |
Erosion Transportation Deposition |
|
|
What happens if base level is raised? Lowered? |
If raised...gradient is reduced, velocity is reduced, sediment transportation is decreased, low energy, sediment buildup If lowered...waterfalls form, rapids occur, then becomes adjusted (increased velocity) |
|
|
Temporary/local base level |
lake, larger stream, layer of resistant rock, anything other than the ocean that restricts the downward erosion of a stream |
|
|
Ultimate base level |
Sea level |
|
|
Effect of retention in ponds of a drainage basin and how it affects dry weather in stream flow |
delay entry of water into stream runoff increase lag time decrease peak discharge dry season discharge is higher |
|
|
Changes from upstream to downstream |
gradient decreases discharge increases width increases depth increases velocity increases sediment size decreases
|
|
|
River with world's largest discharge |
Amazon River-7,500,000 ft^3/sec |
|
|
Mississippi River's Rank |
8 -593,000 |
|
|
Discharge |
volume of water flowing past a point per second discharge increases, then width or depth or velocity must increase (usually all three) |
|
|
Friction |
slows down water in stream increase friction, decrease velocity |
|
|
Gradient |
the slope of stream channel ex. 110ft/50mi = 2.2 ft/mi |
|
|
Factors controlling stream's velocity |
gradient, channel characteristics, discharge |
|
|
Trellis drainage pattern |
occurs in folded mountains |
|
|
Rectangular drainage pattern |
controlled by underlying joints and vaults |
|
|
Radial drainage pattern |
produced from domes or volcanoes |
|
|
Dendritic drainage pattern |
"root-like" controlled by slope of the land |
|
|
Divide |
separates two drainage basins |
|
|
Drainage basin |
all the land area that contributes water to a stream |
|
|
How is a natural bridge formed in a karst area? |
from the collapse of the rood of a cave tunnel |
|
|
What produces a karst topography? |
the action of acidic water over a large area produces a karst topography |
|
|
In what kind of rock do most caves form? |
Limestone |
|
|
What acid is most important in cave formation? |
carbonic acid + calcite = limestone dissolved in water acidic water |
|
|
Where do caves form relative to the water table? |
At or below the water table |
|
|
Where do speleothems form relative to the water table? |
form in caves, below water table |
|
|
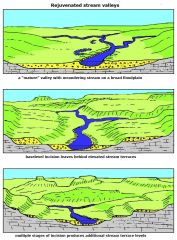
What are stream terraces and how are they formed? |
If base level of a meandering stream drops or if the land is uplifted, downcutting resumes and the meanders become incised. Can be caused by change in climate. |
|
|
What is an entrenched (incised) meander? |
deep valley caused by erosion |
|
|
What causes a rejuvenated stream to form? |
drop in base level for main stream, causing erosion |
|
|
dendritic |

|
|
|
radial |

|
|
|
rectangular |
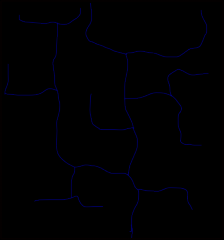
|
|
|
trellis |

|
|
|
retention basin |

|
|
|
pothole |

|
|
|
stalactite |

|
|
|
stalagmite |

|
|
|
soda straw |

|
|
|
natural bridge |

|
|
|
spring |

|
|
|
sinkhole |

|
|
|
delta |
|
|
|
alluvial fan |

|
|
|
distributaries |
|
|
|
stream terrace |
|
|
|
life cycle of meanders |
|
|
|
yazoo tributary |
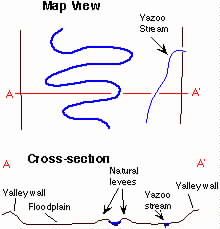
|
|
|
entrenched meander |

|
|
|
cutbank |

|
|
|
headwaters.... |
erosion |
|
|
middle section... |
transportation |
|
|
downstream |
deposition |
|
|
discharge= |
width x depth x velocity |

