![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Mineralogy |
A geoscientist that specializes in the study of minerals. |

Mineral Specialist |
|
|
Mineral |
A homogenous naturally occurring, solid inorganic substance with a definable chemical composition and an internal structure characterized by an orderly arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in lattice. Most minerals are inorganic. |

|
|
|
Biogenic Mineral |
Substances that meet the definition of a mineral and are produced naturally by organisms. |

|
|
|
Crystal Lattice |
The orderly framework within which the atoms or ions of a mineral are fixed. |
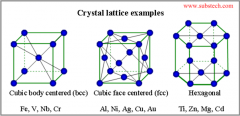
|
|
|
Glass |
A solid in which atoms are not arranged in an orderly pattern. |

|
|
|
Element |
A material consisting entirely of one kind of atom; elements cannot be subdivided or changed by chemical reaction |

|
|
|
Atom |
The smallest piece of an element that has the properties of the element; it consists of nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. |
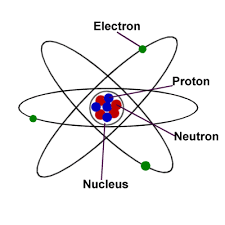
|
|
|
Mass Number |
No definition |
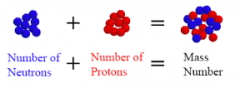
|
|
|
Atomic Mass |
The amount of matter in an atom roughly, it is the sum of the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus. |
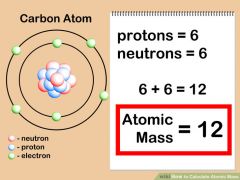
|
|
|
Chemical Bond |
The invisible link that holds together atoms in a molecule and/or in a crystal. |
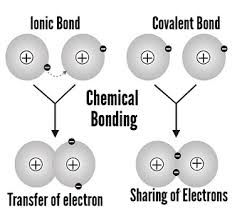
|
|
|
Ion |
A version of an atom that has lost or gained electrons, relative to an electrically neutral version, so that it has a net electrical charge. |
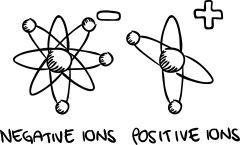
|
|
|
Molecule |
The smallest piece of compound that has the properties of the compound; it consists of two or more atoms attached by chemical bonds. |
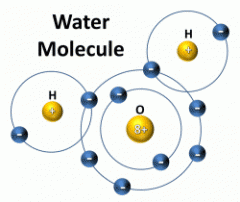
|
|
|
Chemical |
A material consisting of a distinct element or compound. |

|
|
|
Chemical Formula |
The "recipe" that specifies the elements and their proportions in a compound. |
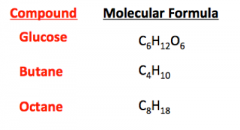
|
|
|
Chemical Reaction |
Interactions among atoms and/or molecules involving breaking or forming chemical bonds. |

|
|
|
Concentration |
The proportion of one substance (the solute) dissolved within another (the solvant) |
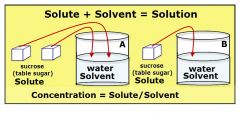
|
|
|
Precipitate |
A solid substance formed when atoms teach and settle out of a solution, or attach to the walls of the container holding the solution; the action of forming a solid substance from a solution; the dropping of snow or rain from the sky. |

|
|
|
Polymorphs |
Two minerals that have the same chemical composition but a different crystal lattice structure. |

|
|
|
Color |
The characteristic of a material due to the spectrum of light emitted or reflected by the material, as perceived by eyes or instruments. |

|
|
|
Streak |
The color of the powder produced by a pulverizing a mineral on an unglazed ceramic plate. |

|
|
|
Luster |
The way a mineral surface scatters light. |

|
|
|
Hardness |
A measure of the relative ability of a mineral to resist scratching; it represents the resistance of bonds in the crystal structure from being broken. |
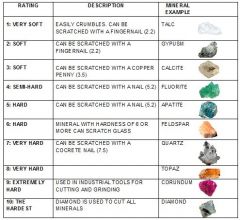
|
|
|
Mohs Hardness Scale |
A list of ten minerals in a squence of relative hardness, with which other minerals can be compared. |
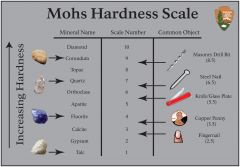
|
|
|
Specific Gravity |
A number representing the density of a mineral, as specified by the ratio between the weight of a volume of the mineral and the weight of an equal volume of water |
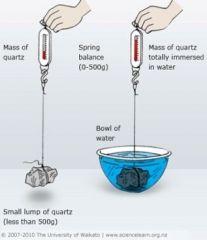
|
|
|
Crystal Habit |
The general shape of a crystal or cluster of crystals that grew unimpeded |
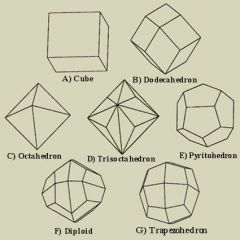
|
|
|
Cleavage |
The tendency of a mineral to break along preferred planes; a type of foliation in low-grade metamorphic rock. |
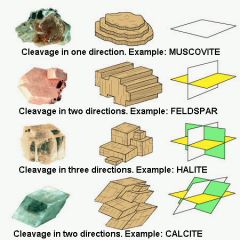
|
|
|
Conchoidal Fractures |
Smoothly curving, clamshell-shaped surfaces along which materials with no cleavage planes tend to break. |

|
|
|
Mineral Classes |
Groups of minerals distinguished from each other on the basis of chemical compsition. |
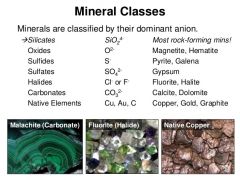
|
|
|
Carbonate Minerals |
Rocks containing calcite and/or dolomite. |

|
|
|
Silicates |
Minerals built from silicon-oxygen tetrahedra arranged in chains, sheets, or 3-D networks, they make up most of the Earth's crust and mantle |
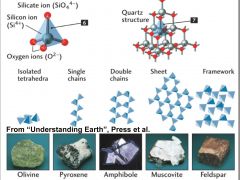
|
|
|
Silicon-Oxygen Tetrahedron |
The SiO44- anionic group, in which four oxygen atoms surround a single silicon atom, thereby defining the corners of a tetrahedron. |

|
|
|
Naturally Occurring |
Formed in nature, not by man |
Naturally made |
|
|
Inorganic |
No carbon-carbon or carbon-hydrogen bonds and not produced by living organs, no sugars, fats, propane, proteins, pearls, or amber |
not made by any organisms |
|
|
Solid |
No liquids, water, oil, no gases, methane, carbon dioxide. |
no liquids |
|
|
Definable Chemical Composition |
A chemical composition that will define the mineral and able to write out the chemical formulas. |
Has formulas |
|
|
Crystalline Structure |
The atoms that make up the mineral are in a fixed orderly pattern |
Glass is disorderly while minerals are orderly |
|
|
What is a crystal? |
Single continuous piece of crystalline and is solid, typically bounded by fly surfaces. faces grow naturally as in mineral forms, and are sometimes prized mineral specimens |
solid crystalline |
|
|
What is Crystal Faces? |
Constancy of interfacial angles, faces occur at the same angle to one another, reflect crystalline structure. |
face and angle of crystallines |
|
|
The shapes of crystals. |
Halite, Diamond, Staurolite, Quartz, Garnet, Stibnite, Calcite, Kyanite |
Cube, pyramid, quartz |
|
|
How are minerals constructed? |
Ordered atoms, tightly together by chemical bond. Hold physical properties (hardness & shape) based on atoms identity, arrangement of atoms, nature of atomic bonds |
Atoms and atomic bonds |
|
|
What controls the characteristics of crystals? |
The nature of atomic bonds. Strong covalent bonds like diamonds, or weak van der Waals bonds like graphite. Polymorph have same composition but different structures. |
The bonds of the atoms |
|
|
What is ionic radius? |
Size and ionic charge control packing |
charge and packing |
|
|
What is an ion? |
Charged atom, due to gain or less of electrons |
atom and electrons |
|
|
What are Cations? |
Positive ions due to loss of electrons |
Loss of electrons + |
|
|
What are Anions? |
Negative ions due to gain of electrons |
Gain of electrons - |
|
|
What defines the geometric shapes in crystals? |
Packing configuration of ions/anions. |
packing configuration |
|
|
What controls the crystal shape? |
The internal pattern of atoms |
atoms |
|
|
X-Ray Diffraction |
XRD: images of crystal lattices, unique lattice spacing used to ID minerals |
Reflective Pattern |
|
|
Transmission Electron Microscope |
TEM: modern instrument to see atomic patterns, shoots beam of electrons at a crystal, passes through space reaching a detector, interacts with atoms, uses dark and light pattern images of the atomic crystal lattice. |
Microscope |
|
|
Solid-State Diffusion |
Garmets in metamorphic environment |
Five ways crystals are formed |
|
|
Biomineralization |
Petrified/fossiled bones |
Five ways crystals are formed |
|
|
Precipitating Directly from Gas |
Sulfur crystals form around a volcanic vent (Yellowstone Park) |
Five ways crystals are formed |
|
|
Crystal Destruction Melting |
heat breaks the bonds holding atoms together |
heat |
|
|
Crystal Destruction Dissolving |
Solvents (mostly water) break atomic bonds (dissolution) |
water |
|
|
Crystal Destruction Chemical Reaction |
Reactive minerals break bonds |
reactive |
|
|
Mineral Property Color |
Varieties often reflect trace impurities, diagnostic for some minerals, light is not absorbed by mineral. |
impurities |
|
|
Mineral Property Streak |
Powder color by scraping mineral on unglazed surface |
powder |
|
|
Mineral Property Luster |
How the surface scatters light, and divided by metallic and nonmetallic |
scattered light |
|
|
Metallic |
Looks like metal |
metal |
|
|
Mineral Properties Hardness |
Scratch resistant, derives strong atomic bonds, determined the Mohs scale |
strong bond |
|
|
Mineral Property Gravity |
The density, weight over volume, the heft (how heavy it feels) |
weight |
|
|
Mineral Property Crystal Habit |
Well formed faces, well formed crystals, faces reflect internal tonic structures, variation of growth rates and direction. |
Formed faces |
|
|
Mineral Property
Fracture |
Break reflects atomic bonding, bond strength in all directions. Some appear like clam shell, smooth curved surfaces, sharp edges
|
Breaking
|
|
|
Mineral Property
Cleavage |
Break along the plane have weaker bonds, are flat, shiny on surface, have multiple planes and angles. |
planes |
|
|
Silicates are called... |
Rock-Forming Minerals |
rock forming |
|
|
What is the most common Silicate mineral? |
Quartz |
SiO2 |
|
|
Gemstones |
Mineral with special value Rare: formed by unusual geological processes Beautiful: strikingly unique color, clarity, and luster |
value |
|
|
Gems |
Are cut and plashed stones created for jewelry Precious: diamond, ruby, sapphire Semiprecious: Tourmaline, Topaz, Aquamarine, Gamet |
jewelry |
|
|
How are diamonds found? |
Rifting causes deep mantle rock to move upwards, where diamond are found in kimberlite pipes. |
rifting |

