![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
_____ _____ have exactly the same atoms connected in exactly the same positions but differ in the locations of double or triple bonds.
|
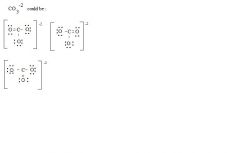
Resonance Structures
|
|
|
Name the 6 steps for drawing resonance structures.
|
1. Determine the total # of available valence electrons.
2. Identify a central atom. 3. Connect all outer atoms to the central atom. 4. Complete the octets of the outer atoms. 5. Any remaining electrons go to the central atom. 6. Check the central atom and form double or triple bonds as necessary (ionic structures are bracketed with the charge indicated). |
|
|
When a compound has non equivalent resonance structures, what is known about one of the structures?
|
There is always a structure that is preferred over the others.
|
|
|
he preferred structure is called the _____ _____.
|
major contributor
|
|
|
How do we identify the major contributor of a set of non equivalent resonance structures?
|
We look at the bonding preferences of the atoms in the structure. The structure that most closely fits the bonding preferences will be considered the major contributor.
|
|
|
How are bonding preferences derived?
|
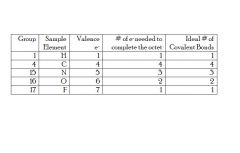
They are derived from the valence e- and the number of electrons needed to achieve an “octet” (see above)
|
|
|
Identify the major contributor for SNCl (with N in the middle).
|

see above
|
|
|
Happy atoms in structures have what?
|
their ideal # of covalent bonds, no more/ no less.
|
|
|
What makes molecules unhappy?
|

when it has atoms that do not have their ideal # of covalent bonds
|
|
|
The electronegative elements (Oxygen & the halogens) are _____ unhappy when they have fewer than their ideal # and _____ unhappy when they have extra bonds.
|
less
more |
|
|
The lesser electronegative elements N, S, P, C are _____ unhappy when they have extra bonds, _____ unhappy when they have fewer than their ideal #.
|
less
more |
|
|
In structures where hydrogen atoms are covalently bonded to _____, _____, _____, _____ or _____, the bond will be polar. In theses bonds the H is the less electronegative element and thereby has a _____ _____ _____.
|
O
N F Cl Br partial positive charge |
|
|
What are the two requirements for a hydrogen bond to be formed?
|
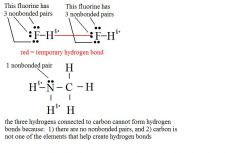
e- sharing can happen in any situation where there is a hydrogen atom w/ a partial charge and:
1) it is attached to an O, N, F, Cl, or Br atom that 2) has at least one lone pair (non-bonded pair of e-). |

