![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is cellular metabolism? |
How refers to all of the chemical processes that occur inside living cells. |
|
|
|
How mang states can energy be in? Explain both |
•Kinetic energy – energy of motion. •Potential energy – stored energy. •Chemical energy – potential energy stored in bonds, released when bonds are broken. •Energy can be transformed form one state to another. |
|
|
|
What is the 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics |
•First law of thermodynamics – energy cannot be created or destroyed – only transformed. •Second law of thermodynamics – a closed system moves toward entropy, increasing disorder. •Living systems are open systems that maintain organization and increase it during development. |
|
|
|
Using energy in what source |
•Free energy – the energy available for doing work. •Most chemical reactions release free energy – they are exergonic. •Downhill •Some reactions require the input of free energy – they are endergonic. •Uphill |
|
|
|
What are catalysts |
•Catalysts are chemical substances that speed up a reaction without affecting the products. •Catalysts are not used up or changed in any way during the reaction. •Enzymes are important catalysts in living organisms. |
|
|
|
What is an enzyme and what is its function |
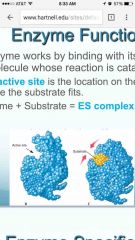
•An enzyme works by binding with its substrate, the molecule whose reaction is catalyzed. •The active site is the location on the enzyme where the substrate fits. •Enzyme + Substrate = ES •
Enzymes reduce the amount of activation energy required for a reaction to proceed |
|
|
|
Model of tranferring energy |
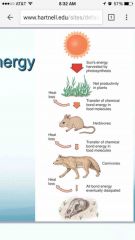
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is the importance of ATP |
•ATP consists of adenosine (adenine + ribose) and a triphosphate group. •The bonds between the phosphate groups are high energy bonds. •A-P~P~P |
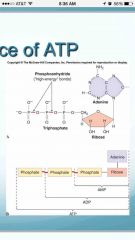
|
|
|
Enzymes being catalyzed (4) |
•Enzyme-catalyzed reactions are reversible. •Indicated by double arrows in reactions. •Tend to go mostly in one direction. •Reactions tend to be catalyzed by different enzymes for each direction. •Catabolic (degradation) reaction catalyzed by enzyme A. •Anabolic (synthesis) reaction catalyzed by enzyme B. |
|
|
|
What is oxidation? What is reduction |
•An atom that loses an electron has been oxidized. Oxygen is a common electron acceptor. •An atom that gains an electron has been reduced. Higher energy. |
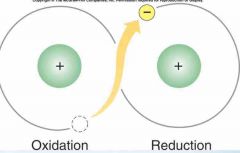
|
|
|
What are redox reactions? |
• always occur in pairs. •One atom loses the electron, the other gains the electron. •Energy is transferred from one atom to another via redox reactions. |
|
|
|
What is cellular respiration? |
•the oxidation of food molecules to obtain energy. •Electrons are stripped away. •Different from breathing (respiration). |
|
|
|
Aerobic vs anareobic respiration |
•Heterotrophs •Aerobes: Use molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor •Anaerobes: Use other molecules as final electron acceptor •Energy yield much lower ATP yield
|
|
|
|
What is cellular respiration? |
•the oxidation of food molecules to obtain energy. •Electrons are stripped away. •Different from breathing (respiration). |
|
|
|
Aerobic vs anareobic respiration |
•Heterotrophs •Aerobes: Use molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor •Anaerobes: Use other molecules as final electron acceptor •Energy yield much lower ATP yield
|
|
|
|
When does anaerobic respiration occur |
•occurs in the absence of oxygen. •Different electron acceptors are used instead of oxygen (sulfur, or nitrate). •Sugars are not completely oxidized, so it doesn’t generate as much ATP. |
|
|
|
What is cellular respiration? |
•the oxidation of food molecules to obtain energy. •Electrons are stripped away. •Different from breathing (respiration). |
|
|
|
Aerobic vs anareobic respiration |
•Heterotrophs •Aerobes: Use molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor •Anaerobes: Use other molecules as final electron acceptor •Energy yield much lower ATP yield
|
|
|
|
When does anaerobic respiration occur |
•occurs in the absence of oxygen. •Different electron acceptors are used instead of oxygen (sulfur, or nitrate). •Sugars are not completely oxidized, so it doesn’t generate as much ATP. |
|
|
|
What are the 3 steps of cellular respiration? |
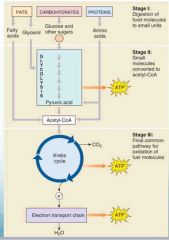
•Food is digested to break it into smaller pieces – no energy production here.
•Glycolysis – coupled reactions used to make ATP. •Occurs in cytoplasm •Doesn’t require O2 •Oxidation – harvests electrons and uses their energy to power ATP production. •Only in mitochondria •More powerful |
|
|
|
What happens when oxygen is avaible for cellular respiration? |
•When oxygen is available, a second oxidative stage of cellular respiration takes place. •First step – oxidize the 3-carbon pyruvate in the mitochondria forming Acetyl-CoA. •Next, Acetyl-CoA is oxidized in the Krebs cycle. |
|
|
|
Using electrons to make ATP |
•NADH & FADH2 contain energized electrons. •NADH molecules carry their electrons to the inner mitochondrial membrane where they transfer electrons to a series of membrane bound proteins – the electron transport chain. |
|
|
|
Using electrons to make ATP |
•NADH & FADH2 contain energized electrons. •NADH molecules carry their electrons to the inner mitochondrial membrane where they transfer electrons to a series of membrane bound proteins – the electron transport chain. |
|
|
|
The krebs cycle part 2 |
•Each glucose provides 2 pyruvates, therefore 2 turns of the Krebs cycle. •Glucose is completely consumed during cellular respiration. |
|
|
|
Give a review of cellular respiration |
•1 ATP generated for each proton pump activated by the electron transport chain. •NADH activates 3 pumps. •FADH2 activates 2 pumps. •The 2 NADH produced during glycolysis must be transported across the mitochondrial membrane using 2 ATP. •Net ATP production = 4 |
|
|
|
What is fermenation? |
It changes sugars into acids |
|

