![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Living organisms consist of mostly |
Carbon-based compaounds |
|
|
Carbon is unparalleled in its ability to form |
Large complex, and diverse molecules |
|
|
Study of compounds that contain carbon |
Organic chemistry |
|
|
Organic compounds range from |
Simple molecules to colossal ones |
|
|
Most organic compounds contain |
hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms |
|
|
______(person) tried to make inorganic salt ammonium cyanate by mixing ammonium ions and cyanate ions instead urea was made. Kolbe made acetic acid |
Wohler |
|
|
Processes of life are governed by |
physical and chemical laws |
|
|
_________(person) classic experiment demonstrated the abiotic synthesis of organic compounds (Vitalism to mechanism) |
Stanley Miller (support the idea that abiotic synthesis of organic compounds could have been a stage int he origin of life) |
|
|
_______ is key to an atom's characteristics and determines the kinds and number of bonds an atom will form with other atoms |
Electron configuration |
|
|
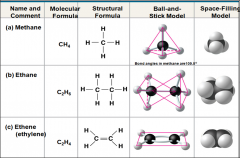
In molecules with multiple carbons each carbon bonded to 4 other atoms has a |
Tetrahedral shape |
|
|
Shape of molecule determines its function |
|
|
|
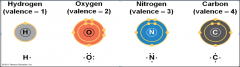
The electron configuration of carbon gives it a |
covalent compatibility with many different elements |
|
|
The valences ofcarbon and its most frequent partners (hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) are the“building code” that governs the architecture of living molecules
|
|
|
|
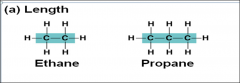
Carbon chains form the _____and vary in length and shape |
skeletons of the most organic molecules |
|
|
Length |
|
|
|
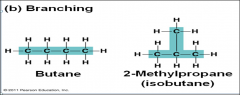
Branching |
|
|
|
Double bond position |
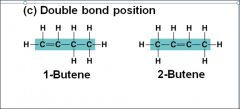
|
|
|
Presence of rings |
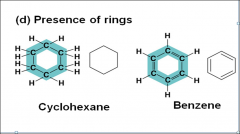
|
|
|
______ are organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen |
Hydrocarbons |
|
|
Many organic molecules such as ___ have hydrocarbon components |
Fats |
|
|
______ are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties |
Isomers |
|
|
Structural isomers have |
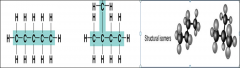
Different covalent arrangements of their atoms |
|
|
_____ have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements |
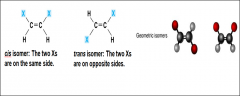
Cis-Trans isomers |
|
|
______ Are isomers that are mirror images of each other |
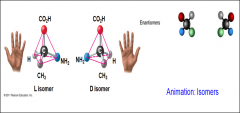
Enantiomers |
|
|
Enantiomers are important because |
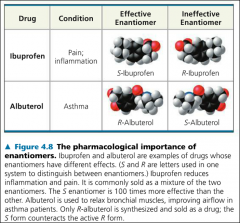
-Two enantiomers of a drug may have different effects -Usually one isomer is biologically active -Differing effects of enantiomers demonstrate that organisms are sensitive to even subtle variation in molecules |
|
|
______ of organic molecules depend on the carbon skeleton and on the molecular components attached to it |
Distinctive properties |
|
|
A number of characteristic groups can replace the hydrogens attached to skeletons of organic molecules |
These groups may participate in the chemical reactions or may contribute to function indirectly by their effects on molecular shape |
|
|
_____ are the components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions |
Functional groups |
|
|
The number and arrangement of functional groups give each molecule |
its unique properties |
|
|
Example of Functional group arrangement |
|
|
|
The 7 functional groups that are most important in the chemistry of life are: The first 6 can act as functional groups; they are hydrophilic and thus increase the solubility of organic compounds in water. |
1. Hydroxyl group 2. Carbonyl group 3. Carboxyl group 4. Amino group 5. Sulfhydryl group 6. Phosphate group 7.Methyl group The methyl group is not reactive but instead serve as a recognizable tag on biological molecules |
|
|
Hydroxyl |
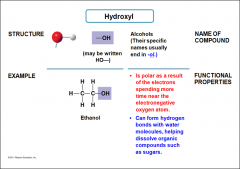
-Ends with -ol -Is polar as a result of the electrons spending more time near the electronegative oxygen atom -Can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, helping dissolve organic compounds such as sugars |
|
|
Carbonyl |
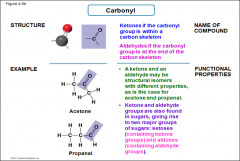
-KETONES if carbonyl group is within a carbon skeleton -ALDEHYDES if carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton -Ketones and aldehydes may be structural isomers with different properties as is the case for acetone and propanal -both are also found in sugars, giving rise to two major groups of sugars ketoses and aldoses. |
|
|
Carboxyl |
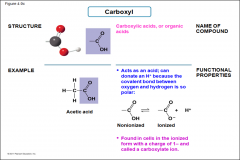
-Carboxylic acids or organic acids -acts as acid; can donate an H+ because the covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar -found in cells in the ionized form with a charge of 1- and called a carboxylate ion |
|
|
Amino |
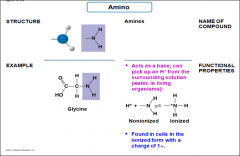
-Amines -Acts as a base; can pick up an H+ from the surrounding solution -found in cells in the ioninzed form of 1+ |
|
|
Sulfhydryl |
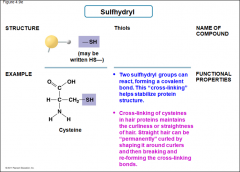
-Thiols -Two sulfhydryl groups can react, forming a covalent bond. Helps stabilize protein structure -Cross-linking of cysteines in hair proteins maintains the curliness or straightness of hair |
|
|
Phosphate |
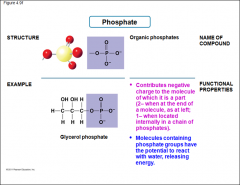
-Organic Phosphates -Molecules containing phosphate group have the potential to react with water, releasing energy |
|
|
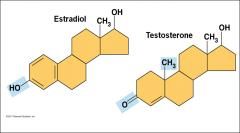
Methyl |
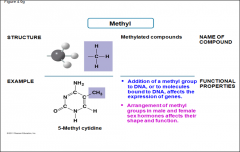
-Methylated compounds -arrangement of methyl groups in male and female sex hormones affects their shape and function |
|
|
Primary energy transferring molecule in the cell (Energy currency) |
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) phosphate molecule |
|
|
ATP consist of |
an organic molecule called adenosine attached to a string of 3 phospate |

