![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skin |
Derm/o, dermat/o, cutane/o, cut/o |
|
|
Layers of the skin |
Epidermis, dermis/corium, hypodermis/subcutaneous |
|
|
What is the dermis composed of? |
Composed of vascular connective tissue |
|
|
Structures in dermis |
Blood, lymphatic vessels, nerves, hair follicles (follicul/o), sebaceous (sebac/o) and sudoriferous glands (sudor/i) |
|
|
Sudoriferous glands |
Sweats through pores. The secretion of sweat is called perspiration. Abundant in soles of feet, palms of hand, armpit, upper lip and forehead |
|
|
Sebaceous Glands |
Secretes sebum(seb/o) which helps lubricate hair and surfaces of skin |
|
|
Hair |
Trich/o, pil/o. Their roots are called follicles (follicul/o). The visible part is called hair shaft and underneath the follicles is the papilla. |
|
|
Nails |
Consists of the nail body, root, bed(highly vascular), lunula, cuticle (eponychium) and the paronychium (fold of skin near side of nail) |
|
|
Primary Skin lesion |
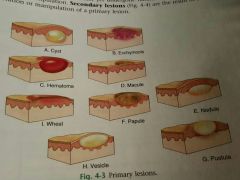
Early skin changes that have not yet undergone natural evolution or change caused by manipulation |
|
|
Secondary Skin Lesion |
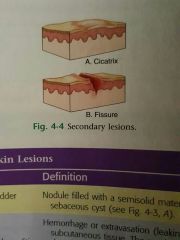
Result of natural evolution or manipulation of a primary Skin lesion |
|
|
Cyst |
Cyst/o . Nodule filled with semi solid material such as keratinous or sebaceous cyst |
|
|
Nodules |
Palpable, solid lesion less than 2 cm |
|
|
Tumor |
Nodules larger than 2 cm, tumor is used to explain mass swelling |
|
|
Hematoma |
Collection of leaked blood trapped in the tissues and can be felt by examiner |
|
|
Ecchymosis |
Hemorrhage or extravasion of blood in the subcutaneous tissue. It is not palpable but darkens skin. Usually called bruise |
|
|
Petechia |
Tiny ecchymosis in the dermal layer |
|
|
Purpura |
Massive hemorrhage into the tissues under the skin |
|
|
Macule |
Flat, non palpable blemish or discoloration that is less than 1 cm. (Ex: freckles, port wine stains, tattoos) |
|
|
Patch |
Large, flat, non palpable macule that is larger than 1 cm |
|
|
Papule |
Raised, solid skin lesion that is less than 1 cm. (Ex: pimple) |
|
|
Plaques |
Raised plateau like papule larger than 1cm |
|
|
Wheals |
Circumcised elevated papule caused by localized edema. (Ex: bug bites, hives) |
|
|
Vesicles/bullae |
Circumcised elevated lesion filled with fluid and smaller than 1/2 cm. If it is larger it is called bulla. Known as blisters |
|
|
Pustules |
Raised lesion due to infection |
|
|
Telangiectasia |
Condition of dilated superficial venules and capillaries |
|
|
Atrophy |
Paper think wasted skin often seen in aged people or as stretch marks |
|
|
Keloid |
Overgrowth of tissue at the sight of injury |
|
|
Eschar |
Dried serum, blood and or pus that can occur at site of injury or burn |
|
|
Fissure |
Crack like lesion of the skin |
|
|
Ulcer |
Circumscribed crater like lesion of skin or mucous membrane. Can occur outside surface and inside |
|
|
Impetigo |
Pediatric disease. Superficial skin infection |
|
|
Acne |
Pediatrics disease. Inflammatory disease of the sebaceous Glands. Has comedones. Open comedones is blackhead while closed is white head |
|
|
Seborrheic dermatitis |
Pediatrics disease. Inflammatory scaling disease of the scalp and face. |
|
|
Cellulitis |
Pediatrics and Geriatrics disease. Diffuse, spreading, acute inflammation within solid tissue |
|
|
Pediculosis |
Pediatrics disease. parasitic infection with lice |
|
|
Corns |
Geriatrics disease. Horry mass of condensed epithelial tissue overlying a bony prominence as result of pressure and friction. |
|
|
Calluses |
Geriatrics disease. Common painless thickening of the stratum cornering at locations of external pressure or friction |
|
|
Excisional biopsy |
Entire tumor removed along with its borders as means of diagnosis and treatment |
|
|
Exfoliation |
Scraping or shaving of samples of friable lesions for examinations. |
|
|
Incisional Biopsy |
Cutting of a wedge of tissue from lesion followed by suturing closed of the site |
|
|
Needless aspiration |
Aspiration of fluid from lesions for culture and examination |
|
|
punch biopsy |
Insertion of a tubular punch through the skin to the subcutaneous tissue to extract a core of tissue for examinations |
|
|
Bacterial analyses |
Cultures and serology of fluid removed from lesions to determine type of bacteria |
|
|
Fungal tests |
Scraping of lesions to determine type of fungus |
|
|
Sweat tests |
Done to tear for abnormally high levels of sodium and chloride as it can mean cystic fibrosis |
|
|
Tuberculosis skin test |
Tests for active and dormant tuberculosis |
|
|
Viral culture |
Samples of vesicular fluid to help identify types of virus in lesion |
|
|
Wound and abscess culture |
Samplings that identify pathogens in ulcers, wounds and abscess |
|
|
Escharotomy |
Incision to cut eschar, the scab that forms over burns. This is done to prevent edema that can cause lack of blood flow |
|
|
Incision and drainage |
Cutting open and removal of the contents of a cyst, wound or other lesion |
|
|
Mohs surgery |
Repeated removal and microscopic examination of layers of a tumor until now cancerous cells are present |
|
|
Shaving/ paring |
Slicing thin sheets of tissues to remove lesion |
|
|
Hypodermic |
Under the skin |
|
|
Subcutaneous |
Under the skin |
|
|
Intradermal |
Within the skin |
|
|
Topical |
Applied directly on skin |
|
|
Emollients |
Softens the skin |

