![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Discrimination |
Occurs when a limited spectrum of Stimuli occassions a response -narrow stimuli control |
|
|
|
Generalization |
Occurs when a large spectrum of stimuli occassions certain responses. - generalization is a critical element as to why the human species has survived and thrived. |
|
|
|
Types of Generalization |
Stimulus generalization, response generalization |
|
|
|
Stimulus generalization |
Responding to antecedent stimuli sharing certain aspects of the original Sd. A broadening of the spectrum of stimuli. |
|
|
|
Over generalization |
Emitted a response for appear to some contexts in an inappropriate contexts |
Calling all women 'mom' |
|
|
Response generalization aka response induction |
The extent to which an individual sits novel responses that are functionally equivalent to the train target response |
|
|
|
Relevance of behavior rule |
Only choose behavior that generate reinforcers after intervention ceases. (How to plan for generalization) |
|
|
|
2 types of contingency |
Naturally existing contingencies, Contrive contingencies |
|
|
|
Naturally existing contingencies |
Any contingency of reinforcement (punishment/reinforcement) that operates independently of your efforts in a generalization setting. |
|
|
|
Contrived Contingencies |
Any contingency of reinforcement (or punishment) designed by you to achieve acquisition maintenance and/or generalization of a behavior change |
|
|
|
Strategies to promote generalization (Acronym; CLEMING) |
Common stimuli, loosely train, Examplars, Mediation, Indiscriminable contingencies, Negative teaching Examplar, General Case Analysis |
Acronym: CLEMING |
|
|
Common stimuli |
The likelihood that the correct response will be occasion in the generalization setting is increased if there is a lot of similarity. 》 Ensuring the SD exist in both the instructional and generalization setting |
|
|
|
Loosley Train |
- expanding the Heterogeriety of Sd |
Method: Teach upstairs in the home and downstairs |
|
|
Examplars |
More examples used during teaching the better |
Teaching with sufficient examples |
|
|
Mediation |
Instruct other who will maintain and generalize the newly acquired behavior. |
|
|
|
Indiscriminable contingencies |
Contingencies in which the individual does NOT know when to discriminate when they will be reinforced. |
Intermittent Schedules of Reinforcement 1. Intermittent reinforcement (IRF), 2. Continuous Reinforcement (CRF) OR Delayed Rewards |
|
|
Negative teaching Examplars |
Instructing individuals regarding settings, times and conditions in which is it NOT appropriate to display a certain behavior 'do not do it' examplars |
|
|
|
General Case Analysis (strategies) |
Teaching all the difference stimulus variations and response variations the individual mat encounter in the generalization post intervention environment. |
|
|
|
Skinner created and published in 1957 |
'verbal behavior' |
|
|
|
Private Events |
Events taking place inside the skin, thoughts and feelings, private events are behaviors too |
|
|
|
Verbal behavior |
Defined by the function of the response, NOT the topography. Behavior that is reinforced through the mediation of another person's behavior. Communication the helps individuals get what they want & avoid undesirable things/events. |
|
|
|
Verbal Behavior includes |
Vocal (spoken), non-vocal (non spoken), behavior (signs/gestures/written etc.) 》involves social interaction btw the speaker and the listener. |
|
|
|
VERBAL operant |
The unit of analysis in verbal behavior( mand, echoics, tact, interaverbal, textual, transcription) 》 Verbal repertoire: is a set of "verbal operants" emitted by someone. |
|
|
|
Acronym: EMITT |
Echoics, mand, tact, intraverbal, textual transcription |
|
|
|
Echoics |
(Has Point to point Correspondence and formal similarity) - Verbal operant that occurs when the speaker repeats the verbal behavior of another speaker. Repeat/ echoing /imitation |
|
|
|
_______Is controlled by the verbal discrimination stimulus (verbal Sd) |
Echoics |
|
|
|
Point to point correspondence |
When the beginning middle end of the verbal stimulus match the beginning middle and end of the response |
|
|
|
Formal similarity |
When the controlling and antecedant stimulus and the response share the same sense mode (e.g Both stimulus and response are visual auditory or tactile) and physically look exactly the same. |
|
|
|
Teaching Echoics |
Shaping, teaching presents a vocal verbal stimulus and reinforces the individual successive approximation Prompt level, physical, touching face gradually shape mouth formation |
|
|
|
Mand |
A type of verbal operant in which the speaker asks (states, demands implies) what he/ she needs or WANTS. 》 Occurs due to a state of deprivation or aversion stimulation. ________ are reinforcer due to attaining the manding item.____ are the 1st verbal operant acquired by humans. |
|
|
|
___________ controlled by the Mo's NOT Sd's |
Mand |
|
|
|
Mand Training |
Involves bringing verbal responses under the control Mo's. 》Using words involving a response form already in the clients repertoire. 》 Use items that related to strong Mo's |
|
|
|
Complex Mand |
Using mands w/ adj. H prepositions to increase the length of mands. 》manding for info. 》attention, etc "come play with me" 》ppl do things for u, etc. "get me water" |
|
|
|
Types of Mands |
Regular mand and contrived mand |
|
|
|
Regular Mand |
Mand's that can actually be reinforced. |
|
|
|
Extended mand |
Emitting mand's to objects or animals that cannot possibly supply an appropriate reinforcing response. 》2 types: superstitious, magical mand |
|
|
|
Superstitious |
An Extended Mand; a mand in which reinforcement sometimes occurs incidentally. |
Manding car to start when sometimes it started sometimes it doesn't. Sometimes car starts Intermittenly reinforced for manding |
|
|
Magical mand |
An Extended Mand: A mand that has never occurred in the past (wishing) |
|
|
|
Interaverbal |
Speaker differentially responds to other ppl. Answering a question!
|
|
|
|
Verbal Discrimination Stimulus (Sd) |
The intervertebral operant occurs when____________ evokes a verbal response that does NOT have a Point to point correspondence with the verbal stimulus. |
|
|
|
Produces Generalized condition reinforcement (GCSR) "doesnt depend on an Mo for its effectiveness" |
Intraverbal Operant |
|
|
|
Tact |
The speaker names things and actions that the speaker has direct contact (present in the environment) with through any of the Senses |
|
|
|
____________ Controlled by a non verbal discriminative stimulus (non-verbal Sd). Controlled by GCSR |
Tact |
|
|
|
Tact training |
Involves bringing the verbal response under the functional control of nonverbal SD. Non-verbal Sd = stimulus |
|
|
|
Intraverbal training |
Involves bringing the verbal response under the functional control verbal SD lacks point to point correspondence with the response 》teaching by prompting, fading, chaining. 》Continue to teach mand and tact |
|
|
|
Prerequisite tact |
》echoics 》labeling voc. 》5-10 mands without prompting |
|
|
|
Prerequisite intraverbal |
》requires 50 mands and tscts 》 |
|
|
|
Tact extension |
There is not one name for 1 thing there are many ways to describe the same thing |
|
|
|
Types of Tacts |
Holistic, Metophorical, Metonymical, Generic |
|
|
|
Solistic |
》Poor use of language 》 Substandard for bold behavior; slang |
|
|
|
Metophorical |
Metaphors; The novel stimulus shares some features associated but not always the original stimulus. |
Ex. Heart is as black as cool |
|
|
Metonymical |
Verbal responses to novel stimuli that share none of the relevant features of the original stimulus But some irrelevant by related features has acquired seniors control |
Ex. Saying 'water' when shown an empty cup. irrelevant related features |
|
|
Generic |
Sharing all of the relevant or defining features of the original stimulus. |
Ex. Saying jujube wen shown an M&M |
|
|
Textual |
Has point a point correspondence but no formal similarity. Reading without any implication that the reader knows/understands what is being read reading written words. |
|
|
|
Textual Operant |
Occurs when a verbal discrimination (Sd) has a point to point correspondence but no formal similarity. |
Ex. See written word 'pizza', says 'pizza' |
|
|
Transcription |
Writing and spelling words spoken to you. Taking Dictation! |
|
|
|
Transcription Operant |
Occurs when he spoken verbal discrimination stimulus (Sd) controls a written, typed or finger spelled response. Produces a GCSR (doesnt depend on Mo). |
|
|
|
Codic: 3 defining features |
The response form is controlled by the Verbal Sd; point to point correspondence the way it is said is the exact way it is formed; No Formal Similarities; the response does not have the same sense as the stimulus. |
|
|
|
Verbal Operants that fall under Codic |
Textual, Transcription |
|
|
|
Duplic: 3 defining features |
The response is controlled by the verbal stimulus (sd); has a point to point correspondence, the response is the same as the verbal stimulus (echo); Formal similarity, the response is exactly the same as the verbal sd (Spoken word pillow, response is the spoken word pillow) |
|
|
|
Verbal operant the falls under Duplic |
Echoics (speaking, written, signing) |
|
|
|
Listener Training |
Skinners term for a certain type of listener behavior in which the listener provides a non verbal response to a verbal Sd. *think Receptive language* skills |
|
|
|
Schedule of reinforcement |
Continuous reinforcement ( CRF), intermittent reinforcement (INT), Extinction (EXT). |
|
|
|
Continuous reinforcement |
-Provide reinforcement for every occurrence of the target behavior. -Utilized for strengthening Novel Behavior when teaching is 1st initiates a new skill that is being acquired |
|
|
|
Intermittent reinforcement |
-Some, not all, occurrences of the behavior are reinforced - Used for maintaining Behaviors that have already been established - helps to fade artificial reinforcers to natural reinforcement |
|
|
|
FVFV |
Fixed ration, favorable ratio, fixed interval, variable interval. |
|
|
|
Fixed Ratio |
Constant, set criteria. A certain # of occurrences of the behavior has to occur before 1 response produces reinforcement |
FR4 - reinforcement is delivered after every 4 correct responses. |
|
|
Variable ratio |
Strongest Basic reinforcement: Changing, means of responses. A # of occurences of the target behavior has to occur in average before 1 response produces reinforcement. |
|
|
|
Postreinforcement Pause |
Follows reinforcement. When the individual does not respond for certain time following reinforcement. Occures after INT; FR and FI |
|
|
|
Rate of Response produced by FR |
Often produces quicker responses, because of quick produces faster rate of reinforcement. The larger the ratio requirement the quicker the responses. |
|
|
|
Pattern of responding produced by FR |
Responses completed with little hesitation. Postreinforcement Pause follows reinforcement. *Large ratio=large pause; *short ratio=short pause |
|
|
|
FR prototype graph |
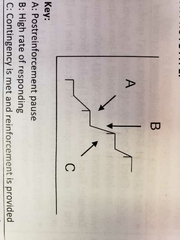
|
Only graph with STEPS |
|
|
VR prototype graph |
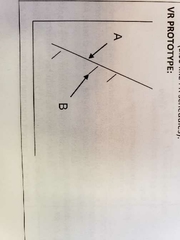
|
Super fast and steep |
|
|
Pattern of responding produced by VR |
Constant responding, steady rate. Doesnt produce postreinforcement pause. May be due to the absence of info. Of when the next response will produce reinforcment. |
|
|
|
Rate of responding produce by VR |
Fast rate (like FR), the larger the ratio the faster the responses (like FR) |
|
|
|
Thinning INT schedule |
Gradually increasing the response ratio or the duration of the time interval |
|
|
|
Ratio Strain |
A result of abrupt increases in ratio requirement when moving form denser (more) rate of reinforcement to thinner (less) rate of reinforcement schedule. |
|
|
|
Limit Hold |
A restriction is place on a interval schedule requiring that to be eligible for reinforcment, the primed response (1st response following the required interval) must occur within a specific span of time following the interval. |
|
|
|
Variation of Basic Intermittent Schedule |
Differential reinforcement of high response rate (DRH), Differential reinforcement of diminishing rate of responding (DRD), Differential reinforcement of low rate of responding (DRL) |
|
|
|
DRH |
A schedule reinforcement that provides reinforcement for emitting behaviors that are above pre-established rate. |
|
|
|
___________ helps increase behaviors that the individual displays too frequently |
DRH |
|
|
|
DRD |
A schedule of reinforcement that provides reinforcement when the # of responses in a specific time period is less than, or equal to the prescribed limit. |
Responses with in a period of time. |
|
|
___________ helps to decrease behaviors that an individual displays to frequently but NOT to eliminate if entirely. |
DRD |
|
|
|
DRL |
Schedule of reinforcement only if the behavior occurs following a specific period of time during which it did not occur or since thats time it occurred. |
Occurs within a time period. |
|
|
Increasing the IRT you are lowering the rate of responding. That is what the ___________ is all about. |
DRL |
|
|
|
Interresponse time |
Idnentifies the duration of time that occurs between two responses. ___________ and rate of response are functionally related. |
|
|
|
Progressive Scedules of reinforcement |
A variation of basic reinforcement schedule (int). Systematically thins successive reinforcement opportunity independent of the participants behavior. |
|

