![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
life cycle of angiosperms
|
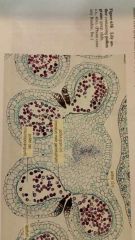
|
|
|
anther containing pollen grains
|
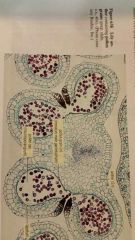
|
|
|
ovary
|

|
|
|
pollen tube
|

|
|

|
tomato, berry
|
|

|
blackberry, aggregate
|
|
|
monocots
|
parallel venation, 1 cotyledon, flower parts in multiples of 3, fibrous roots
lily, corn, onion, palm |
|
|
eudicots
|
netted venation, 2 cotyledons, flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5, taproot
rose, apple, bean |
|
|
3 ways to prevent self-pollination
|
1. female and male parts develop at different times
2. position of male and female parts placed so they can reach each other 3. genetic self-incompatability with S gene |
|
|
simple fleshy fruit
|
fruits that develop from flower with single pistil
|
|
|
berries (simple fleshy fruit)
|
develop compound ovaries, contain more than one seed
tomatoes, grapes, eggplants |
|
|
drupe (simple fleshy fruit)
|
apricot, cherry, peach, plum
|
|
|
pome (simple fleshy fruit)
|
apples, pears
|
|
|
aggregate fleshy fruit
|
develops from a single flower with several to many pistils
raspberry, blackberry, strawberry |
|
|
multiple fleshy fruit
|
from several to many individual flowers in a single inflorescence
pineapple, fig |
|
|
dry fruits
|
mesocarp is dry at maturity
also dry fruit that does not split at maturity |

