![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
115 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the target dose of Metoprolol Succinate ER? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Most cases in US are due to __? |
Damage from an MI or from long-standing hypertension. |
|
|
|
A problem the systolic function of the heart refers to __? |
Contraction |
|
|
|
A problem the diastolic function of the heart refers to __? |
Relaxation |
|
|
|
What test is done when heart failure is suspected? |
Echocardiograph (ECHO) |
|
|
|
An EF < 40% indicates what? |
Systolic dysfunction or heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) *most common type |
|
|
|
1. EF of 55-70% means __? 2. EF of >/= 50% means__? 3. EF of 40-49% means__? 4. EF of <40% means__? |

1. EF of 55-70% means normal 2. EF of >/= 50% means HFpEF (diastolic) 3. EF of 40-49% means HFmrEF 4. EF of <40% means HFrEF (systolic) |
|
|
|
What are the 2 classification systems currently recommended for HFrEF? |
1. The American College of cardiology and the American heart Association (ACC/AHA) —> recommended categorizing patients by the heart failure stage. The staging system is used to guide treatment in order to slow progression in asymptomatic patients (A&B) or in symptomatic patients (C&D). 2. New York heart Association (NYHA) —> classified by the level of limitation in physical function. |
|
|
|
Explain and describe each stage in the ACC/AHA and the NYHA staging system |

Refer to pic |
|
|
|
What are some signs and symptoms of systolic heart failure seen in labs? |

Refer to pic |
|
|
|
What are some left sided signs and symptoms of systolic heart failure? |

Refer to pic |
|
|
|
What are some right sided signs and symptoms of systolic heart failure? |

Refer to pic |
|
|
|
What are some general signs and symptoms of systolic heart failure? |

Refer to pic |
|
|
|
How do you calculate cardiac output (CO)? |

CO = Heart Rate * Stroke Volume |
|
|
|
1. How do you calculate cardiac output (CO)? 2. How do you calculate cardiac index (CI)? |

CO = Heart Rate * Stroke Volume CI = Cardiac Output / Body Surface Area |
|
|
|
During low cardiac output states neurohormones are released that do you what? |

They increase the blood volume or increase the force or speed of contractions which can lead to cardiac remodeling. |
|
|
|
During low cardiac output states neurohormones are released that do what? |

They increase the blood volume or increase the force or speed of contractions which can lead to cardiac remodeling. |
|
|
|
What are the three main pathways activated in heart failure? |

RAAS, SNS, Vasopressin |
|
|
|
What effect does angiotensin II have? |
Vasoconstriction |
|
|
|
What does aldosterone do? |
Causes sodium and water retention (and inc. potassium excretion) |
|
|
|
What does vasopressin do? |
Causes vasoconstriction and water retention |
|
|
|
When the central nervous system is activated what happens? |
Norepinephrine and epinephrine are released, which increases heart rate, contractility (positive inotropy), and vasoconstriction |
|
|
|
What are some lifestyle management options for patients with heart failure? |
My other document body weight daily, notify the provider when weight increases by 2-4 lbs, maintain sodium restriction of <1500 mg/day in stage B heart failure, maintain fluid restriction in stage D, stop smoking, limit EtOH, avoid illicit drugs, get vaccines, exercise |
|
|
|
What are OTC and alternative medication options for patients with heart failure? |
Omega-3 fatty acid supplements, Hawthorn and coenzyme Q10, avoid stimulants |
|
|
|
What are OTC and alternative medication options for patients with heart failure? |
Omega-3 fatty acid supplements, Hawthorn and coenzyme Q10, avoid stimulants |
|
|
|
What drugs cause or worsen heart failure? |

DI NATION |
|
|
|
Drugs that cause or worsen heart failure to do so by what mechanism? |
Fluid retention/edema, by increasing blood pressure or via negative inotropic effect |
|
|
|
1. What medications decrease mortality and are recommended for all patients without CI? 2. What medications decrease mortality for select patients? 3. What medications improve other aspects of HF (not proven to dec mortality)? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Loop diuretics block what ions and where? |
Block Na and Cl reabsorption in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. They increase excretion of Na, K, Cl, Mg, Ca and water. |
|
|
|
T/F: Loop diuretics have not been shown to alter the survival of heart failure patients. |
True |
|
|
|
What are the equivalent doses for the loop diuretics? |

Furosemide 40 mg = Bumetanide 1 mg = Torsemide 20 mg = Ethacrynic acid 50 mg
Furosemide IV:PO ratio 1:2 |
|
|
|
What is the warning associated with loop diuretics? What loop diuretic does not have this warning? |

Sulfa allergy Ethacrynic acid |
|
|
|
How do you properly store furosemide injections? |

At room temperature |
|
|
|
What are the side effects and monitoring parameters for loop diuretics? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Avoid NSAIDs (including COX-2 inhibitors) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
ACEi blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II resulting in what? |
Decreased vasoconstriction and decreased aldosterone secretion |
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of angiotensin receptor blocker‘s? |
Blocks angiotensin II from binding |
|
|
|
T/F: ACEi and ARBs decrease morbidity and mortality. |
True |
|
|
|
T/F: An ACEi (or ARB if intolerant to ACEi) is recommended for select heart failure patients regardless of symptoms. |
False! An ACEi (or ARB if intolerant to ACEi) is recommended for all heart failure patients (NYHA Class I-IV) regardless of symptoms. |
|
|
|
T/F: You do not have to titrate the dose for an ACEi or ARB. |
False! Titrate the drug to the target those if possible |
|
|
|
T/F: Combining an ACEi and an aldosterone receptor antagonist (ARA) is not as common as combining an ACEi and an ARB. |
The combination of an ACE inhibitor and an ARB has been shown to decrease hospitalizations for heart failure, but it is more common to combine either one with an aldosterone receptor antagonist. Triple combination therapy of ACEi + ARB+ ARA is NOT recommended due to higher risk of hyperkalemia and renal insufficiency. |
|
|
|
T/F: Combining an ACEi and an aldosterone receptor antagonist (ARA) is not as common as combining an ACEi and an ARB. |
The combination of an ACE inhibitor and an ARB has been shown to decrease hospitalizations for heart failure, but it is more common to combine either one with an aldosterone receptor antagonist. Triple combination therapy of ACEi + ARB+ ARA is NOT recommended due to higher risk of hyperkalemia and renal insufficiency. |
|
|
|
With what class of medications and what ethnicity is Angioedema most common? What should you do if a pt has experienced this? |
Occurs more frequently with ACEi (than with ARBs or Aliskiren) and in black patients. If a patient develops angioedema with any of these medications the others should be avoided. |
|
|
|
What is the target dose for Vasotec, Zestril, Accupril, and Alsace? |
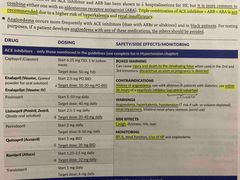
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is the black box warning associated with ACEi? |

Injury and death to the developing fetus (in 2nd and 3rd trimester) discontinue as soon as pregnancy is detected. |
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for ACEi? |
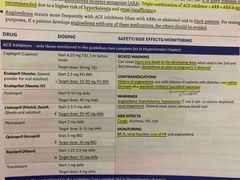
History of angioedema, use within 36 hours of neprilysin inhibitor (Entresto (sacubitril/valsartan)) |
|
|
|
What are the warnings for ACEi? |

Angioedema, hyperkalemia, hypotension, renal impairment |
|
|
|
What are the SE and CI for ACEi? |
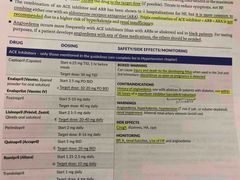
SE: cough CI: BP, renal function, s/sx of HF |
|
|
|
What is the difference between using an ACEi and ARB? |

Less cough and angioedema, no washout period required with neprilysin inhibitor |
|
|
|
An ACEi should not be used within __ hrs of a neprilysin inhibitor? What is an example of an neprilysin inhibitor? |
36 hrs Entresto (Valsartan(ARB) + Sacubitril(neprilysin inhibitor)) |
|
|
|
What is the target dose for losartan and valsartan? |

Losartan: 50-150 mg/day Valsartan: 160 mg BID |
|
|
|
Neprilysin is the enzyme responsible for degrading what? |
Degration of several beneficial vasodilatory peptides |
|
|
|
What is Entresto a combination of and what MOA does each part have? |
Sacubitril: neprilysin inhibitor Valsartan: ARB |
|
|
|
ARNI is indicated in NYHA class 2-4 pts to do what? |
Reduce heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death. It’s recommended as a potential first line option in place of an ACEi or ARB as monotherapy |
|
|
|
What is the black box warning associated with Entresto? |

Injury and death to the developing fetus, discontinue as soon as pregnancy is detected |
|
|
|
What are the CI’s associated with Entresto? |

Use with ACEi or ARB |
|
|
|
What are the warnings associated with Entresto? |

Angioedema, renal impairment, hyperkalemia, hypotension |
|
|
|
What are the SEs and monitoring parameters associated with Entresto? |
SE: cough Monitoring: BP, K, renal function, s/sx of HF |
|
|
|
If the pt is taking Entresto and they come in with a Rx for an ACEi what should you do? |

Do not use with an ACE inhibitor or another ARB. Must have 36 hour a washout period between stopping an ACEi and starting Entresto. |
|
|
|
T/F: ACE inhibitors and ARBs can decrease lithium renal clearance and increase risk of lithium toxicity. |
True |
|
|
|
T/F: Avoid using ACEi +/- ARB +/- Aliskiren and the triple combination with an ACEi, ARB, and ARA. |
True |
|
|
|
Combining an ACEi and ARB with an ARA is very common in HF. |
Combining an ACEi or ARB (not both) with an ARA is very common in HF. |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of beta blockers? |
They antagonize the effects of catecholamines (especially NE) They decrease morbidity and mortality, they are recommended for all heart failure patients. |
|
|
|
What beta blockers are recommended in the guideline to treat heart failure? |
Bisoprolol, Carvedilol (IR & ER), and Metoprolol Succinate ER |
|
|
|
When should beta blockers be avoided and when should they be stopped? |
Beta blockers with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity should be avoided. Beta blockers should only be stopped in ADHF if hypotension or hypoperfusion is present. |
|
|
|
What is the black box warning associated with beta blockers? |

Do not discontinue abruptly |
|
|
|
What are the warnings to watch out for when using beta blockers? |

Caution in patients with diabetes can worsen hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia and mask hypoglycemic symptoms, use caution with bronchospasmic diseases like asthma or COPD |
|
|
|
What are the side effects and monitoring parameters associated with beta blockers? |

Side effects : Decreased heart rate, hypertension, fatigue, dizziness, depression, increased triglycerides Monitoring: HR, BP, s/sx of HF |
|
|
|
What form of metoprolol is used in the heart failure patients? |
Metoprolol succinate XL (Toprol XL) |
|
|
|
What form of metoprolol is used in the heart failure patients? |
Metoprolol succinate XL (Toprol XL) Use succinate for success in HF |
|
|
|
What is the metropolis IV to PO conversion ratio? |

IV:PO 1:2.5 **important cuz med error possible |
|
|
|
T/F: Toprol XL can be cut at the score line. |
True |
|
|
|
What nonselective beta blocker and alpha-1 blocker is used in heart failure patients? |

Carvedilol (Coreg) |
|
|
|
How should you counsel your patient to take Coreg? |

Take with food! |
|
|
|
What is important to know about dosing conversions for carvedilol? What is the target dose for the immediate release form and the controlled release form? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is important to know about dosing conversions for carvedilol? What is the target dose for the immediate release form and the controlled release form? |

|
|
|
|
Where do aldosterone receptor antagonists act? |

In the distal convoluted tubule and collecting ducts |
|
|
|
What is the difference in mechanism between spironolactone and eplerenone? |
Spironolactone is a nonselective ARA (also blocks androgen) and Eplerenone is a selective ARA that does not exhibit endocrine side effects |
|
|
|
T/F: ARAs reduce morbidity and mortality and should not be added to standard treatment in patients with NYHA class II-IV. |
False! They should be added to standard treatment for patients with NYHA class II-IV. |
|
|
|
What is the brand name of spironolactone and what is its target dose? |
Aldactone Target: 25 mg daily or BID |
|
|
|
What are the contraindications associated with spironolactone? |

Hyperkalemia, anuria, significant real impairment (CrCl = 30), Addison’s disease or other conditions that increase potassium |
|
|
|
What are the warnings, side effects, and monitoring parameters associated with aldosterone receptor antagonist? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
T/F: triple combination of ace inhibitor ARA and ARB is recommended. |
False! It is not recommended |
|
|
|
T/F: The triple combination of ace inhibitor ARA and ARB is recommended. |
False! It is not recommended |
|
|
|
T/F: The triple combination of ACE inhibitor ARA and ARB is recommended. |
False! It is not recommended |
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of hydralazine and nitrates? |
Hydralazine is a direct arterial vasodilator which decreases afterload. Nitrates increase the availability of nitric oxide which causes venous vasodilation and decreases preload. The combination of these products improves the survival of patients with heart failure. |
|
|
|
What is the brand name of The medication containing hydralazine and isosorbide dinitrate? |
BiDil |
|
|
|
T/F: BiDil is indicated in self identified black patients with NYHA class III-IV who are symptomatic despite optimal treatment with ACE inhibitors and beta blockers. |
True |
|
|
|
What is contraindicated with the use of BiDil? |
Use of PDE-5 inhibitor and riociguat. The combination can cause severe hypotension. |
|
|
|
What are the side effects and warnings associated with hydralazine? |

Warnings: Drug induced lupus erythematosus SE: headache, hypertension, reflex tachycardia, palpitations |
|
|
|
What are the side effects and contraindications associated with BiDil? |
SE: Hypertension, headache, dizziness, lightheadedness, flushing, tachyphylaxis, syncope CI: Use with PDE-5i or Riociguat |
|
|
|
What is the typical dose and therapeutic range of Digoxin? |

Typical dose: 0.125-0.25 mg daily Therapeutic Range: HF=0.5-0.9 ng/mL (keep serum concentrations <1 ng/mL) and AFib=higher |
|
|
|
What are the brand names for Digoxin? |
Digitek, Digox, Lanoxin |
|
|
|
What is the antidote for Digoxin? |
DigiFab!! 💁🏻♀️ |
|
|
|
What increases the risk of digoxin toxicity? And what should you monitor? |
Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypercalcemia Monitor: electrolytes, renal function |
|
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of digoxin toxicity? |

Nausea/vomiting, loss of appetite, bradycardia (in severe cases you can see yellow/green vision, halos, and blurriness) |
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of digoxin? |
Digoxin inhibits the Na/K ATPase pump which results in a positive inotropic affect (increase in CO) and it exerts a parasympathetic affect which provides a negative chronotropic affect (decrease heart rate) |
|
|
|
When is digoxin used? What benefits does it provide? |
Digoxin improves symptoms exercise tolerance and quality-of-life it does NOT improve survival. Digoxin DOES reduces hospitalizations for heart failure. |
|
|
|
When should you consider lowering the dose of Digoxin? |
Lower doses for renal insufficiency, smaller, older, female |
|
|
|
What does Ivabradine inhibit? |
It inhibits the “funny” current in the sinus node |
|
|
|
When funny current is inhibited what happens? |
Inhibition of the funny current results in the reduction of sinus rate and hence heart rate. |
|
|
|
T/F: Ivabradine reduces the risk of hospitalization for worsening heart failure but does not affect mortality. |
True |
|
|
|
T/F: Ivabradine is recommended as adjunct therapy in symptomatic stable chronic heart failure patients with EF = 35% who are treated with all appropriate first line medications, are in sinus rhythm and have resting heart rate >/= 70 BPM. |
True! |
|
|
|
What is the target resting heart rate when using Ivabradine? |
50-60 BPM |
|
|
|
What are the warnings associated with Ivabradine? |

Bradycardia, increase risk of QT prolongation and ventricle arrhythmias |
|
|
|
What are some side effects of Ivabradine? |

Bradycardia, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, luminous phenomena |
|
|
|
What form of potassium supplementation is most commonly used? And when should you check potassium levels? |

Potassium chloride is used most commonly. Check potassium levels if the renal function changes and after any change in diuretic, ACE inhibitor, ARB, or ARA dose |
|
|
|
T/F: Magnesium level should be checked and correct as needed after correcting the potassium level. |

False!! Check and correct magnesium level prior to correcting the potassium level |
|
|
|
What are the brand names of potassium chloride available? |

Klor-Con, Klor-Con 10, Klor-Con M20, Micro-K |
|
|
|
What is the treatment dose and what is the prevention dose of hypokalemia with potassium chloride? |

Prevent: 20-40 mEq/ day in 1-2 divided doses Treatment: 40-100 mEq/day in 2-5 divided doses |
|
|
|
KCl 10% = __mEq/__mL |
KCl 10% = 20mEq/15mL |
|
|
|
What are the ways that each of the various brand names of potassium chloride can be taken? |

Back (Definition) |
Micro-K: K-Tab, Kylie-Con: Kylie-Con M: |
|
|
HF exacerbations and quality improvement notes: Many HF hospitalizations are you due to non-adherence with medications. Medicare now penalizes hospitals for excessive readmissions due to HF exacerbations. Lifestyle adherence is essential. |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
In the back of this chapter you see an action plan. The yellow means caution possibly indicating a change in medication needed. In the section you will see: |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is the listed medication summary for the treatment of chronic HFrEF? |

Back (Definition) |
|

