![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which body type is this?
|
Hypersthenic
|
|
|
excess fluid within the lung that is most frequently caused by backup pulmonary circulation associated with congestive heart failure?
|
Pulmonary Edema
|
|
|
This is the accumulation of air in the pleural space that causes a partial or total collapse of that lung
|
Pneumothorax
|
|
|
inflammation of the lungs that results in accumulation of fluid
|
Pneumonia
|
|
|
excessive mucous secreted into bronchi
|
Bronchitis
|
|
|
Shortness of breath, creates sensation of difficultly breathing
|
Dyspnea
|
|
|
air spaces in alveoli become greatly enlarged.
|
emphysema
|
|
|
What are the reasons for an erect chest position?
|
1) Allows diaphragm to move down farther
2)Demonstrates air fluid levels 3)prevents engorgement of pulmonary vessels |
|
|
Which two body Habitus are the extremes?
|
Hypersthenic and Asthenic
|
|
|
What are the four different types of body habitus?
|
Hypersthenic (most broad)
Sthenic (most popular) Hyposthenic 35% of population Asthenic (most Vertical) |
|
|
How should the IR be position for a hypersthenic patient?
|
crosswise
|
|
|
the area of each lung where the bronchi and blood vessels enter and leave is called ?
|
helium
|
|
|
The trachea bifurcates and forms what?
|
Left and right bronchi
|
|
|
A prominence or ridge found at the point where the internal distal trachea divides into the right and left bronchi is called?
|
Carina
|
|
|
What are the three layers of pleura surrounded the lungs from inner to outer?
|
inner pulmonary or visceral pleura
pleural cavity outer parietal |
|
|
The extreme outermost lower corner of each lung is called what?
|
costophrenic angle
|
|
|
Which of the following structures is not found in the mediastinum
thymus gland heart and great vessels epiglottis trachea |
epiglottis
|
|
|
The direction or path of the central ray defines which positioning term?
|
Projection
|
|
|
Abduction is which type of movement
|
lateral movement of the arm or leg away from the body
|
|
|
Adduction is which type of movement?
|
movement of arm or leg toward the body
|
|
|
Supination ?
|
movement of hand into the anatomical position
|
|
|
Pronation?
|
The movement of the hand into the opposite position of anatomical position.
|
|
|
which portion of the long bone is responsible for the production of red blood cells?
|
spongy or cancellous
|
|
|
what type of tissue covers the ends of long bones
|
Hyaline or articular cartilage
|
|
|
what is the primary center for endochondral ossification found in long bones
|
Diaphysis
|
|
|
What is the correct classification for tarsal bones
|
Short
|
|
|
What is the medial portion of the thoracic cavity between the lungs called?
|
Mediastinum
|
|
|
What are the four radiographically important structures located in the mediastinum called?
|
thymus gland
heart and great vessels trachea esophagus |
|
|
At which level of vertebra does the trachea divide into the bronchi
|
T4-T5
|
|
|
This means away from the head end
|
Caudad
|
|
|
The trachea extends from C6 to where?
|
T5
|
|
|
What is the outermost layer of pleura?
|
Parietal pleura
|
|
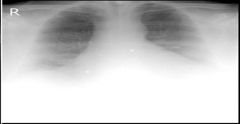
Which Body Habitus is this
|
hypersthenic
|
|
|
Which cervical vertebra is the vertebra prominens?
|
C7
|
|
|
Describe supine position?
|
lying on back facing upward
|
|
|
Describe prone position?
|
Lying on abdomen facing downward
|
|
|
Trendelenburg?
|
head lower than the feet
|
|
|
Fowlers?
|
head higher than feet
|
|
|
How many projections are required when the joints are in the prime interest are?
|
three
|
|
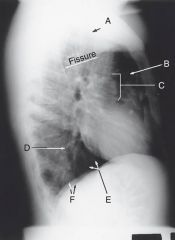
Identify all structures
|
A. Apex
B.Upper lobe C. Helium D. Lower lobe E. Base F. Right and left Hemidiaphragms |
|
|
Which plane divides the body into equal anterior and posterior parts?
|
Midcoronal
|
|
|
A longitudinal plane that divides the body into right and left parts is the?
|
Sagittal plane
|
|
|
List all parts of the bony thorax
|
2 Clavicles
2 scapulae 12 ribs Sternum 12 thoracic Vertebrae |
|
|
What are the four radio-graphically important parts of the respiratory system
|
Larynx
trachea bronchi lungs |

