![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Robert Boyle |
He defined element as the simplest composition of matter and cannot be further broken down. He suggested that atoms of elements combine to form compounds |
|
|
|
Dephlogisticated air |
By Joseph Priestly. Process of isolating oxygen gas. |
|
|
|
Anton-Laurent Lavoisier |
He found out that the gas, which he already called oxygen, is involved in combustion and respiration |
|
|
|
Law of conservation of mass |
In chemical reaction, the mass of substances produced is equal to the mass of the substances created. |
Formulated by Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier Ex. Balancing equations |
|
|
Law of definite proportions / law of definite composition |
Established by French chemist Josheph-Louis Proust. Any sample of a given compound will always be composed of the same elements in the same proportion by mass |
|
|
|
Law of multiple proportions |
Proposed by British scientist John Dalton. For elements that can form different compounds, masses of second element combined with fixed mass of first element is in a ratio of small whole number |
|
|
|
Protons, neutrons, electrons |
Subatomic Particles |
|
|
|
Joseph John Thomson |
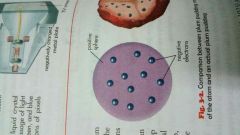
-Discovered electrons(negatively charged particles) while studying the nature of cathode rays -Proposed plum pudding model of the atom; the bread are positive charge while the plums are negatively charge |
|
|
|
Robert Millikan |
He determined the actual charge of the electron |
|
|
|
Ernest Rutherford |
-He discovered and described alpha and beta rays as positively and negatively charged radiation -He discovered the proton |
|
|
|
James Chadwick |
Former student of Rutherford, discovered another type of particle in the nucleus - the neutron |
|
|
|
Nucleons |
Nucleus at the center, consisting of protons and neutrons |
|
|
|
Atomic Number (Z) |
-Represents the number of protons in its nucleus -number of protons = number of nuetrons |
|
|
|
Mass Number (A) |
-Total number of protons and neutrons A = number of protons + number of neutrons |
|
|
|
Henry Mosley |
-He corrected some elements in the earlier versions of the periodic table |
|
|
|
Isotopes |
Atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons. They have different mass numbers but same atomic number |
|
|
|
Protium, deuterium, tritium |
A nuetral hydrogen atom, consisting of only one proton and electron, has three different isotopes |
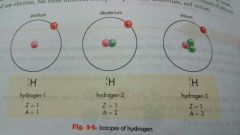
|
|
|
Ions |
Electrically charged particle that happens when a neutral atom gains or loses one of more electrons |
|
|
|
Cations |
Positively charged due to metals losing electrons |
|
|
|
Anions |
Negatively charged which happens when nonmentals gain electrons |
|
|
|
Neutral atoms |
Can either share or exchange electrons |
|
|
|
Charged number |
The number of electrons lost or gained |
|

