![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 basic cell components |
Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus |
|
|
Plasma membrane lipids |
Phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids |
|
|
Glycoproteins provide... |
Identification for immune system |
|
|
Glycolysis occurs where |
Cytosol |
|
|
Three main layers of lipid bilayer |
Phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids |
|
|
Advantages of membrane fluidity |
Allows interactions within plasma membrane, enables movement of membrane components, permits lipid bilayer to self seal when torn |
|
|
Functions of plasma membrane |
Separates cytoplasm from ECF, regulates exchange with ECF, sensitivity to change in concentration in ECF, structural support |
|
|
Plasma membrane is impermeable to... |
Ions and charged molecules |
|
|
Nuclear pores |
Allows communication between nucleus and cytosol |
|
|
Integral proteins |
Binds to ligands, regulates passage of ions, act as carrier molecules for various solutes |
|
|
Integral and peripheral proteins |
Act as anchors for cell membrane and as enzymes |
|
|
Glycoproteins function in membrane |
Cell identity markers |
|
|
Receptors |
membrane proteins that recognize and bind to hormones and neurotransmitters |
|
|
Functions of glycocalyx on cell membrane |
Lubricate and protect cell membrane |
|
|
Functions of glycocalyx on immune system |
Identify cells |
|
|
Functions of glycocalyx with hormones |
Act as receptors |
|
|
Organelle that has a membrane |
Lysosome |
|
|
Cytoskeleton is a... |
Networks or protein filaments that extends throughout cytosol |
|
|
Cytoskeleton is made up of... |
Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules |
|
|
Tubulin assembles into |
microtubules |
|
|
Actin assembles into |
Microfilaments |
|
|
Ribosomes are made up of... |
One small and one large subunit |
|
|
Two subunits of ribosomes are created separately in the |
Nucleolus |
|
|
Location of lipid synthesis |
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Ribosomes attach to the |
Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum produces... |
Secretory proteins, membrane proteins, and many proteins of organelles |
|
|
Mitochondria has its own... |
DNA |
|
|
The matrix in mitochondria contains... |
Metabolic enzymes involved in energy production |
|
|
Mitochondria play an important and early role in... |
Apoptosis |
|
|
Histones help organize... |
The coiling and folding of DNA |
|
|
Genes are... |
Functional units of DNA |
|
|
mRNA consisting of a set of three consecutive nucleotides is a... |
Codon |
|
|
One end of tRNA consists of a triplet of nucleotides called... |
Anticodon |
|
|
Translation |
Process of protein formation where the nucleotide sequence in an mRNA molecule specifies the amino acid sequence of a protein |
|
|
Transcription |
Process of forming mRNA |
|
|
mRNA is very important to cells because... |
mRNA can leave the cell and DNA cannot |
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement of molecules or ions from an area of high concentration to low concentration |
|
|
What moves through a membrane using simple diffusion |
Gas like oxygen and carbon dioxide |
|
|
Tonicity |
Solution's ability to change the volume of cells by allowing water content |
|
|
Hypotonic |
Contains lower solute concentration than the cytosol inside the cell. |
|
|
Hypertonic |
Solution that contains higher solute concentration than the cytosol |
|
|
Hemolysis |
Occurs when blood is placed in a hypotonic solution |
|
|
Crenation |
Occurs when blood is placed in a hypertonic solution |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
Molecules moved into cells along their concentration gradient with the help of membrane-bound carrier proteins. |
|
|
What limits facilitated diffusion |
Number of available carrier proteins |
|
|
Active transport requires... |
ATP |
|
|
Active transport moves substances... |
Against its concentration gradient |
|
|
Secondary active transport uses what to transport substances? |
Energy supplied by sodium or hydrogen |
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. |
|
|
Osmosis moves from_____ concentration to ______ concentration. |
Low to high |
|
|
Exocytosis |
Ejection of cytoplasmic materials |
|
|
Substances transferred by exocytosis include... |
Neurotransmitters, hormones, digestive enzymes |
|
|
Endocytosis |
Packaging of extracellular materials at the cell surface for importation to the cells |
|
|
Transcytosis |
Movement of a substance through a cell as a result of endocytosis on one side and exocytosis on the other |
|
|
Ligands are |
Specific molecules that binds to a receptor |
|
|
When is cell membrane condition normal? |
Cell interior is more negatively charged than the exterior |
|
|
Different concentrations of hydrogen and sodium in cytosol and ECF is a main reason for: |
Maintaining normal cell volume and the ability of some cells to generate electrical signals |
|
|
What happens during mitosis? |
Two identical daughter cells are formed. |
|
|
How many chromosomes does each daughter cell have after mitosis? |
46 |
|
|
Interphase |
Cells perform normal functions and prepare for division |
|
|
S-Phase |
A cell duplicates its chromosomes (DNA replication) |
|
|
Anaphase |
Chromatids separate |
|
|
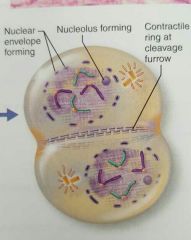
Telophase |
Chromosomes uncoil. Nuclear membrane is formed. Cytokinesis may occur |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Cleavage furrow forms. |
|
|
Meiosis |
Produces haploid gametes. |
|
|
How many chromosomes in each daughter cell after meiosis |
23 |
|
|
How many chromosomes in diploid cells? |
46 |
|
|
How many chromosomes in haploid cells? |
23 |
|
|
Apoptosis |
Genetically controlled death of cells |
|
|
Necrosis |
Abnormal death of cells that results from tissue injury |
|
|
Order of cell division |
Interphase, prophase, anaphase, telophase |
|
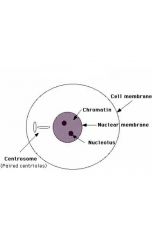
|
Interphase |
|
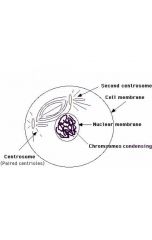
|
Prophase |
|
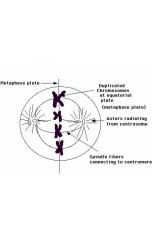
|
Metaphase |
|
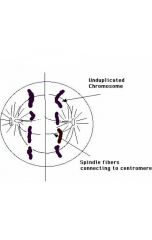
|
Anaphase |
|
|
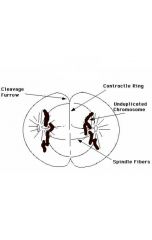
Telophase |
|
|
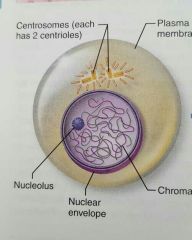
Interphase |
|
|
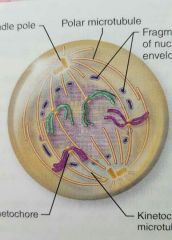
Prophase |
|

|
Metaphase |
|
|
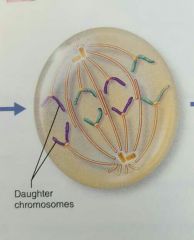
Anaphase |
|
|
Telophase |

