![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What happens to NaCl is placed in water? |

|
|
|
|
What happens to KCl when placed in water? |

|
|
|
|
What happens to CaPO4 is placed in water? |
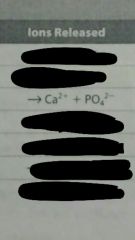
|
|
|
|
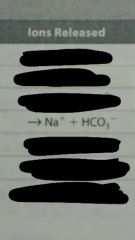
What happens to NaHCO3 is placed in water? |
|
|
|
|
What happens to MgCl2 is placed in water? |
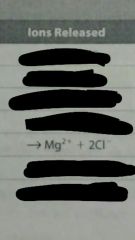
|
|
|
|
Example of a strong acid? |
HCl ➡ Na+ + OH- |
|
|
|
What happens when Na2SO4 is placed in water? |

|
|
|
|
What happens when Na2HPO4 is placed in water? |

|
|
|
|
Acid |
Proton donor and releases H+ in a solution |
|
|
|
Base |
Proton acceptor, a solute that generates OH- |
|
|
|
As H+ increases in a solution what does pH do? |
Decreases and acidity increases |
|
|
|
As the H+ decreases what happens to the pH? |
Increases and alkalinity increases |
|
|
|
pH range? |
7.35 - 7.45 |
|
|
|
What are the physiological buffers? |
Kidneys and lungs |
|
|
|
What does pH mean? |
Power of hydrogen |
|
|
|
What's the carbonic acid-bicarbonate sytem equation? |
H2CO3 ➡ HCO3- + H1 or H2CO3 ⬅ HCO3- + H1 |
|
|
|
What's a chemical buffer do? |
Stabilize the body |
|
|
|
Dehydration synthesis |
Polymers are made when many monomers are joined together |
|
|
|
What are carbohydrates? |
Sugars, starches, polymers, and contain C, H, O |
|
|
|
What are the three types of sugar? |
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides |
|
|
|
Examples of monosaccharides |
Glucose, fructose, and galactose |
|
|
|
Examples of disaccharides |
Sucrose, lactose, and maltose |
|
|
|
Example of polysaccharides |
Glycogen |
|
|
|
What can monosaccharides do? |
Enter the cell through the plasma membrane |
|
|
|
Where can you find polysaccharides? |
In liver and skeletal muscles |
|
|
|
Lipids are _____________ in water |
Insolube |
|
|
|
Lipids provide twice as much as energy as carbohydrates. TRUE OR FALSE? |
True |
|
|
|
Main functions of triglycerides? |
Energy storage, insulation, and protection |
|
|
|
Triglycerides are called ______ when solid and _______ when liquid |
Fat/oil |
|
|
|
Phospholipids |
Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail |
|
|
|
What are proteins? |
Most abundant and important organic molecules |
|
|
|
What are the seven major protein functions? |
Support (bone/ligaments), movement (actin/myosin), transport (canals/carriers), buffering (regulate pH), metabolic regulation (enzymes), defense (antibodies), and coordination (hormones). |
|
|
|
Primary structure |
Held together by peptide bonds |
|
|
|
Secondary structure |
Involves hydrogen bonding |
|
|
|
Tertiary structure |
Involves hydrogen and covalent bonding |
|
|
|
Fibrous proteins |
Strandlike, water-insolube, and stable |
Structural |
|
|
Example of fibrous? |
Keratin, collagen, and skeletal muscle |
|
|
|
Globular protein |
Compact, spherical, water-soluble, and sensitive to environment |
Functional |
|
|
Example of globular protein |
Antibodies, hormones, and enzymes |
|
|
|
What are the building blocks from functional units called cells? |
Lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates |
|

