![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the three stages from conception to birth and when do they occur?
|
Germinal period
First 2 weeks of development during formation of primitive germ layers Embryonic period 2nd to end of 8th week, organ systems develop Fetal period Last 30 weeks, organ systems grow and mature |
|
|
++
|
++
|
|
|
what happens once the sperm head contacts the zona pellucida?
|
the perivitelline space developes, the male and female pronucleus merge to form a singe nucleus withing a zygote
|
|
|
what develops in the first two weeks after fertilization?
|
3 germ layers
1. endoderm 2. mesoderm 3. ectoderm |
|
|
what develops from the endoderm?
|
G.I. tract
|
|
|
what develops from the mesoderm?
|
bones, muscle, connective tissue
|
|
|
what develops from the ectoderm?
|
skin and nervous system
|
|
|
what happens during the embryonic period?
|
2 months
organ systems develop including cardiovascular and nervous system Fetus remains small - not much growth here |
|
|
what happens during the fetal period?
|
last 30 weeks
growth differentiation/maturation of organ systems |
|
|
what prevents polyploidy?
|
after sperm's acerzome penetrates, the perivitelline space develops, which is a new protective barrier that prevents other sperm from entering
|
|
|
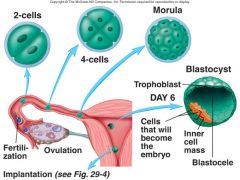
when does the first division occur?
|
Zygote divides to form 2 cells about 18-39 hours after fertilization
|
|
|
describe the cells of the morula
|
Pluripotent: Ability to develop into wide range of tissues
Solid ball of 12 or more cells |
|
|
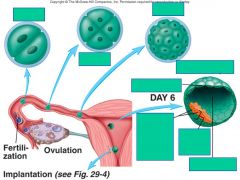
what comes after the morula?
what is significant about it? |
blastocyst on day 6
first stage of differentiation occurs now |
|
|
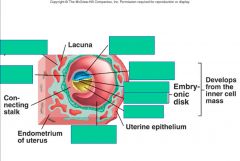
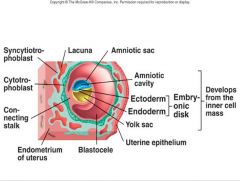
describe the blastocyst
|
hollow sphere of cells with trophoblast cells making up the outer layer of the sphere
Contains an inner cell mass that will become the embryo With Blastocele - the empty space |
|
|
from what cells does the placenta develop?>
|
the trophoblast cells
|
|
|
|
|
|
what is the purpose of the placenta?
|
protects the zygote
|
|
|
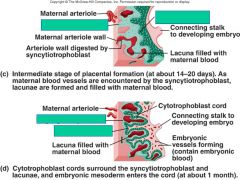
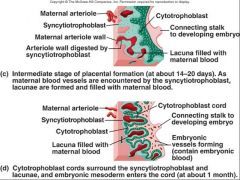
what are the 2 layers of the placenta formation?
|
cytotrophoblast
syncytiotrophoblast |
|
|
describe the cytotrophoblast
|
fetal side - connects fetus to the placenta
|
|
|
describe the syncytiotrophoblast
|
maternal side - protects the zygote fro maternal immune cells
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
the embryonic disc is composed of what?
|
the ectoderm and endoderm
|
|
|
how does the neural tube form?
|
ectoderm develops a neural groove, a neural fold, and a notochord (together called the neural plate)
the neural groove deepens and the crest of the neural fold eventually joins forming the neural tube |
|
|
++
|
++
|
|
|
describe the gut formation
|
Developing digestive tract pinches off from yolk sac as a tube but remain attached by yolk stalk
Oropharyngeal membrane Cloacal membrane Evaginations Celom or body cavity development |
|
|
++
|
++
|
|
|
when endodermal tissue pinches off toward the front, it develops the _________
|
oropharyngeal membrane = early mouth
|
|
|
when endodermal tissue pinches off toward the rear, it develops the _________
|
cloacal membrane = early rectum
|
|
|
in what stage does the limb bud and face develop?
How does it occur |
embryonic stage (at about 28 days)
limb tissue laid down in proximal to distal sequence |
|
|
what is the epidermis derived from?
|
Epidermis derived from ectoderm
|
|
|
what is the dermis derived from?
|
Dermis derived form mesoderm or neural crest cells as in face
|
|
|
what is the skeleton derived from
|
mesodermal cells
|
|
|
what is muscle derived from?
|
mesoderm
|
|
|
what is nervous system derived from?
|
ectoderm
|
|
|
what is circulatory derived from
|
mesodermal
|
|
|
describe what happens in the heart when the baby is born and begins to breathe
|
there is a decrease in pressure in the right atria, causing the septum primum and septum secundum to stick together, thus closing the foramen oval
|
|
|
what does the respiratory system develop from?
urinary? reproductive? |
endoderm
mesoderm mesoderm |
|
|
what are the three parts of a developing kidney?
which ones are vestigial? |
pronephros, mesonephros, meetanephros
pronephros and mesonephros are vestigial (degrades from primitive stages) |
|
|
describe kidney development
|
pronephros is the first urinary structure to develop, it degrades and the mesonephros takes over, then the metanephorse takes over and becomes the permanent kidney
|
|
|
describe reproductive system development in females
|
E2 causes mesonephric ducts to degrade and the paramesonephric duct to develope which becomes the uterine tube
|
|
|
describe reproductive system development in males
|
gonadal ridge releases testosterone causing the paramesonephric duct to develop into the vas deferens
|
|
|
what is the vernix caseosa?
|
waxy coat of protection that protects the fetus from amniotic fluid containing fetal wastes
|
|
|
what happens at 60 days?
|
embryo becomes a fetus
|
|
|
describe the stages of parturition
|
first stage - getting ready to expel fetus - minimal uterine cxn and cervix dliation
second stage - maximal uterine cxn and cervix dilation - fetus expelled third stage - placenta expulsion |
|
|
why is it important that the placenta be expelled?
|
because it dies and it would cause infection if it remained in the mother
|
|
|
why does parturition start?
|
in response to stress b/c of the small space, the Fetus pituitary releases ACTH which influences adrenal cortex to release adrenal steroids which changes the hormonal levels of the placenta including P4 synthesis decreases and E2 synthesis increases, and prostaglandin synthesis increases, which causes cxn to begin.
|
|
|
++
|
++
|
|
|
What type of feedback occurs in the parturition process?
|
positive feedback
the uterine cxn stimulate maternal hypthalamus to stimulated oxytocin release from anterior pit. Oxytocin increases uterine cxn, which causes more oxytocin to be released, more and more and more |
|
|
++
|
++
|
|
|
what are the structures that cause the foramen ovale to close after birth?
|
primum on the left, secundum on the right,
stick together, closing the f.o. |
|
|
define genotype
|
Actual set of alleles a person has for a given trait
|
|
|
define phenotype
|
Person’s appearance or expression of the trait caused by the genes
|
|
|
gene
|
a piece of DNA that controls a trait
|
|
|
sex-linked traits are...
|
Traits affected by genes on sex chromosomes
|
|
|
incomplete dominance
give i.e. |
Dominant gene doesn’t completely mask effects of recessive gene
Sickle-cell disease |
|
|
polygenic traits are determined by....
give i.e. |
expression of multiple genes on different chromosomes
Person’s height, eye and skin color, intelligence |
|
|
define homozygous
|
alleles are the same
i.e. TT |
|
|
define heterozygous
|
alleles are different
ie. Tt |
|
|
define dominant-recessive:
|
dominant allele masks a recessive allele
|
|
|
define codominance or incomplete dominance
|
each allele exerts an effect on the phenotype, one allele does not mask the other, the two alleles blend
|
|
|
if a Tt mother and a TT father combined, what would you get in a incomplete dominance situation?
|
add Punnett Square
|
|
|
if a homozygous dominant mother combined with a heterozygous father, what would you get in a dominant-recessive situation?
|
add Punnett Square
|

