![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Invasive fungal infections are associated with high morbidity and mortality. Fungi are classified as ____, ____, or ____. |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What form of amphotericin B has more toxicities in which form has fewer toxicity’s ? |
Amphotericin B deoxycholate (conventional form) = more toxicities Amphotericin B Lipid formulation = fewer toxicities |
|
|
How is Amphotericin B supplied? What are the black box warnings? What are the major side effects? What is important to note about conventional formulation versus lipid formulation, when administering? |

Back (Definition)
|
|
|
How does flucytosine work? When should it be used? What is the notable side effect associated with it? What is the brand name? |

|
|
|
What is the MOA of azole antifungal‘s? |
Azole anti-fungal decrease ergosterol synthesis and cell membrane formation. Azoles are inhibitors of the fungal CYP450 system. |
|
|
What are the key issues with azole antifungals? What are the class effects? What are the specific effects? What is the doc for Aspergillosis? What is the only azole that requires renal dose adjustment? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the boxed warning for ketoconazole and for itraconazole? What is the generic name for fluconazole? What is the dose to treat vaginal candidiasis with fluconazole? What side effects are associated with azole antifungal‘s? |

|
|
|
What antifungal’s penetrate the CNS and can be used to treat fungal meningitis? |
Fluconazole and Voriconazole |
|
|
What is the brand name of Voriconazole? What is the CrCl decrease that requires a dose change to PO and why? What should you monitor for? What are the warnings associated with Voriconazole? What should you counsel the pt on? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the brand name of Posaconazole? What are the warnings associated with it? How should the tablet form be taken? What can happen when CrCl < 50? What is the important note with Isavuconazonium? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What azole antifungals are dependent on pH? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What azole antifungals are dependent on pH? What should you counsel the patient if they are taking a H2RA? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the moa of echinocandins? What formulation are they available in? What is it active against? What is the brand name of Micafungin and Caspofungin? What are the warnings associated with echinocandins? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the contraindication associated with Griseofulvin? What is Griseofulvin indicated for? What are the SE’s and patient counseling point for Griseofulvin? What should you counsel a patient who is taking hormonal contraceptive? What is the moa of Terbinafine? What warning and SE’s are associated with Terbinafine? What is the brand name of Clotrimazole that comes in topical and vaginal forms? What other form does Clotrimazole come in? What is Clotrimazole used to treat? What forms does Nystatin come in? What is the brand name of Nystatin? What is Nystatin used to treat and what are some counseling points for the patient taking this medication? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the first line treatment for: Oropharyngeal infection (Thrush)? (Mild dz, mod/severe, if HIV+) Esophageal infection? Candida glabrata? Candida krusei? Aspergillosis? Criptococcus neoformans? (Consolidation, induction in serious infcn like meningitis) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the first line treatment for: Oropharyngeal infection (Thrush)? (Mild dz, mod/severe, if HIV+) Esophageal infection? Candida glabrata? Candida krusei? Aspergillosis? Criptococcus neoformans? (Consolidation, induction in serious infcn like meningitis) Dermatophytes? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Viruses depend on the host cell, for this reason there are sometimes referred to as ____. What are some examples of neuraminidase inhibitors and their moa? What are they used for? Baloxabir marboxil is a endonuclease inhibitor and comes in a _______ regimen? When should it be started? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What are some Neuraminidase Inhibitors? What is the generic name for Tamiflu? What forms does it come in? What is the treatment dose and prophylaxis dose? At what age can you use this medication? What are the warnings associated with the medication? What is the treatment age for Zanamivir? What formulation does it come in? What are the warnings associated with the medication? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Baloxavir marboxil is a endonuclease inhibitor, how often should the dose be given? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is HSV-1 affect? What is HSV-2 affect? What is the chickenpox virus called? What Else can it cause and how? What is the brand name of a acyclovir? What can the cream formulation be used to treat? What is the prodrug acyclovir (brand and genetic)? What is dose based on in morbidly obsess pts? What is famciclovir a prodrug of? What are the warnings associated with antivirals used to treat herpes symplex virus and varicella zoster virus? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What does HSV-1 affect? What does HSV-2 affect? What is the chickenpox virus called? What Else can it cause and how? What is the brand name of a acyclovir? What can the cream formulation be used to treat? What is the prodrug acyclovir (brand and genetic)? What is dose based on in morbidly obsess pts? What is famciclovir a prodrug of? What are the warnings associated with antivirals used to treat herpes symplex virus and varicella zoster virus? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the brand name of docosanol? How can you buy it? How do you apply it? What is the brand name of acyclovir? How do you apply it? |
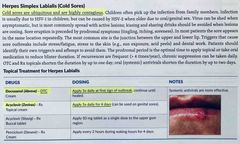
Back (Definition) |
|
|
When should you initiate treatment for genital herpes? What can be used to treat it and how often should it be given? |
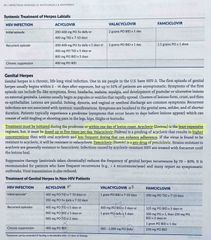
Back (Definition) |
|
|
HSV is the most commonly identified cause of ______ in the US? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
The varicella zoster virus (chickenpox) can lie dormant in the nerves for decades and reoccur causing what? When should you initiate antiviral therapy? What are the treatment options and for how long should you treat for? How would you treat the pain? How can you vaccinate against this reoccurrence? |
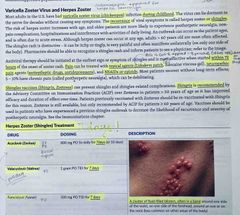
Back (Definition) |
|
|
What does cytomegalovirus cause? What medications are the treatment of choice and which should be reserved for refractory cases? |
Treatment of choice: gangciclovir and valgangciclovir Refractory: foscarnet and cidofovir |
|
|
What does cytomegalovirus cause? What medications are the treatment of choice and which should be reserved for refractory cases? |
Causes: retinitis, colitis, esophagitis Treatment of choice: gangciclovir and valgangciclovir Refractory: foscarnet and cidofovir |
|
|
What does cytomegalovirus cause? What medications are the treatment of choice and which should be reserved for refractory cases? |
CMV causes: retinitis, colitis, esophagitis Treatment of choice: gangciclovir and valgangciclovir Refractory: foscarnet and cidofovir |
|
|
What is the brand name of ganciclovir and valganciclovir? What is the boxed warning for these drugs? What should you advise a pt taking a suspension? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the brand name of ganciclovir and valganciclovir? What is the boxed warning for these drugs? What should you advise a pt taking a suspension? If a pt has CMV retinitis or resistant HSV what medication should they take? What is the boxed warning for foscarnet? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
What is the common name for the Epstein-Barr virus? How is it transmitted? |

Back (Definition) |

