![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Plantae Phylogeny
|

Nonvascular
Vascular Seed |
|
|
Nonvascular Plants
|
Liverworts, Mosses, Hornworts
Some have conduction cells, but no tracheids Live in moist habitats Have thin cuticles Mostly small bc no vascular system Gametophyte is photosynthetic |
|
|
Liverworts
|

Green leafljke gametophytes
Sporophyte attached to larger gametophyte Asexual and sexual repro. |
|
|
Mosses
|

Have stomata
Cells called hydroids, bc when die leave a channel through which water can move |
|
|
Hornworts
|

Sporophytes look like small horns
Cells contain one chloroplast |
|
|
Vascular Plants
|
Lycophytes, Horsetails, Ferns
Well developed vascular system with tracheids VS consists of tissues specialized for transport of water and materials from one part of plant to another |
|
|
Rhyniophytes
|

Earliest vascular plant
No roots Anchored in soil by rhizomes Dichotomous branching system |
|
|
Lycophites
|

Club mosses
True branching roots Leaflike structure (microphylls) Sporangia in clublike clusters |
|
|
Monilophytes
|
Horsetails, Ferns
Horsetails monophyletic, ferns not Synapomorphy - leaf gaps in stem where leafs emerge |
|
|
Horsetails
|

Genus Equisetum
True leaves in whorls True roots Independent sporophyte and gametophyte |
|
|
Seed Plants
|
Secure and lasting dormant stage for the embryo
Seeds remain viable for long periods Adaptations to aid in dispersal Embryo draws on nutrients stored in seed |
|
|
Gymnosperms
|
Seed plants that dont form flowers or fruits
Four Grouos: - Cycads- tropical earliest diverging clade - Gingkos- common in Mesozoic, today only one sp Gingko biloba - Gnetophytes- some characteristics similar to angiosperms - Conifers- cone bearing plants |
|
|
Angiosperms
|
Reproductive organs in flowers
Seeds enclosed in fruits Female gametophyte very reduced Synapormorphies: - Double fertilization - Nutritive tissue called endosperm - Flowers - Fruits |
|
|
Double Fertilization
|
Two sperm in one pollen grain:
one combines with egg to form zygote, other combines with two other haploid nuclei to form triploid cell (endosperm) |
|
|
Types of Flowers
|
Perfect - have both megasporangia and microsporangia
Imperfect - two flower tyeps, male and female Monoceius - male and female flowers occur on the same place Dioecious - male and female flowers are produced in different plants |
|
|
Fruits
|
Develop from the ovaries after fertilization
Protect seeds and aid in dispersal Single - peaches Reduced - dandelions Aggregate - raspberries Accessory - pear |
|
|
Monocots
|
1 cotyledon
Parallel veins |
|
|
Dicots
|
2 cotyledons
Webby veins |
|
|
Pollination
|
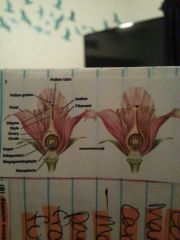
Arrival of pollen grain near a female gametophyte
Pollen tube forms and grain digests its way to megagametophyte where fertilization occurs |
|
|
Evolution of Flowers
|
Reduced # of parts
Differentiation of petals and sepals From radial to bilateral symmetry Fusion of flower parts |
|
|
Evolution of Stamen, Carpel, and Leaf
|

|

