![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Name the three layers of the heart. |
Endocardium Myocardium Endocardium |
|
|
|
Describe the location of the heart |
The heart rests on the diaphragm in the thoracic cavity heart is in the mediastinum extends from the sternum to the diaphragm and between the lungs. |
|
|
|
Name the two layers of the pericardium. |
Fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium. |
|
|
|
Name the function of the pericardium. |
Protection prevents the heart from overstretching and anchors the heart to the mediastinum. |
|
|
|
Myocardium |
Cardiac muscle tissue, striated and involuntary. |
|
|
|
Name the four chambers of the heart |
Right atrium Left atrium Right ventricle Left ventricle |
|
|
|
Auricle |
On the anterior surface of the Atria a pouch like outer Layer that allows the Atria to expand while Contracting. |
|
|
|
Right atrium receives-------from --------,--------,-------. |
Oxygen poor blood, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus. |
|
|
|
Veins carry blood -------- the heart. |
Towards |
|
|
|
Right atrialventricular valve |
Tricuspid valve, between right atrium and right ventricle. |
|
|
|
Heart strings |
Cordae tendineae |
|
|
|
Angina pectoris |
Severe chest pain due to a partial obstruction of the coronary arteries a tight squeezing sensation in the chest |
|
|
|
Myocardial infarction |
Complete obstruction in the coronary artery that blocks blood flow heart attack causes the death of heart tissue |
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis |
Thickening of artery walls and loss of elasticity. |
|
|
|
Autorhythmic fibers |
Self excitable cardiac muscle fibers the source of electrical activity that keeps the heart beating generates an action potential that triggers contractions of the heart. |
|
|
|
Sinoatrial node |
Pacemaker starts cardiac excitation found in the right atrial wall |
|
|
|
The SA node has an unstable resting potential. repeatedly--------- two thresholds spontaneously called pacemaker. |
Depolarizes |
|
|
|
The five steps through the electrical cardiac system |
1. SA node 2. AV node 3. Atrioventricular bundle 4. Interventricular septum to apex. 5. Perkinji fibers. |
|
|
|
Describe the three steps of the action potential caused by the SA node in the conduction system of the heart. |
1. Depolerization- Na+ channels open, rapid influx of sodium into cells rapidly depolerizes. 2. Plateau- a maintained depolerization, Ca2+ channels open, calcium flows into cell slowly, K+ channels open also, alows potasium to leave the cell. 3. Repolerization- recovery, most K+ channels open, K+ flows out of cell to restore negative resting potential. Ca2+ channels close as well. |
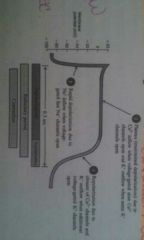
|
|
|
Electrocardiogram EKG |
Record electrical signals traveling through the heart recorded by an electrocardiograph. |
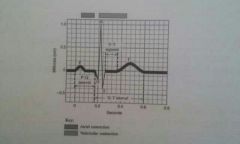
Three main components of an EKG P wave QRS wave and T wave. |
|
|
P wave |
Represents atrial depolarization |
|
|
|
QRS wave |
Represents rapid ventricular depolarization |
|
|
|
T wave |
Represents ventricular repolarization. |
|
|
|
EKG measure time span between waves called intervals name three. |
1. PQ interval 2. ST segment 3. QT interval |
|
|
|
PQ interval |
Represents conduction time from the start of atrial excitation to the start of ventricular excitations. |
|
|
|
ST segment |
Represents depolarization of ventricular contractile fibers during the plateau |
|
|
|
QT interval |
Represents the start of ventricular depolarization to the end of ventricular repolarization. |
|
|
|
Arrhythmia |
Abnormal Rhythm caused by the defect in the heart conduction system. |
|
|
|
Name three arrhythmias |
Bradycardia refers to a slow heart rate less than 50 beats per minute Tachycardia refers to a fast heart rate over 100 beats per minute Fibrillation rapid uncoordinated Heartbeats. |
|
|
|
Systole |
Phase of contraction |
|
|
|
Diastole |
Phase of relaxation |
|
|
|
Cardiac cycle |
All the events that take place in one heartbeat. |
|
|
|
Phases of the cardiac cycle |
Atrial systole Ventricle systole Relaxation period |
|
|
|
End-diastolic volume (EVD) |
The amount of blood contained in each ventricle during the relaxation period. |
|
|
|
Isovolumetric contraction |
Ventricles contract with no volume change heart valves are all closed |
|
|
|
End systolic volume (ESV) |
Refers to the amount of blood remaining in each ventricle after it is sent out. |
|
|
|
Stroke volume |
Volume of ejected blood per beat from each ventricle. |
|
|
|
Auscultations |
Listening to sounds within the body with a stethoscope the closing of heart valves create the sound of the heartbeat love is the first sound caused by the AV valves closing dub is the second sound caused by the SL valves closing. |
|
|
|
Heart murmur |
Abnormal sound heard when listening to heart sounds. |
|

