![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Astronomical Unit (AU) |
The mean distance from the centre of the Earth to the centre of the Sun |
|
|
Light year (Ly) |
The distance travelled by light in a vacuum in one year. |
|
|
Parsec (pc) |
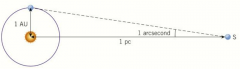
The distance at which a radius of one AU subtends an angle of one arcsecond |
|
|
Arc minute |
1° = 60 arcminutes |
|
|
Arc second |
1 arc minute = 60 arc seconds so 1°= 1/3600 arc seconds |
|
|
Stellar parallex |
A technique used to determine the distance to stars that are less than 100pc away from the earth, by comparing their apparent positions against 'stationary' stars 6 months apart. |
|
|
Doppler Effect |
The change in frequency and wavelength of waves from an object moving relative to an observer compared with what would be observed without relative motion |
|
|
Blue-Shift |
The shortening of observed wavelengths that occurs when a wave source is moving towards the observer as the absorption lines is moved towards the blue end of the spectrum |
|
|
Red-shift |
The lengthening of observed wavelengths that occurs when a wave source is moving towards the observer as the absorption lines is moved towards the red end of the spectrum |
|
|
Hubble's Law |
v ∝ d The recessional speed (v) of a galaxy is almost directly proportional to its distance (d) from the Earth |
|
|
Expanding Universe |
The idea that the fabric of space and time is expanding in all directions, and the further two points are, the faster their relative motion away from each other is |
|
|
Cosmological Principle |
The assumption that when viewed on a large enough scale, the universe is homogeneous and isotropic |
|
|
Homogeneous |
The uniform distribution of matter across the universe when viewed on a sufficiently large scale, with the laws of physics being universal |
|
|
Isotropic |
Appearing the same in all directions to an observer, regardless of position |

