![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Trace Elements in the Human Body "Christy Can Cut Flowers In My Mothers Small Sandbox To Visit Zombies" |
Chromium (CR) Cobalt (CO) Copper (CU) Fluorine (F) Iodine (I) Manganese (Mn) Molybdenum (Mo) Selenium (Se) Silicon (Si) Tin (Sn) Vanadium (v) Zinc (zn) |
|
|
Chemistry
|
Science that deals with the structure of matter |
|
|
mass |
physical property that determines the weight of an object in earth's gravitational field |
|
|
Atom |
The Smallest Unit of an element -Can NOT be divided into smaller units without losing the chemical and physical properties of the element ex) hydrogen, magnesium, etc |
|
|
Element |
The simplest form of matter to have unique chemical properties 3N= 3(ATOMS) and N (THE ELEMENT NITROGEN) 3-Reflects quantity N-Reflects substance |
|
|
Most abundant elements in the body |
1) Oxygen (O) 2) Hydrogen (H) 3) Carbon (C) |
|
|
Lesser Elements in the human body "Sad Ponys Sing Corny Music Impressions" |
Sulfur (S) Potassium (K) Sodium (NA) Chlorine (CI) Magnesium (MG) Iron (FE) |
|
|
Major Elements in the Human Body "Only Cats Have No Cream Pies" |
Oxygen (O) Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Nitrogen (N) Calcium (CA) Phosphorus (P) |
|
|
How Lipids are used by the body |
* Converted to carbohydrates (heat through cell respiration, stored atp, protein synthesis) *Used to make hormones (estrogen, progesterone, testosterone) *Structural Purposes |
|
|
Prostaglandin |
A local hormone that influences the functions of neighboring cells, important in coordinating cells or tissue |
|
|
Catabolic Reactions |
1)Hydrolysis 2)Decomposition |
|
|
Anabolic Reactions |
1) Dehydration Synthesis 2) Condensation |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
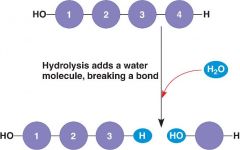
Catabolic Reaction where water breaks covalent bonds |
|
|
Hydrophilic |
molecules that love water (water soluble) ex) Carbohydrates, polar molecules |
|
|
Hydrophobic |
molecules that repel water (NOT water soluble) ex) oils, non polar molecules |
|
|
Lipids |
Functions) *Insulation *Stored Energy with Slow Release *Structural Purposes *Hormone Productory *Bile Production ex) waxes, oils |
|
|
Triglyceride |
Most commonly ingested lipid (1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids) "E" -Energy storage, thermal insulation, filling space, binding organs together, cushioning organs |
|
|
Buffers |
A substance that accepts Hydrogens or bonds Hydrogens, thus maintaining a stable ph |
|
|
Neutral Substances |
ability to donate=ability to receive |
|
|
Organic Compounds |
1) Carbohydrates 2) Lipids 3) Proteins 4) Nucleic Acids *Carbon with attached hydrogens ex) c6h12o6 |
|
|
Glucose |
A simple sugar C6H12O6 |
|
|
Complex Carbohydrate |
2 Or More Sugar Units |
|
|
Disaccaride |
2 sugar units |
|
|
Oligosaccharide |
short chain sugar units |
|
|
Polysaccharide |
many sugar units |
|
|
Starch |
Plant form of stored carbohydrates |
|
|
Animal |
animal form of stored carbohydrates (liver) |
|
|
Fiber |
Plant structural carb |
|
|
simple carbohydrates |
composed of one sugar unit Mono-Saccaride "One-Sugar" |
|
|
How Carbohydrates are used in the body |
*Digested-->Cellular respiration-->Released as heat, stored as atp, used for protein synthesis *Converted to glycogen (Liver) *Structural purposes *converted to fats (insulation) |
|
|
Decomposition |
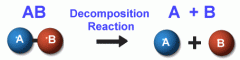
a reaction such as digestion and cell respiration, in which larger molecules are broken down into smaller ones |
|
|
catabolism |
the sum of all decomposition reactions in the body |
|
|
Synthesis |

A reaction such as protein and glycogen synthesis, in which two or more smaller molecules are combined into larger ones |
|
|
Anabolism |
The sum of all synthesis reactions in the body |
|
|
Acids/Bases |
*Inorganic Compound that helps maintain ph |
|
|
acid |
a hydrogen ion donor ex) H2C03, HCI, H2SO4 (H up front) |
|
|
base |
a hydrogen ion acceptor ex) KOH, NaOH, Ca(OH)2 |
|
|
carbon dioxide |
*An inorganic compound *Gas *Waste product of cellular respiration Function: Maintain blood ph |
|
|
Salts |
*Inorganic compound -ionically bonded compounds found mainly in the blood and tissue fluids of the human body. *Dissociate into ions in water solutions Functions: Provide necessary ingredients for reactions |
|
|
Minerals |
*an inorganic compound -elements and compounds derived from soil Functions: *Give hardness to bones *Provide necessary ingredients for chemical reactions |
|
|
Water |
*an inorganic compound -Most abundant compound, human body is composed of 60-70% water by weight Functions: *Universal solvent for the body *Cleansing/Lubricant agent for the body *Regulates body temperature |
|
|
Organic Chemistry |
Less abundant (10-30%) ARE unique to life ALWAYS contain carbon structured as a carbon backbone |
|
|
Inorganic Chemistry |
Most abundant (70-90%) NOT unique to life or living things may or may not contain carbon |
|
|
Polar Covalent |
-When two covalently bonded atoms have an unequal pull on the shore of electrons. *water soluble *atoms with more protons - *atoms with fewer protons + |
|
|
Non Polar Covalent |
-When two covalently bonded atoms have equal pull on the shared electrons ex) lipids *strongest chemical bonds *NOT water soluble |
|
|
Atom Diagram |
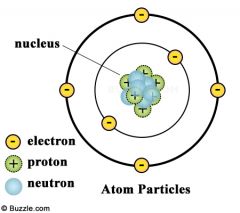
|
|
|
Atomic Number |
-The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom -Generally the # protons = electrons (when atoms are in ground state) |
|
|
atomic mass |
The number of protons + number of neutrons |
|
|
covalent bond |
a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms or molecules -Stronger than ionic or hydrogen bonds |
|
|
ionic bond |
-a chemical bond formed between two ions with opposite charges. *formed when one atom gives up one or more electrons to another atom -weaker than covalent bonds |
|
|
Hydrogen Bonds |
Weak bonds, break down due to ph shifts or high temperatures. -Important in coiling molecules such as proteins |
|
|
Dissociation |

the process in which molecules (or ionic compounds) separate or split into smaller particles such as atoms, ions, or radicals |
|
|
cation |
ions with a net positive charge |
|
|
anions |
ions with a net negative charge |
|
|
single covalent |
sharing of one electron pair |
|
|
double covalent |
sharing of two electron pairs *often occurs between carbon atoms, between carbon and oxygen, and between carbon and nitrogen |
|
|
Major Electrolytes |
*Calcium Chloride (cAcl2) *Disodium Phosphate (Na2HPO4) *Magnesium Chloride (MgCI2) *Potassium Chloride (KCI) *Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3) *Sodium Choride (NaCI) |
|
|
Sucrose
|
Glucose + Fructose |
|
|
Bile Acids |
Steroids that aid in fat digestion and nutrient absorption |
|
|
cholesterol |
component of cell membranes, precursor of other steroids |
|
|
fat soluble vitamins |
-involved in a variety of functions including blood clotting, wound healing, vision, and calcium absorption * A, D, E, K |
|
|
fatty acids |
precursor of triglycerides, source of energy *glycerol |
|
|
phospholipids |
major component of cell membranes, aid in fat digestion |
|
|
steroid hormones |
chemical messengers between cells |
|
|
proteins |
composed of amino acids *Basic elements: C, H, O, N, FE, S, P, Mg needed for: *structural proteins, hormones, enzymes, hemoglobin, mucous |
|
|
amino acids |
building blocks of proteins |
|
|
hemoglobin |
protein found in red blood cells *binds oxygen |
|
|
enzymes |
speeds up processes |
|
|
fatty acids |
building blocks of lipids |
|
|
simple sugars |
building blocks of complex carbohydrates |
|
|
structural proteins |
-provide strength and waterproofing (Keratin) -provides strength (Collagen) *Found in skin surface, hair, nails (Keratin) *Found in dermis of skin, tendons (Collagen) ex) KERATIN, COLLAGEN |
|
|
Contractile proteins |
-perform contraction and movement *found in muscle cells ex) ACTIN, MYOSIN |
|
|
Transport Proteins |
-transports fatty acids and steroid/thyroid hormones (albumin) -transports iron (transferrin), glycerides (apolipoproteins), and oxygen in blood (hemoglobin) *Found in Circulating blood ex) ALBUMIN, TRANSFERRIN, APOLIPOPROTEINS, HEMOGLOBIN |
|
|
Buffers |
-Stabilize PH *Found in cells and body fluids ex) Intracellular and Extracellular proteins |
|
|
Enzymes |
-Catalyze hydrolysis or organic molecules (Hydrolases) *all cells -Attach phosphate groups to organic substrates (Kinases) *all cells -Break down proteins (proteases) *all cells, pancreas, digestive secretions of stomach -Break down carbohydrates (carbohydrases) *all cells, digestive secretions of salivary glands, pancreas -break down lipids (Lipases) *all cells, digestive secretions of pancreas |
|
|
hormones |
-coordinate and or control metabolic activites *Found in Circulating Blood ex) Insulin, glucagon |
|
|
antibodies (immunoglobulins) |
-attack foreign proteins and pathogens *found in circulating blood ex) gamma globulins |
|
|
nucleic acids |
-composed of nucleotides ex) rna, dna |
|
|
RNA |
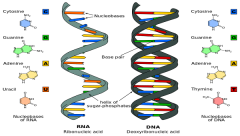
single chain of nucleotides, needed for protein synthesis |
|
|
DNA |
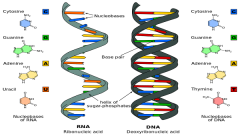
double chain of paired nucleotides twisted into a helical shape held together by hydrogen bonds. *blueprint for all inherited characteristics and for all protein synthesis |
|
|
Actin, myosin |
-contractile proteins found in muscle cells that perform contracion and movement |
|
|
keratin |
-Structural protein found in skin surface, hair, and nails that provides strength and waterproofing |
|
|
Collagen |
-Structural protein found in dermis of skin and tendons that provides strength |
|
|
Albumin |
-Transport protein found in circulating blood that transports fatty acids and steroid/thyroid hormones |
|
|
Transferrin |
-Transport protein found in circulating blood that transports iron |
|
|
Apolipoproteins |
-Transport protein found in circulating blood that transports glycerides |
|
|
Hemoglobin |
-Transport protein found in circulating blood that transports oxygen in blood (red blood cells) |
|
|
intracellular and extracellular proteins |
-Buffers found in cells and body fluids that stabilize ph |
|
|
Hydrolases |
-Enzymes found in all cells that catalyze hydrolysis of organic molecules |
|
|
Kinases |
Enzymes found in all cells that attach phosphate groups to organic substrates |
|
|
proteases |
Enzymes found in all cells, digestive secretions of stomach, and pancreas that break down proteins |
|
|
Carbohydrases |
enzymes found in all cells, digestive secretions of the salivary glands, and pancreas that break down carbohydrates |
|
|
Lipases |
Enzymes found in all cells, digestive secretions of the pancreas that break down lipids |
|
|
Insulin, Glucagon |
Hormones found in circulating blood that coordinate and or control metabolic activites |
|
|
Gamma Globulins |
Antibodies (immunoglobulins) found in circulating blood that attack foreign proteins and pathogens |
|
|
Inorganic compounds |
*Minerals *salts *water *carbon dioxide *acids/bases -NO attached hydrogens |
|
|
Dehydration synthesis |
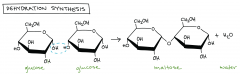
the process of joining two molecules, or compounds, together following the removal of water. When you see the word dehydration, the first thing that may come to mind is 'losing water' or 'lacking water.'
|
|
|
Condensation |
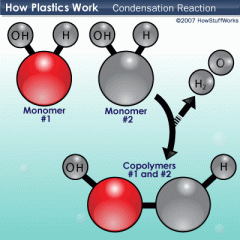
a reaction in which two molecules combine to form a larger molecule, producing a small molecule such as H2O as a byproduct.
|

