![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Energy |
Strength and vitality required for physical or mental activity |
Ex: Kinetic energy Kinetic energy is used in things due to motion. |
|
|
Chemical Energy |
A type of potential energy stored in chemicals. |
Dry wood is an example of storing chemical energy. |
|
|
Free energy |
A thermodynamic equivalent to the space of a system to do work. |
An example of free energy would be sunlight. |
|
|
Heat energy |
Transfers among particles in a substance. |
An example of heat energy would be boiling water or a volcano. |
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics |
Energy remains constant in a system. It can not be created or destroyed |
First Law of Thermodynamics is a version of the Law of conservation os energy. |
|
|
Second Law of Thermodynamics |
Entropy of a system never decreases. |
|
|
|
Entropy |
Always increases or stays constant in a system |
Entropy never decreases in the second law of thermodynamics. |
|
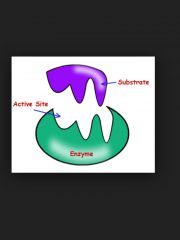
Enzymes |
Produced by a living organism and acts as a catalysts |
Some enzymes make bonds and break them |
|
|
Actives site |
Specific reaction catalyzed by an enzyme depends on a small area of its tertiary structure |
Subrate and active site bring enzyme and substrate closer together |
|
|
Substrate |
Close fit of the starting molecule |
Substrate and enzymes need to get along |
|
|
Metabolism |
Consists of all the chemical activities and changes that take place continuously in a cell or an organism. |
There are 2 types of it. "building-up" and "breaking-down" |
|
|
Synthesis |
a complex whole formed by combining |
biosynthesis reactions are included |
|
|
Decomposition |
The state of being decomposed |
Decay |
|
|
Biosysnthesis |
Formation of chemical compounds by a living organism |
Is included in synthesis reactions |
|
|
Oxidation |
Combination of a substance with oxygen |
CO2 |
|
|
ATP |
High energy molecule that stores the energy we need |
Biologists say this the energy currency of life |

