![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
NADH |
Part of the electron transport chain (10 NADH) where 1 NADH will create 3 ATPs |
3 ATPs |
|
|
FADH2 |
Part of electron transport chain. Creates 2 ATPs. |
First stage of mitosis |
|
|
Interphase |
Not really a phase of mitosis, at first, the cell is just living. It grows and brings in nutrition. All that. Then the chromosomes replicate (still not in mitosis yet.) then the growth is continued. Chromosomes are still in chromatin form (not tightly wound all over the place). |
|
|
|
Prophase |
Second phase of mitosis. Chromatin starts to become tightly wound. Nuclear envelope disappears. Centrosomes attach themselves to chromosomes centromeres. |
|
|
|
Metaphase |
3rd phase, aligning of the chromosomes. |
|
|
|
Energy organelles |
Mitochondria (cells engine) Chloroplast (occur only in photosynthetic organisms) |
|
|
|
Mitochondria |
Cite of cellular respiration. |
|
|
|
Chloroplasts |
Site of photosynthesis. Contains chlorophyll which is necessary for this process. |
|
|
|
Plant cells differ from animal |
They have a cell wall, have chloroplasts, often contain large vacuoles (storage spaces for starch or toxic substances) |
|
|
|
Energy |
Capacity to do work |
|
|
|
Laws of energy |
Cannot be destroyed, only transformed. Some must be lost in transformations. |
|
|
|
Equation for cellular respiration |
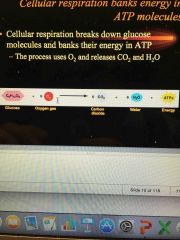
Yeah. |
|
|
|
Cellular respiration. |
A way to create ATP. Three main steps include glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. |
|
|
|
Glycolysis |
Anaerobic, glucose is split in two. Formed in cytoplasm. Harvests chemical energy by converting glucose to purification acid. |
|

