![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nucleus ( plant and animal) |
-controll center -conatains DNA -protected by neclear envelope |
|
|
Cell membrane ( plant and animal) |
- controls the materials that move in and out of the cell -selective of what goes in and out -composed of two layer structure composed of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates -protective barrier that separates cell from surroundings |
|
|
Cytoplasm ( plant and animal) |
-gell like substance that is inside the cell membrane -movement of organelles and molecules inside the cell ( cytoplasmic straming) |
|
|
Cell wall (plant) |
Gives cell the shape and provides strength and support |
|
|
Chloroplasts ( plant ) |
-Contains chlorophyll -where photosynthesis occurs |
|
|
Vacuoles |
Membrane bound structures that store nutrients, cell products and fats ( animal) |
|
|
Enoplasmic recticulum (both) |
Series of interconnected small tubes that branch from the nuclear envelope. Materials can be transported through these tubes.
There are also two types of Enoplasmic recticulum |
|
|
Rough Enoplasmic recticulum (both) |
Rbosomes are attached to it and it is associated with protien synthesis |
|
|
Smooth ensoplasmic recticulum (both) |
Has no ribosomes and is associated with fat and oil production |
|
|
Ribosomes (both) |
Is responsible for protein synthesis (amino acids assembled into proteins here) |
|
|
Lysosomes (animal) |
-Membrane-bound sacs containing strong digestive enzymes -kills invading becteria and destroys damaged cell organelles -some time called suicide sacs |
|
|
Golgi apparatus (Both) |
-composed of flat disc like sacs -receives endoplasmic recticulum and "packages" them for transport out of the cell |
|
|
Mitochondrion (both) |
-rod like structures that specializes in cellular respiration -power house of the cell 6O2(g) + C6 H12 O6 (aq)= 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) + ATP |
|
|
Chemical composition of the cell |
Carbon is the building block of a cell and there is also hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen all cell are made up of organic compounds |
|
|
For types of organic compounds |
- lipids - carbohydrates - protein - nucleic acids |
|
|
Lipids |
Fats and oils |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Sugars, starches and glycogen |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Make up our DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) |
|
|
Importance of the cell membrane |
- Structure: contains the cells contents - Equilibrium: controls what enters and exits -Communication:uses receptor proteins -Protection & Defence: recognizes foreign invaders -Transportation: all materials must go through it |
|
|
Fluid mosaic model |
Accepted model for the structure of the cell membrane -fluid because the membrane is flexible -mosaic because it is a mixture of substances |
|
|
Solids |
Definite shape and volume Have the least amount of motions Does not flow or compress readily |
|
|
Liquids |
Takes the shape of the container but has definite volume Does compress readily but flows readily Has some vibrational, rotational and translational motion |
|
|
Gasses |
Take both the shape and the volume of their container Higly compressible and flows readily Has the most amount of movement |
|
|
Particle model of matter |
1.All matter is made up of particles they may be different in size and composition 2. Particles are always moving heating particles makes them move faster 3. Particles of matter are attracted to one another or bonded together 4. Particles have spaces between. Them |
|
|
Concentration Gradient |
Concentration-amount of substance dissolved in a solvent Concentration Gradient- there is a difference in the amount of solute on either side of a membrane |
|
|
Solutes |
Naturally move down the gradient -High area concentration too low area of concentration |
|
|
What is it called when the solute is equal on both sides of the membrane |
It is called equilibrium |
|
|
What is another way of saying selectively permeable |
Semi permeable |
|
|
The 3 types of permeable |
Impermeable Completely permeable Selectively permeable |
|
|
Diffusion |
Method of transport for small or fat-soluble molecules like O2 and CO2 -there movement is not restricted by the cell membrane |
|
|
Diffusion is classified as |
Passive transport because it flows down the concentration gradient it needs no extra energy |
|
|
Osmosis |
-It is a passive transport -And is the movement of water and it occurs when there is a a solute concentration difference -Membrane is not permeable to the solute |
|
|
Osmosis part 2 |
Water will move until the concentration is equal on either side of the membrane |
|
|
Tonicity |
Concentration of solutes outside and inside the cell there are three types |
|
|
Isotonic solution |
Concentration inside and outside is equal When the cell is placed in an isotonic solution there is not net movement which means that the water is moving in and out at the same rate |
|
|
Isotonic solution: In a plant cell it will look limp because |
It has a lack of turgor pressure |
|
|
Hypotonic |
The concentration of solutes outide the cell is lower than inside the cell And In effort to find equilibrium water will flow from the extracellular fluid into the cell |
|
|
What is plasmolysis |
When a cell becomes overfull or bloated and eventually bursts |
|
|
Hypotonic solution |
Water is flowing faster into the cell than it is flowing out |
|
|
Hypotonic when in a plant |
Plants will apear turgid and the plant will appear healthy |
|
|
Hypertonic |
The concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside the cell and in an effort to find equilibrium water will flow from the cell into the EFC The cell becomes shriveled and dried up |
|
|
Hypertonic solution |
Water is flowing out faster than it is flowing in And plants will pull away from the ridged cell wall |
|
|
Facilitated diffusion |
Facilitate means to assist Facilitated diffusion is diffusion that is helped along by proteins embedded in the cell membrane It is still passive transport It is for substances that are not water soluble because the cant pass through the membrane |
|
|
There are two types of protein asists |
Channel proteins and carrier proteins |
|
|
Channel proteins |
Shaped like tubes Form tunnels through the membrane which the water soluble molecules can pass |
|
|
Carrier proteins |
Attach to larger molecules that can't fit through the protein Channels The protein will attach to the molecule on the outside of the cell then rolls over to deposit the molecule inside the cell |
|
|
Active transport |
Against the concentration gradient It is called active transport because it requires extra energy by the cell From low to high concentration |
|
|
ATP stands for |
Adenosine triphosphate and it is created through cellular respiration |
|
|
Endocytosis |
Endo= In Cyto= cell A vesicle forms around the solute the vesicle has the same phospolipid structure as the cell membrane this requires ATP this allows even bigger molecules to enter |
|
|
Exocytosis |
Exo= out When it needs to remove waste that has been packaged by the Golgi apparatus releasing it into the EFC |
|
|
Recognition proteins |
On the outside of the cell membrane so for some substances to enter the cell they must doc at these receptor molecules first |
|
|
Receptor proteins |
They will bind with the substance and move it by Endocytosis |
|
|
Receptor proteins part 2 |
Medication cannot work unless it can into the cell The closer the macth between the shape of medication and the receptor protein the more targeted and effective the medicine can be |
|
|
Viruses |
Some viruses like HIV gain access by mimicking harmless molecules |
|
|
Cancer |
Treatments for cancer do not target cancerous cells but also healthy cells |
|
|
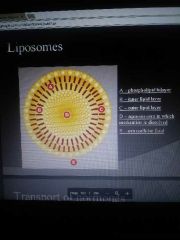
Lonesomes |
A form of medication that surrounds fluid filled sac with a phospolipid bilayer the medicine is able to dissolve directly through the cell membrane |
|
|
Liposomes |
|
|
|
Transport of hormones |
Made by one part ofbthe body but act upon another part |
|
|
Insulin |
Is produced by the pancreas and acts on all body cells to tell them to pick up glucose for celular respiration |
|
|
Diabetics |
Are either not able to produce insulin or it is not properly used by the body |
|
|
Dialysis |
Dialysis treatments are used by patients who have malfunctioning kidneys your kidneys filter your blold and remove excess water and waste which is removed by the body in the form of urine |
|
|
Peritoneal Dialysis |
A catheter is inserted into the abdominal cavity a sterile fluid containing water, glucose and electrolytes is pumped into the cavity nutrients from the fluid diffuse into the blood and waste diffuses out |
|
|
Hemodialysis |
Patients blood is removed from the body and cleand using the fluid and returned into the body this requires patient tobe in the hospital |
|
|
Cell volume |
The volume of the contents of the cell |
|
|
Larger cell |
Requires larger nutritional needs and has greater waste production |
|
|
Internal transport system |
Blood in animals and xylem/pholem in plants designed to deliver nutrients to all cells This reduces the cell's reliance on diffusion and osmosis |
|
|
Maximizing potential for plants |
For areas where there is alot of sunlight plant leavesare large to capture more sunlight And roots increase root hairs to have more contact with the soil |
|
|
Maximizing potential for animals |
Brain folding Small intestines Alveoli in lungs |

