![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cell theory |
Cells are the fundamental units of all living organisms. They are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals They are produced by division of existing cells They are the smallest structural unit that performed! All vital functions. |
|
|
Cell membrane |
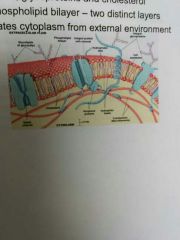
Thin, complex structure of phospholipids, proteins, glyoproteins and cholesterol, phosphosolipid bilayer, isolated cytoplasm from external environment. |
|
|
Passive transport |
Diffusion a movement from high to low Osmosis- movement of water Facilitated- molecules travel across through trans membrane carrier proteins that facilitate diffusion |
|
|
Functions of cell membrane |
Physical isolation of cell Regulation of exchange with environment Sensitivity and communication Structural support for tissues |
|
|
Active transport |
Requires energy Trans membrane proteins bind and transport molecules using ATP Endocytosis- Several processes result in membrane sacs endosomes containing material from outside the cell entering the cell Exocytosis- material is transported out, vesicle fuses with PM, ejecting waste or secretions. |
|
|
Phagocytosis |
Solid materials brought into endosome |
|
|
Pinocytosis |
Liquid materials (dissolved in extracellular fluid) brought into endosome. |
|
|
Receptor mediated endocytosis |
Molecules bind to specific proteins on cell surface Receptors with ligands are brought into cell Ligand is removed, receptors are recycled to cell surfaces |
|
|
Tight junction |
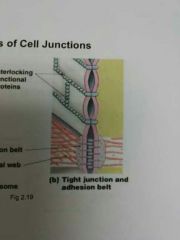
Very tight connection. Block water and thee solutions from moving across the cells, digestive tract. |
|
|
Gap junctions |
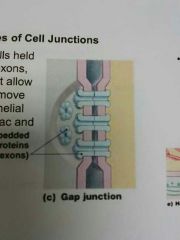
Cells held together with connexons which are pores that allow small molecules to move between cells. Epithelial, cilia, cardiac, smooth muscle. |
|
|
Desmosomes |
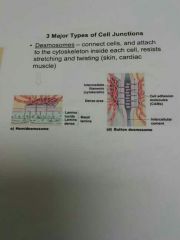
Connect cells and attach to the cytoskeleton inside each cell, resists stretching and twisting. Skin, cardiac, muscles |

