![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Elements |
building blocks of all forms of matter |
|
|
Ion |
An atom that gives up or gains electrons |
|
|
Compound |
Substance that contains atoms of two or more different elements |
|
|
Inorganic compounds |
Small and usually lack carbon |
|
|
Organic compounds |
Always contain carbon, covalent bonds, and usually contain hydrogen |
|
|
Mixtures |
Combinations of elements or compounds that are physically blended together but not bound by chemical bonds |
|
|
Free radical |
An atom or group of atoms with an unpaired electron in the outermost shell |
|
|
Antioxidants |
Inactivate oxygen-derived free radicals |
|
|
Hydrogen bond |
Weakest bond |
|
|
Covalent bond |
Strongest bond |
|
|
Ionic bonds |
When electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another |
|
|
Polar covalent bonds |
Formed when a pair of electrons is unequally shared between two atoms |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
Weak attractive forces |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
Can occur within molecules |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
Can form between neighboring molecules |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds |
Responsible for many of the unique properties of water |
|
|
Potential energy |
Energy stored by matter due to its position |
|
|
Kinetic energy |
Energy associated with matter in motion |
|
|
Chemical energy |
Form of potential energy that is stored in the bonds of compounds and molecules |
|
|
Synthesis reaction |
A + B = AB |
|
|
Exergonic reaction |
A + B = AB + energy (ATP) |
|
|
Decomposition reaction |
AB = A + B |
|
|
Endergonic reaction |
AB + energy (ATP) = A + B |
|
|
Exchange reactions |
Replacement of one atom or atoms by another atom or atoms |
|
|
Reverse reaction |
End products can reverse to the original reactants |
|
|
Turnover rate |
Average time between synthesis and recycling |
|
|
Enzymes |
Proteins that function as a catalyst |
|
|
Apoenzyme |
Protein portion in enzymes |
|
|
Cofactor |
Non-protein portion of enzymes |
|
|
Enzymes |
Lower the activation energy |
|
|
Enzymes |
Affect only the rate of a chemical reaction |
|
|
Enzymes (specificity) |
Catalyze only one type of reaction |
|
|
Inorganic compounds in the body |
Water, acids, bases, and salts |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds in water |
Why water molecules are cohesive |
|
|
Polar covalent bonds in water |
Why water is such an excellent solvent |
|
|
Electrolytes |
Can conduct an electrical current |
|
|
Danger of acidosis |
Excess of hydrogen ions in body fluids |
|
|
Effects of acidosis |
Break down chemical bonds to disrupt tissue function, changes the shape of large complex molecules rendering then non-functional |
|
|
Role of water molecules in synthesis of polysaccharides |
Water is released in the dehydration synthesis of polysaccharides |
|
|
Fibrous proteins |
Insoluble in water. Skin, muscle, blood |
|
|
Globular proteins |
Soluble in water. Enzymes, antibodies, hemoglobin |
|
|
3 basic bonds |
Ionic, covalent, hydrogen |
|
|
Anion |
Negative. Gaining electron |
|
|
Cation |
Positive. Lose electron |
|
|
Factors influencing a chemical reaction |
Concentration, temperature, speed |
|
|
Dehydration synthesis |
Reaction gives you water |
|
|
Decomposition hydrolysis |
Water is required to break a molecule |
|
|
Solution |
Solvent plus solute |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Largest carb in the body. Principle one is glycogen. Insoluble. |
|
|
Prostaglandins |
Coordinate local cellular activities |
|
|
Leucotrienes |
Allergic and inflammatory responses; injury |
|
|
7 functions of protein |
Support, movement, transport, buffering, metabolic regulation, coordination and control, defense |
|
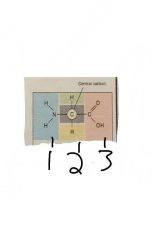
|
Structure of an amino acid 1- amino acid 2- R group 3- carboxylic acid group |
|
|
Levels of structural organization |
Primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary |
|
|
1- primary 2- secondary 3- tertiary 4- quaternary |
|
|
enzymes are what kind of catalyst |
Protein catalyst |

