![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is virtual endoscopy?
|
The creation of inner views of tubular structures by means of virtual reality concepts.
|
|
|
What are the 4 technical requirements for CT virtual endoscopy?
|
1. data acquisition
2. image preprocessing 3. 3D rendering 4. image display and analysis |
|
|
What does image preprocessing involve?
|
Image preprocessing involves the use of various noise filtering algorithms, image segmentation, cropping and cutting.
|
|
|
What is image segmentation?
|
Image segmentation can be done by the operator or automatically.
Certain images are selected and are windowed appropriately, while leaving other nonessential objects out. Then they are prepared for rendering. |
|
|
1. Facial nerve canal
2. Round window 3. Cochlea 4. Cochlear aqueduct 5. Hypotympanon 6. Malleus 7. Incus 8. Stapes 9. Pyramidal eminence 10. Mesotympanon 11. Jugular bulb 12. Sinus tympani 13. Posterior semicircular canal 14. Vestibular aqueduct 15. Oval window 16. Vestibule 17. Internal auditory canal 18. Lateral semicircular canal 19. Antrum 20. Epitympanon 21. Geniculate ganglion 22. Aditus 23. Superior semicircular canal 24. Subarcuate canal |
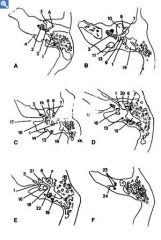
Name labeled parts
|
|
|
Origin of the left main coronary artery (LMCA)
origin of the right coronary artery (RCA) near the diaphragmatic surface of the heart. AO = aorta D1 = first diagonal branch GCV = great cardiac vein LA = left atrium LAD = left anterior descending coronary artery; LCX = circumflex coronary artery LV = left ventricle OM1 = first obtuse marginal branch RV = right ventricle RVOT = right ventricular outflow tract. |
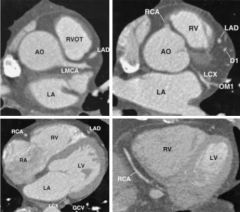
study heart
|
|
|
1. Falx cerebri
2. Frontal sinus 3. Optic chiasma 4. Infundibular stork of hypophysis 5. Internal carotid a. 6. Frontal lobe 7. Basilar a. 8. Hippocampus 9. Parietomastoid suture 10. Basis pontis 11. Superior cerebellar peduncle (brachium conjunctivum) 12. Fourth ventricle 13. Confluence of sinuses 14. Anterior (superior) medullary velum 15. Locus ceruleus 16. Greater occipital nerve 17. Parietosquamosal suture 18. Mastoid air cells 19. Superficial temporal a. and v. 20. Temporal lobe 21. Amygdaloid nucleus 22. Middle cerebral a., brs. 23. Temporalis m. 24. Middle cerebral a. 25. Orbital fat 26. Superior rectus m. 27. Frontal bone 28. Internal carotid |
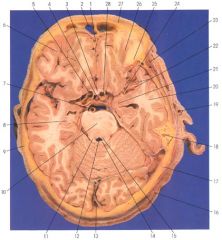
Label
|

