![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Species |
The basic grouping used in biological classification |
organisms that is capable of breeding, or mating with each other |
|
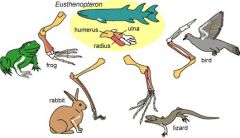
Homologies |
structures that indicate a related evolutionary ancestry |
Not just simmilarity |
|
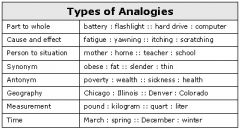
Analogies |
Structures that are similar in appearance and function but are not the result of shared ancestry |
It is not a result of shared ancestory |
|
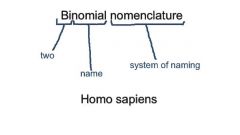
Binomial nomenclature |
Two- word naming system, to isentify each species |
Linnean system |
|
Eubacteria |
MOnera, so different that many biologists now treat them as two kingdoms. |
MOnera |
|
|
Archaea |
Monera is also in this group, many biologists now treat them as two kingdoms. |
MOnera |
|
|
Protista |
Kingdom protista consists mostly of microscopic unicellular eukaryotes |
Kingdom protista |
|
|
Fungi |
The kingdom Fungi includes heterotrophs that absorb small molecules from their surroundings through their outer walls. |
The kingdom Fungi |
|
|
Plantae |
Photoautotrophic multicellular eukaryotes that develop from embryos belong to the kingdom plantae |
Photoautotrophic multicellular |
|
|
Animalia |
Heterotrophic multicellular eukaryotes that develp from emryos are placed in the kingdom Animalia |
Kingdom Animalia |
|
|
Clade |
Groups species according to encestry and homologous characteristics not found in other organisms |
Group species |
|
|
Coevolution |
The development of woody cactus stems and flared tortoise shells |
The continuous adaptation of different species to each other. |
|
|
Adaptation |
Dtermine whether in short repeated nucleotide sequences called microsatellites |
Microsatellites |
|
|
Speciation |
The appearance of new species |
Although most evolutionary change is too slow to see |
|
|
Geographic isolation |
Term that refers to a population of animals |
Plants or oher organisms |
|
|
Adaptive radiation |
The adaptations of Darwin's finches to different food sources and nesting sites on the Galapagos islands. |
Galapagos islands |
|
|
Common ancestor |
A group of organisms who share common descent |
Common descent |
|
|
Stasis |
State of stability |
Where all forces are equal and opposing |
|
|
Gradualism |
Another pattern of evolution |
Called punctuated equilibrium |
|
|
Punctuated equilibrium |
Involves a short period of rapid change just after a population becomes isolated and forms a new species |
Involves a short period |

