![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
377 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Resolved Clients |

Increased understanding, empathy, forgiveness
More intense emotions during empty-chair technique
Best treatment outcomes |
|
|
Process of Therapy |
Relationship between client and therapist
Application of therapists' own technique
Client's commitment to change |
|
|
What Clinical Psychologists? |
Hold Ph.D (of philosophy) or Psy.D (of psychology)
5/+ years of training |
|
|
What are psychiatrists? |
Medical doctors
Specialize in psychotherapy and biomedical treatments |
|
|
What is the goal of psychoanalysis? |
Insight
Conscious awareness of psychodynamics underlying their problems |
|
|
Why do psychoanalysts believe insight will help the client? |
Repeatedly encounters and deals with buried emotions & conflicts
Psychic energy can be released |
|
|
How did Freud view mental events? |
Meaningfully associated with one another
Clues contents of unconscious found in constant stream of thoughts |
|
|
Technique of Free Association |
Clients report verbally any thoughts, feeling, images that enter awareness
Without censorship
Thoughts primarily determined by internal factors
|
|
|
What does the analyst want to get out of Free Association? |
Does not expect it will lead directly to unconscious matter
Thoughts provide clues concerned important themes
E.g., client's stream of thoughts stop after she mentioned father |
|
|
Psychoanalysts on Dream Interpretations |
Dreams express impulses that defences keep in unconscious
Threatening material still disguised to prevent anxiety |
|
|
Free Association and Dreaming |
Ask client to freely associated each element of the dream
Arrive at understanding of what the symbols represent |
|
|
What is "resistance"? |
Defensive manoeuvres
Hinder process of therapy
Strong unconscious investment in maintains status quo |
|
|
Why is "resistance" important in therapy? |
Sign that anxiety-arousing sensitive material is being approached
Must explore reasons for resistance |
|
|
What is "transference"? |
Client responds as if therapist was important figure from client's past
Responses are irrational |
|
|
Why is "transference" important? |
Bring out into open repressed feelings and maladaptive behaviour patterns
Therapist can then point out to client
Must be analyzed & resolved for full resolution |
|
|
Positive Transference |
Client transfers feelings of intense affection, dependency or love to analyst |
|
|
Negative transference |
Irrational expressions of anger, hatred, or disappointment |
|
|
Psychoanalysts on Dream Interpretations |
Dreams express impulses that defences keep in unconscious
Threatening material still disguised to prevent anxiety |
|
|
Free Association and Dreaming |
Ask client to freely associated each element of the dream
Arrive at understanding of what the symbols represent |
|
|
What is "resistance"? |
Defensive manoeuvres
Hinder process of therapy
Strong unconscious investment in maintains status quo |
|
|
Why is "resistance" important in therapy? |
Sign that anxiety-arousing sensitive material is being approached
Must explore reasons for resistance |
|
|
What is "transference"? |
Client responds as if therapist was important figure from client's past
Responses are irrational |
|
|
Why is "transference" important? |
Bring out into open repressed feelings and maladaptive behaviour patterns
Therapist can then point out to client
Must be analyzed & resolved for full resolution |
|
|
Positive Transference |
Client transfers feelings of intense affection, dependency or love to analyst |
|
|
Negative transference |
Irrational expressions of anger, hatred, or disappointment |
|
|
What is "interpretation"? |
Any statement by the therapist
Intended to provide the client with insight into his or her behaviour or dynamics |
|
|
Importance of an interpretive statement? |
Confronts client with something they have not previously admitted into consciousness |
|
|
What is the general rule in psychoanalytic treatment? |
Interpret what is already near the surface and just beyond client's current awareness |
|
|
Why might offering "deep" interpretations be considered poor technique? |
Even if they are correct they are so far removed from clients current awareness they cannot be informative or helpful
It is the client who must eventually arrive at insight |
|
|
Classical Psychoanalysis |
Expensive & time-consuming
To rebuild the client's personality
Client seen 5X a week for 5 yrs (Practiced by Freud) |
|
|
Humanistic psychotherapy |
Seen as human encounters between equals
Environment where client can self-explore without needing to block natural tendencies |
|
|
Criticisms of Classical Psychoanalysis |
Impractical and unnecessary
Rate of improvement highest at beginning and decreases over time (after 10 sessions) |
|
|
Support for Classical Psychoanalysis |
More effective in treating certain disorders than brief therapy
Greater improvement in 3-year follow up |
|
|
Brief Psychodynamic Therapy |
Emphasized maladaptive influences of past and relating them to current pattern of self-defeating behaviour
Importance of insight and interpretation |
|
|
How are therapist and client situated in brief psychodynamic therapy? |
Sit facing each other
Conversation replaces free association
Client seen 1-2 times a week |
|
|
What is the goal of brief psychodynamic therapy? |
Help clients deal with specific life problems
Teach client specific interpersonal and emotion-control skills |
|
|
Interpersonal Therapy |
Focused on clients current interpersonal problems E.g., loss of relationship
Highly structured
Takes 15-20 sessions |
|
|
Effectiveness of Interpersonal therapy? |
Effective therapy for depression and somatic system disorder |
|
|
How do humanistic theorists view humans? |
Capable of consciously controlling their actions
Taking responsibility for their choices and behaviour
Posses resources for self-heal and personal growth |
|
|
How do humanistic theorists view disorders? |
Blocking of natural growth process
Brought about by distorted perceptions, lack of awareness about feelings, negative self-image |
|
|
Humanistic vs. Psychoanalytic Therapy (past, present, future)? |
Humanistic = focuses on present & future
Psychoanalytic = focus on past |
|
|
Goal of "empty-chair technique"? |
Evoke powerful feelings
Make client aware of unresolved issues that affect other relationships in their lives |
|
|
Rogers's (Client-Centred Therapy) attitude toward research on humanistic therapy |
Identity favours contributing to therapeutic success
Pioneer in tap-recording therapy session & analyzing |
|
|
Perls's (Gestalt Therapy) attitude toward research on humanistic therapy |
Anti-scientific attitude (no systemic research)
As a result influence began to wane following his death |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Resolved Clients |
Increased understanding, empathy, forgiveness
More intense emotions during empty-chair technique
Best treatment outcomes |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Unresolved Clients |
Less understanding, forgiveness
Expressed less emotions during empty-chair technique
Less significant improvement in interpersonal problems after treatment |
|
|
Cognitive approach to psychotherapy |
Role of irrational and self-defeating thought patterns
Help clients discover and change the cognitions underlying their problems |
|
|
Cognitive therapists vs Psychoanalysts |
Do not emphasis unconscious
Rather, point out that we reflect reality based on habitual thought patterns |
|
|
Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Irrational thoughts = immediate cause of self-defeating emotions |
|
|
ABCD model of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
A = activating event B = belief system C = cognitive sequences D = disputing |
|
|
A's of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Activating event that triggers emotion |
|
|
Humanistic vs. Psychoanalytic Therapy (goal of therapy)? |
Humanistic Directed to help clients become aware of feelings as they occur
Psychoanalytic Achieving insight into childhood origins of feelings |
|
|
B's of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Belief system that underlies the way a person appraises the event |
|
|
C's of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Emotional and behavioural consequences of that appraisal |
|
|
D's of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Disputing/challenging an erroneous belief system
Key to changing maladaptive emotions and behaviours |
|
|
How does Ellis believe people are accustomed to viewing their emotions? |
Caused directly by event
However it is actually caused by belief system
E.g., young man feels depressed when rejected from date actually because he believed he must be loved and accepted by everyone |
|
|
How do rational-emotive therapists help clients? |
Introduce them to common irrational idea E.g., it's necessary that I be loved and approved by everyone
Train them to ferret out particular ideas underlying maladaptive emotional responses E.g., self worth does not depends on approval of others |
|
|
Beck's Cognitive Therapy |
Help client identity and reprogram "automatic" thought patterns |
|
|
Beck's Cognitive Therapy in helping clients |
Help client realize their thoughts (not situation) cause their maladaptive emotional behaviour E.g., "if I fail the test I won't get into law school and I will never be happy"
Realization helps change their maladaptive thoughts |
|
|
Cognitive Therapy and Depression |
Sessions decreased depression
Improved maintenance of depressed clients |
|
|
Extensions of cognitive therapy in treating other disorders |
Anger disorders Anxiety disorders Personality disorders Eating disorders |
|
|
Self-Instructional Training |
Influential in treatment related to stress and coping |
|
|
Client-Centred Therapy (Carl Rogers) |
Unconditional positive regard
Empathy
Genuineness |
|
|
What do behavioural therapists believe? |
Behavioural disorders leaner the same way normal behaviours are learned
Can be unlearned by classical/operant conditioning |
|
|
Classical Conditioning Treatments |
Used to reduce anxiety
Condition new anxiety responses to a particular stimuli E.g., alcoholic beverages |
|
|
Classical Extinction of the Anxiety Response |
Most direct way to reduce fear
Exposure to feared CS in a sense of UCS
Using response prevention to keep operant avoidance response from occurring |
|
|
What is "flooding"? (Extinction Approach) |
Client is exposed to real-life stimuli |
|
|
What is "implosion therapy"? (Extinction Approach) |
Client asked to imagine scenes involving stimuli |
|
|
Effectiveness of Extinction Approach |
Highly effective for extinguishing anxiety repose in animals and humans
Degree of improvement maintains or increase in follow-up |
|
|
Added advantage of Extinction Approach |
Clients can administer treatment to themselves under therapists direction
Proved highly successful |
|
|
Systematic Desensitization |
Learning-based treatment for anxiety disorders
High success rate (80%)
Can treat test, math, highway driving anxiety |
|
|
Counterconditioning |
New responses incompatible with anxiety is conditioned to anxiety-arousing CS
Eliminates anxiety |
|
|
Process of Systematic Desensitization |
Train client in voluntary muscle relaxation
Constructs stimulus hierarchy (Arranged from low-high anxiety) |
|
|
Importance of "unconditional positive regard" in Client-Centred Therapy? |
Therapists show care and acceptance without judgment
Sense of trust communicated in therapists refusal to offer guidance |
|
|
Systematic desensitization vs Exposure |
Systematic desensitization preferred (less anxiety)
Exposure reduces anxiety more quickly |
|
|
Aversion Therapy |
Therapist pairs attractive stimulus with noxious UCS
Condition an aversion to CS
E.g., inject alcoholics with nausea-producing drugs and having them drink |
|
|
Effectiveness of Aversion Therapy |
More likely to succeed if client also learns specific coping skills for avoiding relapses |
|
|
Behavioural Modification |
Operant conditioning used to increase or decrease a certain behaviour |
|
|
Effectiveness of behavioural modification |
Success at treating population difficult to treat with traditional therapies
E.g., chronic hospitalized schizophrenics, profoundly disturbed children |
|
|
Purpose of "token economies"? |
System for strengthening desired behaviours E.g., personal grooming
Positive reinforcement
Desired behaviour started with tangible reinforcers
Eventually come under control of social reinforcers and self-reinforcers |
|
|
Effectiveness of token economies |
Highly effective in most challenging populations E.g., chronic schizophrenics
Applied within business, school, prison, home environments |
|
|
Punishment as a way to control behaviour? |
Least preferred way
Aversive qualities, potential negative side effects |
|
|
Before using punishment as therapy, what questions do therapists ask themselves? |
Is there a less painful alternative?
Is the behaviour to be eliminated sufficiently to individual or to society? |
|
|
When might punishment be used as therapy? |
Self-destructing behaviours E.g., severely disturbed autistic children bite their flesh
Used 15 electric shocks to eliminate behaviour |
|
|
Importance of "empathy" in Client-Centred Therapy? |
Willingness to view world through client's eyes
Reflects back to client what they are communicating E.g., rephrasing client |
|
|
Social Skills Training |
Clients learn new skills by observing and imitating a model who form socially skillful behaviour |
|
|
Effectiveness of Social Skills Training |
Increased self-efficacy
When clients believe they are capable of performing desired behaviours they succeed |
|
|
Importance of "genuineness" in Client-Centred Therapy? |
Consistency between how therapist feels and behaves
Therapist must be open enough to honestly express feelings (+/-) |
|
|
Outcome of Client/Centred therapy? |
Increased self-acceptance, self-awareness, comfort, improved life functioning |
|
|
When is Client-Centred Therapy proved most effective? |
When therapist is performed as genuine, warm, and empathetic |
|
|
Gestalt Therapy |
To bring client into immediate awareness so they can be "whole" again
Carried out in groups |
|
|
What is the "empty chair technique"? (Gestalt therapy) |
Asked to imagine someone sitting in the chair
Carry on conversation alternatively role playing for himself and other person
Telling person how they honestly feel |
|
|
Humanistic vs. Psychoanalytic Therapy (past, present, future)? |
Humanistic = focuses on present & future
Psychoanalytic = focus on past |
|
|
Goal of "empty-chair technique"? |
Evoke powerful feelings
Make client aware of unresolved issues that affect other relationships in their lives |
|
|
Rogers's (Client-Centred Therapy) attitude toward research on humanistic therapy |
Identity favours contributing to therapeutic success
Pioneer in tap-recording therapy session & analyzing |
|
|
Perls's (Gestalt Therapy) attitude toward research on humanistic therapy |
Anti-scientific attitude (no systemic research)
As a result influence began to wane following his death |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Resolved Clients |
Increased understanding, empathy, forgiveness
More intense emotions during empty-chair technique
Best treatment outcomes |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Unresolved Clients |
Less understanding, forgiveness
Expressed less emotions during empty-chair technique
Less significant improvement in interpersonal problems after treatment |
|
|
Cognitive approach to psychotherapy |
Role of irrational and self-defeating thought patterns
Help clients discover and change the cognitions underlying their problems |
|
|
Cognitive therapists vs Psychoanalysts |
Do not emphasis unconscious
Rather, point out that we reflect reality based on habitual thought patterns |
|
|
Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Irrational thoughts = immediate cause of self-defeating emotions |
|
|
ABCD model of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
A = activating event B = belief system C = cognitive sequences D = disputing |
|
|
A's of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Activating event that triggers emotion |
|
|
Humanistic vs. Psychoanalytic Therapy (goal of therapy)? |
Humanistic Directed to help clients become aware of feelings as they occur
Psychoanalytic Achieving insight into childhood origins of feelings |
|
|
B's of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Belief system that underlies the way a person appraises the event |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Resolved Clients |
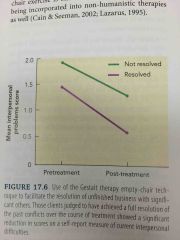
Increased understanding, empathy, forgiveness
More intense emotions during empty-chair technique
Best treatment outcomes |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Unresolved Clients |
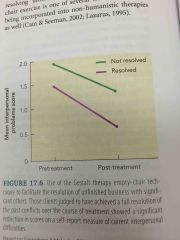
Less understanding, forgiveness
Expressed less emotions during empty-chair technique
Less significant improvement in interpersonal problems after treatment |
|
|
How does Ellis believe people are accustomed to viewing their emotions? |
Caused directly by event
However it is actually caused by belief system
E.g., young man feels depressed when rejected from date actually because he believed he must be loved and accepted by everyone |
|
|
How do rational-emotive therapists help clients? |
Introduce them to common irrational idea E.g., it's necessary that I be loved and approved by everyone
Train them to ferret out particular ideas underlying maladaptive emotional responses E.g., self worth does not depends on approval of others |
|
|
Beck's Cognitive Therapy |
Help client identity and reprogram "automatic" thought patterns |
|
|
Beck's Cognitive Therapy in helping clients |
Help client realize their thoughts (not situation) cause their maladaptive emotional behaviour E.g., "if I fail the test I won't get into law school and I will never be happy"
Realization helps change their maladaptive thoughts |
|
|
Cognitive Therapy and Depression |
Sessions decreased depression
Improved maintenance of depressed clients |
|
|
Extensions of cognitive therapy in treating other disorders |
Anger disorders Anxiety disorders Personality disorders Eating disorders |
|
|
Self-Instructional Training |
Influential in treatment related to stress and coping |
|
|
Client-Centred Therapy (Carl Rogers) |
Unconditional positive regard
Empathy
Genuineness |
|
|
What do behavioural therapists believe? |
Behavioural disorders leaner the same way normal behaviours are learned
Can be unlearned by classical/operant conditioning |
|
|
Classical Conditioning Treatments |
Used to reduce anxiety
Condition new anxiety responses to a particular stimuli E.g., alcoholic beverages |
|
|
Classical Extinction of the Anxiety Response |
Most direct way to reduce fear
Exposure to feared CS in a sense of UCS
Using response prevention to keep operant avoidance response from occurring |
|
|
What is "flooding"? (Extinction Approach) |
Client is exposed to real-life stimuli |
|
|
What is "implosion therapy"? (Extinction Approach) |
Client asked to imagine scenes involving stimuli |
|
|
Effectiveness of Extinction Approach |
Highly effective for extinguishing anxiety repose in animals and humans
Degree of improvement maintains or increase in follow-up |
|
|
Added advantage of Extinction Approach |
Clients can administer treatment to themselves under therapists direction
Proved highly successful |
|
|
Systematic Desensitization |
Learning-based treatment for anxiety disorders
High success rate (80%)
Can treat test, math, highway driving anxiety |
|
|
Counterconditioning |
New responses incompatible with anxiety is conditioned to anxiety-arousing CS
Eliminates anxiety |
|
|
Process of Systematic Desensitization |
Train client in voluntary muscle relaxation
Constructs stimulus hierarchy (Arranged from low-high anxiety) |
|
|
Importance of "unconditional positive regard" in Client-Centred Therapy? |
Therapists show care and acceptance without judgment
Sense of trust communicated in therapists refusal to offer guidance |
|
|
Systematic desensitization vs Exposure |
Systematic desensitization preferred (less anxiety)
Exposure reduces anxiety more quickly |
|
|
Aversion Therapy |
Therapist pairs attractive stimulus with noxious UCS
Condition an aversion to CS
E.g., inject alcoholics with nausea-producing drugs and having them drink |
|
|
Effectiveness of Aversion Therapy |
More likely to succeed if client also learns specific coping skills for avoiding relapses |
|
|
Behavioural Modification |
Operant conditioning used to increase or decrease a certain behaviour |
|
|
Effectiveness of behavioural modification |
Success at treating population difficult to treat with traditional therapies
E.g., chronic hospitalized schizophrenics, profoundly disturbed children |
|
|
Purpose of "token economies"? |
System for strengthening desired behaviours E.g., personal grooming
Positive reinforcement
Desired behaviour started with tangible reinforcers
Eventually come under control of social reinforcers and self-reinforcers |
|
|
Effectiveness of token economies |
Highly effective in most challenging populations E.g., chronic schizophrenics
Applied within business, school, prison, home environments |
|
|
Punishment as a way to control behaviour? |
Least preferred way
Aversive qualities, potential negative side effects |
|
|
Before using punishment as therapy, what questions do therapists ask themselves? |
Is there a less painful alternative?
Is the behaviour to be eliminated sufficiently to individual or to society? |
|
|
When might punishment be used as therapy? |
Self-destructing behaviours E.g., severely disturbed autistic children bite their flesh
Used 15 electric shocks to eliminate behaviour |
|
|
Importance of "empathy" in Client-Centred Therapy? |
Willingness to view world through client's eyes
Reflects back to client what they are communicating E.g., rephrasing client |
|
|
Social Skills Training |
Clients learn new skills by observing and imitating a model who form socially skillful behaviour |
|
|
Effectiveness of Social Skills Training |
Increased self-efficacy
When clients believe they are capable of performing desired behaviours they succeed |
|
|
What is "mindfulness"? |
Mental state of awareness, focus, openness, and acceptance of immediate experience
Nonjudgmental appraisal |
|
|
How is mindfulness like association cognitive techniques? |
Focusing non-judgementally on sensations
Increase ability to tolerate painful stimuli |
|
|
What is an important tool for learning mindfulness? |
Meditation technique
People develop tranquil state and focus closely on sensations
Used for stress reduction and relapse prevention |
|
|
How does mindfulness mediation add to relapse prevention? |
Increase awareness of thoughts and emotions that trigger lapses
Neutralizes self-blame
Interrupt cycle of automatic substance abus |
|
|
Importance of "genuineness" in Client-Centred Therapy? |
Consistency between how therapist feels and behaves
Therapist must be open enough to honestly express feelings (+/-) |
|
|
Outcome of Client/Centred therapy? |
Increased self-acceptance, self-awareness, comfort, improved life functioning |
|
|
When is Client-Centred Therapy proved most effective? |
When therapist is performed as genuine, warm, and empathetic |
|
|
Gestalt Therapy |
To bring client into immediate awareness so they can be "whole" again
Carried out in groups |
|
|
What is the "empty chair technique"? (Gestalt therapy) |
Asked to imagine someone sitting in the chair
Carry on conversation alternatively role playing for himself and other person
Telling person how they honestly feel |
|
|
Humanistic vs. Psychoanalytic Therapy (past, present, future)? |
Humanistic = focuses on present & future
Psychoanalytic = focus on past |
|
|
Goal of "empty-chair technique"? |
Evoke powerful feelings
Make client aware of unresolved issues that affect other relationships in their lives |
|
|
Rogers's (Client-Centred Therapy) attitude toward research on humanistic therapy |
Identity favours contributing to therapeutic success
Pioneer in tap-recording therapy session & analyzing |
|
|
Perls's (Gestalt Therapy) attitude toward research on humanistic therapy |
Anti-scientific attitude (no systemic research)
As a result influence began to wane following his death |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Resolved Clients |
Increased understanding, empathy, forgiveness
More intense emotions during empty-chair technique
Best treatment outcomes |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Unresolved Clients |
Less understanding, forgiveness
Expressed less emotions during empty-chair technique
Less significant improvement in interpersonal problems after treatment |
|
|
Cognitive approach to psychotherapy |
Role of irrational and self-defeating thought patterns
Help clients discover and change the cognitions underlying their problems |
|
|
Cognitive therapists vs Psychoanalysts |
Do not emphasis unconscious
Rather, point out that we reflect reality based on habitual thought patterns |
|
|
Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Irrational thoughts = immediate cause of self-defeating emotions |
|
|
ABCD model of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
A = activating event B = belief system C = cognitive sequences D = disputing |
|
|
A's of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Activating event that triggers emotion |
|
|
Humanistic vs. Psychoanalytic Therapy (goal of therapy)? |
Humanistic Directed to help clients become aware of feelings as they occur
Psychoanalytic Achieving insight into childhood origins of feelings |
|
|
B's of Ellis's Rational-Emotive Therapy |
Belief system that underlies the way a person appraises the event |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Resolved Clients |
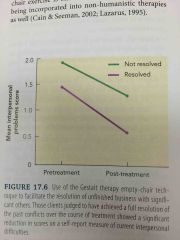
Increased understanding, empathy, forgiveness
More intense emotions during empty-chair technique
Best treatment outcomes |
|
|
Effects of Empty chair Technique: Unresolved Clients |
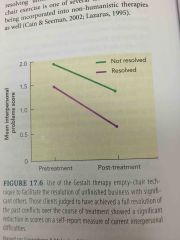
Less understanding, forgiveness
Expressed less emotions during empty-chair technique
Less significant improvement in interpersonal problems after treatment |
|
|
How does Ellis believe people are accustomed to viewing their emotions? |
Caused directly by event
However it is actually caused by belief system
E.g., young man feels depressed when rejected from date actually because he believed he must be loved and accepted by everyone |
|
|
How do rational-emotive therapists help clients? |
Introduce them to common irrational idea E.g., it's necessary that I be loved and approved by everyone
Train them to ferret out particular ideas underlying maladaptive emotional responses E.g., self worth does not depends on approval of others |
|
|
Beck's Cognitive Therapy |
Help client identity and reprogram "automatic" thought patterns |
|
|
Beck's Cognitive Therapy in helping clients |
Help client realize their thoughts (not situation) cause their maladaptive emotional behaviour E.g., "if I fail the test I won't get into law school and I will never be happy"
Realization helps change their maladaptive thoughts |
|
|
Cognitive Therapy and Depression |
Sessions decreased depression
Improved maintenance of depressed clients |
|
|
Extensions of cognitive therapy in treating other disorders |
Anger disorders Anxiety disorders Personality disorders Eating disorders |
|
|
Self-Instructional Training |
Influential in treatment related to stress and coping |
|
|
Client-Centred Therapy (Carl Rogers) |
Unconditional positive regard
Empathy
Genuineness |
|
|
What do behavioural therapists believe? |
Behavioural disorders leaner the same way normal behaviours are learned
Can be unlearned by classical/operant conditioning |
|
|
Classical Conditioning Treatments |
Used to reduce anxiety
Condition new anxiety responses to a particular stimuli E.g., alcoholic beverages |
|
|
Classical Extinction of the Anxiety Response |
Most direct way to reduce fear
Exposure to feared CS in a sense of UCS
Using response prevention to keep operant avoidance response from occurring |
|
|
What is "flooding"? (Extinction Approach) |
Client is exposed to real-life stimuli |
|
|
What is "implosion therapy"? (Extinction Approach) |
Client asked to imagine scenes involving stimuli |
|
|
Effectiveness of Extinction Approach |
Highly effective for extinguishing anxiety repose in animals and humans
Degree of improvement maintains or increase in follow-up |
|
|
Added advantage of Extinction Approach |
Clients can administer treatment to themselves under therapists direction
Proved highly successful |
|
|
Systematic Desensitization |
Learning-based treatment for anxiety disorders
High success rate (80%)
Can treat test, math, highway driving anxiety |
|
|
Counterconditioning |
New responses incompatible with anxiety is conditioned to anxiety-arousing CS
Eliminates anxiety |
|
|
Process of Systematic Desensitization |
Train client in voluntary muscle relaxation
Constructs stimulus hierarchy (Arranged from low-high anxiety) |
|
|
Importance of "unconditional positive regard" in Client-Centred Therapy? |
Therapists show care and acceptance without judgment
Sense of trust communicated in therapists refusal to offer guidance |
|
|
Systematic desensitization vs Exposure |
Systematic desensitization preferred (less anxiety)
Exposure reduces anxiety more quickly |
|
|
Aversion Therapy |
Therapist pairs attractive stimulus with noxious UCS
Condition an aversion to CS
E.g., inject alcoholics with nausea-producing drugs and having them drink |
|
|
Effectiveness of Aversion Therapy |
More likely to succeed if client also learns specific coping skills for avoiding relapses |
|
|
Behavioural Modification |
Operant conditioning used to increase or decrease a certain behaviour |
|
|
Effectiveness of behavioural modification |
Success at treating population difficult to treat with traditional therapies
E.g., chronic hospitalized schizophrenics, profoundly disturbed children |
|
|
Purpose of "token economies"? |
System for strengthening desired behaviours E.g., personal grooming
Positive reinforcement
Desired behaviour started with tangible reinforcers
Eventually come under control of social reinforcers and self-reinforcers |
|
|
Effectiveness of token economies |
Highly effective in most challenging populations E.g., chronic schizophrenics
Applied within business, school, prison, home environments |
|
|
Punishment as a way to control behaviour? |
Least preferred way
Aversive qualities, potential negative side effects |
|
|
Before using punishment as therapy, what questions do therapists ask themselves? |
Is there a less painful alternative?
Is the behaviour to be eliminated sufficiently to individual or to society? |
|
|
When might punishment be used as therapy? |
Self-destructing behaviours E.g., severely disturbed autistic children bite their flesh
Used 15 electric shocks to eliminate behaviour |
|
|
Importance of "empathy" in Client-Centred Therapy? |
Willingness to view world through client's eyes
Reflects back to client what they are communicating E.g., rephrasing client |
|
|
Social Skills Training |
Clients learn new skills by observing and imitating a model who form socially skillful behaviour |
|
|
Effectiveness of Social Skills Training |
Increased self-efficacy
When clients believe they are capable of performing desired behaviours they succeed |
|
|
What is "mindfulness"? |
Mental state of awareness, focus, openness, and acceptance of immediate experience
Nonjudgmental appraisal |
|
|
How is mindfulness like association cognitive techniques? |
Focusing non-judgementally on sensations
Increase ability to tolerate painful stimuli |
|
|
What is an important tool for learning mindfulness? |
Meditation technique
People develop tranquil state and focus closely on sensations
Used for stress reduction and relapse prevention |
|
|
How does mindfulness mediation add to relapse prevention? |
Increase awareness of thoughts and emotions that trigger lapses
Neutralizes self-blame
Interrupt cycle of automatic substance abus |
|
|
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) |
Process of mindfulness as a vehicle for change
Therapist teaches client to "just notice" and accept thoughts |
|
|
Importance of "genuineness" in Client-Centred Therapy? |
Consistency between how therapist feels and behaves
Therapist must be open enough to honestly express feelings (+/-) |
|
|
Outcome of Client/Centred therapy? |
Increased self-acceptance, self-awareness, comfort, improved life functioning |
|
|
When is Client-Centred Therapy proved most effective? |
When therapist is performed as genuine, warm, and empathetic |
|
|
Gestalt Therapy |
To bring client into immediate awareness so they can be "whole" again
Carried out in groups |
|
|
What is the "empty chair technique"? (Gestalt therapy) |
Asked to imagine someone sitting in the chair
Carry on conversation alternatively role playing for himself and other person
Telling person how they honestly feel |
|
|
Importance of "just notice" acceptance of thought (ACT) |
Reduces emotional impact of the thought
Diffuse anxiety it would ordinarily evoke
Even if anxiety evoked, accepted as temporary experience |
|
|
Biggest problem in mental-healthy services in minority cultures |
Too few skilled counsellors who can provide culturally responsive forms of treatment
Operate on basis of inaccurate stereotypes, inappropriate goals |
|
|
What can be done to increase access of culturally diverse groups to psychological treatment? |
Take therapy to the people
Establishing mental-health service agencies in minority population areas
Ethnically similar therapists |
|
|
Importance of "commitment" in ACT |
Examining one's life
Deciding what's most important to one's true self
Setting life goals
Therapist helps client develop strategies to remain committed to goals |
|
|
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) |
Treatment specifically for borderline personality disorder
"Package of elements" to treat: cognitive, behavioural, humanistic, psychodynamic therapies |
|
|
Behavioural Techniques in DBT |
Help client learn interpersonal, problem-solving, emotion-control skills |
|
|
Cognitive approaches in DBT |
Help client learn more adaptive thinking about the world, relationships, themselves |
|
|
DBT vs Control Treatment |
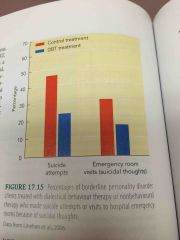
Fully reduced self-destructive behaviour over 2 years
Less suicide attempts, less psychiatric hospitalization
Less likely to drop out of therapy |
|
|
Goal of DBT treatment |
Bring self-destructive behaviours under control
E.g., suicide attempts |
|
|
DBT vs Control Treatment |
Fully reduced self-destructive behaviour over 2 years
Less suicide attempts, less psychiatric hospitalization
Less likely to drop out of therapy |
|
|
Utilization of mental-health services in different cultures |
Far lower in minority groups than the majority white population
Even when minorities seek treatment likely to drop out |
|
|
Barriers in seeking mental-healthy services |
Cultural norm against turning to professions inside one's own culture for help
History of frustrating experiences
Language barriers
Cannot afford
Located far away |
|
|
Importance of cultural competence in a therapist |
Able to use knowledge of client's culture to achieve a broad understanding of the client
Attentive to how client may differ from cultural stereotype |
|
|
Can a therapist be trained to be more culturally sensitive? |
Yes
Exposure to ethnic training important in outcome
Clients rated therapist with greater empathy and expertise |
|
|
Why is anxiety more common in women in western cultures? |
Poverty
Lack of opportunity (sexism)
Multiple roles of mother
History of abuse/violence |
|
|
Goal of therapist in treating women |
Focus on what can be done to change womens' life circumstances
Rather than adapting to expectations |
|
|
Research on therapy with women clients |
Not necessary to be treated by female therapists
More important for therapist to be sensitive to gender issues |
|
|
Importance of cultural competence in a therapist |
Able to use knowledge of client's culture to achieve a broad understanding of the client
Attentive to how client may differ from cultural stereotype |
|
|
Result of Eysenck's conclusions on effectiveness of therapy |
Stimulated increase in research on psychotherapy
Development of more sophisticated methods for evaluating treatment outcome s |
|
|
Randomized Clinical Trials (RCTs) |
Individuals (with well-defined psychological disorders) randomly assigned to experimental group (gets treatment) or control group
See if group that got drug+therapy does better than group who received drug or therapy |
|
|
Meta-analysis |
Allows researchers to combine the results of many studies
Arrive at overall condition |
|
|
Effect size statistic |
Common measure of treatment effectiveness
Tells researchers what percentage of clients who received therapy had a more favourable outcome |
|
|
Result of meta-analysis in assessing effectiveness of therapy? |
Aver haw therapy client had a more favourable outcome that untreated cases
Therapy does have positive effect beyond spontaneous remission |
|
|
Can a therapist be trained to be more culturally sensitive? |
Yes
Exposure to ethnic training important in outcome
Clients rated therapist with greater empathy and expertise |
|
|
Why is anxiety more common in women in western cultures? |
Poverty
Lack of opportunity (sexism)
Multiple roles of mother
History of abuse/violence |
|
|
Goal of therapist in treating women |
Focus on what can be done to change womens' life circumstances
Rather than adapting to expectations |
|
|
Research on therapy with women clients |
Not necessary to be treated by female therapists
More important for therapist to be sensitive to gender issues |
|
|
Specificity Question |
Which types of therapy Which kinds of therapists Which kinds of clients Which kinds of problems Produce which kinds of effects
Still not fully answered Demands answers |
|
|
Why is it difficult to design good psychotherapy? |
Many variables cannot be completely controlled
Difficult to measures the effects (Which measures are most important depends on type of therapist) |
|
|
Spontaneous Remission |
Symptoms reduction in the absence of any treatment |
|
|
Rate of spontaneous remission |
As high as success rates reported by psychotherapists |
|
|
What was Hans Eysenck's view on therapy effectiveness? |
Troubles people who received psychotherapy are no more likely to improve than those who go untreated
Evaluations were biased (based on therapists evaluation of client) b/c need to see themselves as successful |
|
|
Importance of cultural competence in a therapist |
Able to use knowledge of client's culture to achieve a broad understanding of the client
Attentive to how client may differ from cultural stereotype |
|
|
Result of Eysenck's conclusions on effectiveness of therapy |
Stimulated increase in research on psychotherapy
Development of more sophisticated methods for evaluating treatment outcome s |
|
|
Randomized Clinical Trials (RCTs) |
Individuals (with well-defined psychological disorders) randomly assigned to experimental group (gets treatment) or control group
See if group that got drug+therapy does better than group who received drug or therapy |
|
|
Meta-analysis |
Allows researchers to combine the results of many studies
Arrive at overall condition |
|
|
Effect size statistic |
Common measure of treatment effectiveness
Tells researchers what percentage of clients who received therapy had a more favourable outcome |
|
|
Result of meta-analysis in assessing effectiveness of therapy? |
Aver haw therapy client had a more favourable outcome that untreated cases
Therapy does have positive effect beyond spontaneous remission |
|
|
What is the "dodo bird verdict"? |
Finding of similar efficacy for widely differing therapies
Alice in wonderland dodo bird: "everybody has won. All must have prizes" |
|
|
Differential Effectiveness |
Specific therapies might be highly effective for treating some clinical disorders but not others |
|
|
Definition of success according to "Clinical Significance"? (Neil Jacobson) |
Success of therapy is defined that at the end of therapy, client's depression scores fall within range of non-depressed |
|
|
Definition of success according to meta-analysis? |
Greater positive change in treatment group than in control group of similarly depressed people |
|
|
Effectiveness of survey method in assessing psychotherapy effectiveness? |
More representative of real-life outcomes than data yielded by highly controlled clinical trials |
|
|
Can a therapist be trained to be more culturally sensitive? |
Yes
Exposure to ethnic training important in outcome
Clients rated therapist with greater empathy and expertise |
|
|
Factors affecting outcome of therapy |
Openness to therapy
Self-relatedness
Nature of the problem |
|
|
What does quality of therapeutic relationship account for? |
30% of variance in treatment outcomes
Without it clients get worse |
|
|
Dose-response Effect |
Relation between the amount of treatment received and the quality of the outcome |
|
|
Common Factors shared by diverse forms of therapy |
Faith in therapist
Plausible explanation for their problems
Protective setting
Opportunity to practice new behaviours
Increase optimism & self-efficacy |
|
|
Purpose of anti-anxiety drugs |
Reduce anxiety as much as possible without affecting alertness or concentration
Temporary reduction in anxiety may allow client to enter anxiety-arousing situation and learn to cope |
|
|
Use of anti-anxiety drugs |
15% Americans age 18-74 |
|
|
Drawback of anti-anxiety drugs |
Psychological and physical dependence from long-term use
Symptoms return when people stop taking them |
|
|
What is "buspirone"? |
Newer anti-anxiety drug that is slow-acting
Fewer fatiguing side effects
Less potential for abuse |
|
|
Effectiveness of buspirone in treatment of specific disorders? |
Generalized anxiety PTSD |
|
|
How does buspirone work physiologically? |
Slows down excitatory synaptic activity in NS
Enhances post-synaptic activity of GABA (inhibitory transmitter associated with emotional arousal) |
|
|
Why is anxiety more common in women in western cultures? |
Poverty
Lack of opportunity (sexism)
Multiple roles of mother
History of abuse/violence |
|
|
3 Major categories of Antidepressant Drugs |
Tricyclics
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAO)
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) |
|
|
How do tricyclics work? |
Increase activity of excitatory neurotransmitters
Prevent reuptake of excitatory transmitters into presynaptic neurons |
|
|
How do monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO) work? |
Increase activity of excitatory neurotransmitters
Reduce activity of monoamine oxidase (enzyme that breaks down neurotransmitters in synapse) |
|
|
Sides effects in tricyclics vs. MAO? |
MAO inhibitors have more severe side effects
Cause dangerous elevations in blood pressure |
|
|
How do selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) work? |
Increase activity of serotonin
Decreased side effects |
|
|
Benefits of SSRIs over tricyclics |
Milder side effects
Reduce depressive symptoms more rapidly
Reduce anxiety symptoms |
|
|
Risk of SSRIs |
Relation to suicide
Warnings placed on packaging
|
|
|
Clinical data relating to use of SSRIs |
Effectiveness lower
Adverse effects underestimated |
|
|
Effect of warning labels on antidepressants on suicide rates |
Increased since addition of warning labels
Highest in groups not on antidepressants |
|
|
Effects of combining drugs and psychotherapy |
Psychotherapy or combined treatments superior to drugs alone |
|
|
Goal of therapist in treating women |
Focus on what can be done to change womens' life circumstances
Rather than adapting to expectations |
|
|
Relapse rates psychotherapy vs drugs? |
Lower relapse rates for psychotherapy
Particularly if patients stop taking their medication
After successful drug therapy 1/2 patients relapse |
|
|
Primary effect of anti-psychotic drugs |
Decrease dopamine in schizophrenic patients |
|
|
Effect of anti-psychotic drugs on positive vs negative symptoms in schizophrenia? |
Dramatic effects on positive symptoms (e.g., hallucinations)
Little effect on negative symptoms (e.g., withdrawal) |
|
|
Prevalence of relapse in anti-psychotic drugs? |
Relapse very quickly
Patients recommended to take it indefinitely once they return to community |
|
|
What is "tardive dyslinesia"? |
Severe movement disorder
Uncontrollable and grotesque movements of the face and tongue
Patients arms and legs flail uncontrollably |
|
|
Which is more debilitating: tardive dyskinesia or psychotic symptoms? |
Tardive Dyskinesia
Irreversible once it develops |
|
|
Prevalence of Tardive Dyskinesia when on anti-psychotic drugs? |
Within 4 years
20% of young 30% of adults |
|
|
What is "clozapine"? |
Anti-psychotic drug
Reduce both positive and negative symptoms
Does not produce Tardive dyskinesia |
|
|
Drawback of clozapine? |
Produced fatal blood disease in 1-2% of patients
Requires expensive weekly blood tests |
|
|
Onset of blood disease in clozapine? |
Early in treatment
Young people most likely to be effected |
|
|
Research on therapy with women clients |
Not necessary to be treated by female therapists
More important for therapist to be sensitive to gender issues |
|
|
Antipsychotic drugs used in conjunction with psychotherapy? |
Drugs bring psychotic symptoms under control
Other approaches used to maintain initial improvement e.g., social skills training |
|
|
Electro-convulsion Therapy (ECT) |
Method to treat schizophrenic patients
Attach electrodes to their skulls and induce seizures administered to brain |
|
|
Drawbacks of ECT |
Cannot relieve anxiety
Questionable for treating schizophrenic patients |
|
|
Benefits of ECT |
Can treat severe depression especially if high risk of suicide
Effects are immediate |
|
|
ECT procedure |
Patient given sedative and muscle relaxant to prevent injuries from convulsions
Placed on padded mattress
Electrodes attached one side of head
Duration often < 1 second |
|
|
Criticism of ECT |
Possibility of depressive relapse is high (85%)
Concerns of safety
Permanent memory loss, brain damage |
|
|
What did the American Psychiatric Association conclude about ECT? |
Useful procedure for major depression in patients who cannot take medication |
|
|
Psychosurgery |
Surgical procedure that remove or destroy brain tissue to change disordered behaviour |
|
|
Effectiveness of Psychosurgery |
Cutting of nerve tracts connecting frontal lobes and subcortical areas calm psychotic and uncontrollably violent patients |
|
|
Lobotomy Operation |
Insert ice pick-like instrument through eye socket into brain
Wiggle it back and forth to sever the targeted nerve tracts |
|
|
Specificity Question |
Which types of therapy Which kinds of therapists Which kinds of clients Which kinds of problems Produce which kinds of effects
Still not fully answered Demands answers |
|
|
Cingulotomy procedure |
Cutting a small fibre bundle near corpus callosum that connects frontal lobes with limbic system |
|
|
Effectiveness of Cingulotomy |
Treat severe depression and OCD that failed with drug treatment |
|
|
Limitations of Cingulotomy |
Produce side effects including seizures |
|
|
Deinstitution |
Movement to transfer the primary focus of treatment from mental institution to the community |
|
|
Effect of Deinstitution |
80% decrease in number of institutionalized patients |
|
|
Benefits of community treatment |
Allows people to remain in their social and work environments
Treated with minimal disruption of their lives |
|
|
Drawbacks of Community treatment |
Requires availability of high-quality mental health care in community clinics |
|
|
Revolving door phenomenon |
Repeated hospitalizations
Patients release into communities ill-prepared to care for needs |
|
|
Situation-focused prevention |
Reducing or eliminating environmental causes of behaviour disorders
Enhancing situational facts that help prevent development of disorders
E.g., reduce stress of employment |
|
|
Competency-focused prevention |
Designed to increase personal resources and coping skills
E.g., strengthen resistance to stress |
|
|
Why is it difficult to design good psychotherapy? |
Many variables cannot be completely controlled
Difficult to measures the effects (Which measures are most important depends on type of therapist) |
|
|
Spontaneous Remission |
Symptoms reduction in the absence of any treatment |
|
|
Rate of spontaneous remission |
As high as success rates reported by psychotherapists |
|
|
What was Hans Eysenck's view on therapy effectiveness? |
Troubles people who received psychotherapy are no more likely to improve than those who go untreated
Evaluations were biased (based on therapists evaluation of client) b/c need to see themselves as successful |
|
|
Importance of cultural competence in a therapist |
Able to use knowledge of client's culture to achieve a broad understanding of the client
Attentive to how client may differ from cultural stereotype |
|
|
Result of Eysenck's conclusions on effectiveness of therapy |
Stimulated increase in research on psychotherapy
Development of more sophisticated methods for evaluating treatment outcome s |
|
|
Randomized Clinical Trials (RCTs) |
Individuals (with well-defined psychological disorders) randomly assigned to experimental group (gets treatment) or control group
See if group that got drug+therapy does better than group who received drug or therapy |
|
|
Meta-analysis |
Allows researchers to combine the results of many studies
Arrive at overall condition |
|
|
Effect size statistic |
Common measure of treatment effectiveness
Tells researchers what percentage of clients who received therapy had a more favourable outcome |
|
|
Result of meta-analysis in assessing effectiveness of therapy? |
Aver haw therapy client had a more favourable outcome that untreated cases
Therapy does have positive effect beyond spontaneous remission |
|
|
What is the "dodo bird verdict"? |
Finding of similar efficacy for widely differing therapies
Alice in wonderland dodo bird: "everybody has won. All must have prizes" |
|
|
Differential Effectiveness |
Specific therapies might be highly effective for treating some clinical disorders but not others |
|
|
Definition of success according to "Clinical Significance"? (Neil Jacobson) |
Success of therapy is defined that at the end of therapy, client's depression scores fall within range of non-depressed |
|
|
Definition of success according to meta-analysis? |
Greater positive change in treatment group than in control group of similarly depressed people |
|
|
Effectiveness of survey method in assessing psychotherapy effectiveness? |
More representative of real-life outcomes than data yielded by highly controlled clinical trials |
|
|
Can a therapist be trained to be more culturally sensitive? |
Yes
Exposure to ethnic training important in outcome
Clients rated therapist with greater empathy and expertise |
|
|
Factors affecting outcome of therapy |
Openness to therapy
Self-relatedness
Nature of the problem |
|
|
What does quality of therapeutic relationship account for? |
30% of variance in treatment outcomes
Without it clients get worse |
|
|
Dose-response Effect |
Relation between the amount of treatment received and the quality of the outcome |
|
|
Common Factors shared by diverse forms of therapy |
Faith in therapist
Plausible explanation for their problems
Protective setting
Opportunity to practice new behaviours
Increase optimism & self-efficacy |
|
|
Purpose of anti-anxiety drugs |
Reduce anxiety as much as possible without affecting alertness or concentration
Temporary reduction in anxiety may allow client to enter anxiety-arousing situation and learn to cope |
|
|
Use of anti-anxiety drugs |
15% Americans age 18-74 |
|
|
Drawback of anti-anxiety drugs |
Psychological and physical dependence from long-term use
Symptoms return when people stop taking them |
|
|
What is "buspirone"? |
Newer anti-anxiety drug that is slow-acting
Fewer fatiguing side effects
Less potential for abuse |
|
|
Effectiveness of buspirone in treatment of specific disorders? |
Generalized anxiety PTSD |
|
|
How does buspirone work physiologically? |
Slows down excitatory synaptic activity in NS
Enhances post-synaptic activity of GABA (inhibitory transmitter associated with emotional arousal) |
|
|
Why is anxiety more common in women in western cultures? |
Poverty
Lack of opportunity (sexism)
Multiple roles of mother
History of abuse/violence |
|
|
3 Major categories of Antidepressant Drugs |
Tricyclics
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAO)
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) |
|
|
How do tricyclics work? |
Increase activity of excitatory neurotransmitters
Prevent reuptake of excitatory transmitters into presynaptic neurons |
|
|
How do monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO) work? |
Increase activity of excitatory neurotransmitters
Reduce activity of monoamine oxidase (enzyme that breaks down neurotransmitters in synapse) |
|
|
Sides effects in tricyclics vs. MAO? |
MAO inhibitors have more severe side effects
Cause dangerous elevations in blood pressure |
|
|
How do selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) work? |
Increase activity of serotonin
Decreased side effects |
|
|
Benefits of SSRIs over tricyclics |
Milder side effects
Reduce depressive symptoms more rapidly
Reduce anxiety symptoms |
|
|
Risk of SSRIs |
Relation to suicide
Warnings placed on packaging
|
|
|
Clinical data relating to use of SSRIs |
Effectiveness lower
Adverse effects underestimated |
|
|
Effect of warning labels on antidepressants on suicide rates |
Increased since addition of warning labels
Highest in groups not on antidepressants |
|
|
Effects of combining drugs and psychotherapy |
Psychotherapy or combined treatments superior to drugs alone |
|
|
Goal of therapist in treating women |
Focus on what can be done to change womens' life circumstances
Rather than adapting to expectations |
|
|
Relapse rates psychotherapy vs drugs? |
Lower relapse rates for psychotherapy
Particularly if patients stop taking their medication
After successful drug therapy 1/2 patients relapse |
|
|
Primary effect of anti-psychotic drugs |
Decrease dopamine in schizophrenic patients |
|
|
Effect of anti-psychotic drugs on positive vs negative symptoms in schizophrenia? |
Dramatic effects on positive symptoms (e.g., hallucinations)
Little effect on negative symptoms (e.g., withdrawal) |
|
|
Prevalence of relapse in anti-psychotic drugs? |
Relapse very quickly
Patients recommended to take it indefinitely once they return to community |
|
|
What is "tardive dyslinesia"? |
Severe movement disorder
Uncontrollable and grotesque movements of the face and tongue
Patients arms and legs flail uncontrollably |
|
|
Which is more debilitating: tardive dyskinesia or psychotic symptoms? |
Tardive Dyskinesia
Irreversible once it develops |
|
|
Prevalence of Tardive Dyskinesia when on anti-psychotic drugs? |
Within 4 years
20% of young 30% of adults |
|
|
What is "clozapine"? |
Anti-psychotic drug
Reduce both positive and negative symptoms
Does not produce Tardive dyskinesia |
|
|
Drawback of clozapine? |
Produced fatal blood disease in 1-2% of patients
Requires expensive weekly blood tests |
|
|
Onset of blood disease in clozapine? |
Early in treatment
Young people most likely to be effected |
|
|
Research on therapy with women clients |
Not necessary to be treated by female therapists
More important for therapist to be sensitive to gender issues |
|
|
Antipsychotic drugs used in conjunction with psychotherapy? |
Drugs bring psychotic symptoms under control
Other approaches used to maintain initial improvement e.g., social skills training |
|
|
Electro-convulsion Therapy (ECT) |
Method to treat schizophrenic patients
Attach electrodes to their skulls and induce seizures administered to brain |
|
|
Drawbacks of ECT |
Cannot relieve anxiety
Questionable for treating schizophrenic patients |
|
|
Benefits of ECT |
Can treat severe depression especially if high risk of suicide
Effects are immediate |
|
|
ECT procedure |
Patient given sedative and muscle relaxant to prevent injuries from convulsions
Placed on padded mattress
Electrodes attached one side of head
Duration often < 1 second |
|
|
Criticism of ECT |
Possibility of depressive relapse is high (85%)
Concerns of safety
Permanent memory loss, brain damage |
|
|
What did the American Psychiatric Association conclude about ECT? |
Useful procedure for major depression in patients who cannot take medication |
|
|
Psychosurgery |
Surgical procedure that remove or destroy brain tissue to change disordered behaviour |
|
|
Effectiveness of Psychosurgery |
Cutting of nerve tracts connecting frontal lobes and subcortical areas calm psychotic and uncontrollably violent patients |
|
|
Lobotomy Operation |
Insert ice pick-like instrument through eye socket into brain
Wiggle it back and forth to sever the targeted nerve tracts |
|
|
Specificity Question |
Which types of therapy Which kinds of therapists Which kinds of clients Which kinds of problems Produce which kinds of effects
Still not fully answered Demands answers |
|
|
Cingulotomy procedure |
Cutting a small fibre bundle near corpus callosum that connects frontal lobes with limbic system |
|
|
Effectiveness of Cingulotomy |
Treat severe depression and OCD that failed with drug treatment |
|
|
Limitations of Cingulotomy |
Produce side effects including seizures |
|
|
Deinstitution |
Movement to transfer the primary focus of treatment from mental institution to the community |
|
|
Effect of Deinstitution |
80% decrease in number of institutionalized patients |
|
|
Benefits of community treatment |
Allows people to remain in their social and work environments
Treated with minimal disruption of their lives |
|
|
Drawbacks of Community treatment |
Requires availability of high-quality mental health care in community clinics |
|
|
Revolving door phenomenon |
Repeated hospitalizations
Patients release into communities ill-prepared to care for needs |
|
|
Situation-focused prevention |
Reducing or eliminating environmental causes of behaviour disorders
Enhancing situational facts that help prevent development of disorders
E.g., reduce stress of employment |
|
|
Competency-focused prevention |
Designed to increase personal resources and coping skills
E.g., strengthen resistance to stress |
|
|
Why is it difficult to design good psychotherapy? |
Many variables cannot be completely controlled
Difficult to measures the effects (Which measures are most important depends on type of therapist) |
|
|
Spontaneous Remission |
Symptoms reduction in the absence of any treatment |
|
|
Rate of spontaneous remission |
As high as success rates reported by psychotherapists |
|
|
What was Hans Eysenck's view on therapy effectiveness? |
Troubles people who received psychotherapy are no more likely to improve than those who go untreated
Evaluations were biased (based on therapists evaluation of client) b/c need to see themselves as successful |

