![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Stoichiometry |
The study of chemical quantities consumed or produced in a chemical reaction |
|
|
Steps to Solving a Stoichiometry Problem |
Step 1: Balance the equation. This equation is already balanced Step 2: Find the moles of the reactant. Step 3: Use the mole ratio between the reactant and product to find the moles of product made. Step 4: Convert moles of product to the desired unit. |
|
|
Mole to Mole Calculations |

Mole to mole ratio comes from balanced chemical equations |
|

|
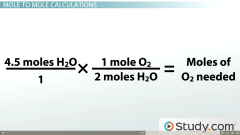
= 2.25 moles of O2 |
|
|
Rules for Mole to Mole Calculations |

|
|

Mole Ratio |

As the ratio of moles of one substance to the moles of another substance in a balanced equation |
|
|
Moles to Mass Caculations |

|
|
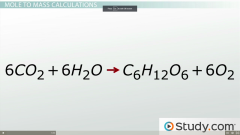
Moles to Mass: How many grams of glucose are produced when 3 moles of water react with carbon dioxide. |

= 90g or C6H12O6 |
|
|
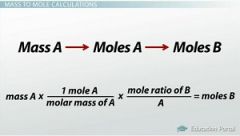
Mass To Moles |
|
|

Mass to Moles: If 8g of SO2 reacts, how many moles of CS2 are formed? |
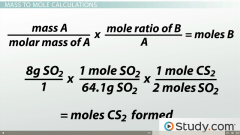
= 0.06 moles CS2 |
|
|
Mass to Mass |

|
|
|
Mass to Mass: How many grams of NH4NO3 are needed to produce 33g of N2O in the following reaction: NH4NO3 --> N2O + 2H2O? |

|
|
|
Molar Volume |
22.4L = 1 mol or 22.4L / 1 mol |
|
|
How many moles of nitrogen are present in a 2 L sample held at STP? |
2L X 1 mol / 22.4L = 0.089 mols |
|
|
We have approximately 68.02 g of liquid hydrogen peroxide. How many liters of oxygen gas will be produced in this reaction if carried out at STP? |
Step 1: 2H2O2 --> 2H2O(gas) + 02(gas) Step 2: 68.02g 2H2O2 / 1 X 1 mole / 34.01g = 2 moles Step 3: 2 moles 2H2O2 X 1 mol O2 / 2H2O2 = 1 mol O2 Step 4: 1 mol O2 X 22.4L / 1 mol = 22.4L of O2 |
|
|
Molarity (M or mol/L) |
Is the ratio of moles of solute to liters of solution. Molarity is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the liters of solution. Molarity = moles solute /Liters solution This give you the concentration of the solution Represented by = # M |

