![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the special senses?
|
Smell, taste, sight, and hearing
|
|
|
What are the accessory structures of the eye?
|
Eyebrows, eyelids, conjuctiva, lacrimal apparatus, and extrinsic eye muscles
|
|
|
Eyebrows
|
Shade the eyes and prevent sweat from trickling into them
|
|
|
Eyelid
|
Protect the eye
|
|
|
Palpebral fissure
|
the eyelid slit
|
|
|
Medial and lateral commissures
|
Corners of the eye
|
|
|
Lacrimal carnucle
|
In medial commisure and contains sebaceous and sweat glands and produces the whitish, oily secretion
|
|
|
Eyelashes
|
Richly innervated so anything slight will cause us to blink to protect eyes
|
|
|
Tarsal Glands
|
A modified sebaceous gland that produces an oily solution that lubricates the eye and prevents the eyelids from sticking together
|
|
|
Conjuctiva
|
Thin transparent mucous membrane. Palpebral is under eyelid and bulbar is covers the whites of the eyes
|
|
|
Lacrimal Apparatus
|
Consists of the lacrimal gland and the ducts that drain excess lacrimal secretions into the nasal cavity
|
|
|
What is the path of tears?
|
Tears come from the lacrimal gland, and blinking spreads the tear across the eye. It enter two little holes in the medial commisure called the lacrimal puncta, through the lacrimal canaliculi, and into the lacrimal sac. This drains to the nasolacrimal duct which empties into the nasal cavity
|
|
|
Rectus eye muscles
|
Move eyeball by their names, inferior, superior, lateral or medial rectus
|
|
|
Oblique eye muscles
|
Move eyeball in a vertical plane when the eyeball is already turned medially by the rectus muscles
|
|
|
Lateral rectus
|
Moves eye laterally
|
|
|
Medial rectus
|
Moves eye medially
|
|
|
Superior rectus
|
Elevates eye and turns it medially
|
|
|
Inferior rectus
|
Depresses eye and turns it medially
|
|
|
Inferior oblique
|
Elevates eye and turns it laterally
|
|
|
Superior oblique
|
Depresses eye and turns it laterally
|
|
|
Fibrous layer of eye
|
Outermost layer of eye consisting of the sclera and cornea
|
|
|
Sclera
|
Glistening white part. Protects and shapes the eye ball and provides a sturdy anchoring for the extrinsic eye muscles
|
|
|
Cornea
|
Crystal-clear layer that lets light through
|
|
|
Vascular layer of eye
|
Pigmented layer containing the choroid, ciliary body, and iris
|
|
|
Choroid
|
Dark brown membrane that has blood vessels and provides nutrients for the eye
|
|
|
Ciliary body
|
Anterior portion of the choroid that contains ciliary muscles and ciliary zonules that control the shape of the lens
|
|
|
Iris
|
Colored portion of eye
|
|
|
Pupil
|
Allows light to enter
|
|
|
Inner layer of eye
|
Consists of the retina which is two layers. Pigmented and neural layer.
|
|
|
Neurons of neural layer
|
Photoreceptors, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells
|
|
|
Optic disc
|
Blind spot because there are no photoreceptors
|
|
|
Rods
|
More abundant and provide dim-light and peripheral vision
|
|
|
Cones
|
Operate in bright light and provide high-acuity color vision
|
|
|
Fovea centralis and Macula lutea
|
The retinal structures abutting the vitreous humor are displaced to the sides. These region have a lot of cones and since it has less layers adds to accuity
|
|
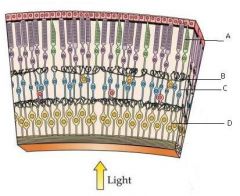
What are the labeled structures?
|
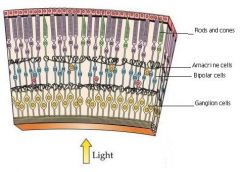
Neural layer of retina
|
|
|
Posterior segment is filled with _________?
|
Vitreous humor
|
|
|
Vitreous humor
|
Transmits light, supports the posterior surface of the lens and holds the neural retina firmly against the pigmented layer, and contributes to intraocular pressure
|
|
|
Anterior chamber
|
between cornea and iris
|
|
|
Posterior chamber
|
between the iris and the lens
|
|
|
Anterior segment is filled with _________?
|
Aqueous humor which is similar to blood plasma
|
|
|
Scleral venous sinus
|
Drains aqueous humor
|
|
|
Lens
|
Biconvex, transparent, flexible structure that changes shape to focus light
|
|
|
Percentage of sensory receptors in eyes?
|
70%
|
|
|
Tarsal Plate
|
Dense connective tissue that anchor obicular oculi and other muscles
|
|
|
Muscles of pupil
|
Sphincter pupillae muscle - smaller
Dilator pupillae muscle - larger |
|
|
Visible light
|
380 nm - 740 nm
|
|
|
How does lens shape itself for far and short vision?
|
Buldges for close vision and flattens for distant vision
|
|
|
Emmetropic eye
|
no correction needed
|
|
|
Myopic eye
|
too long of an eye so focal point doesnt reach so nearsighted
|
|
|
Hyperopic eye
|
Eyeball is to short so farsighted
|

