![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explain the significance of the following people's work: Ewin Chargaff, Watson and Crick (and Franklin)
|
Chargaff found equal amounts of adenine and thymine, and of cytosine and guanine, in DNA.
The Watson - Crick: DNA consists of two antiparallel polynucleotide strands wrapped about a common helical axis. Strands held together by hydrogen bonds forming specific base pairs. |
|
|
What are some of the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic replication?
|
Prokaryotic replication starts at a single origin; the E. coli origin has AT-rich sequences that are easily opened. The chromosome and its origin form a replicon.
Eukaryotic replication requires multiple origins; the sheer size and organization of eukaryotic chromosomes requires multiple origins of replication to be able to replicate DNA in the time available in S phase. |
|
|
Draw or explain (or both) the structure of DNA, please be sure to include the structure of a
nucleotide, the direction of each strand and the base pairing rules. What is the function of this molecule? Where do we see it in the human body? |
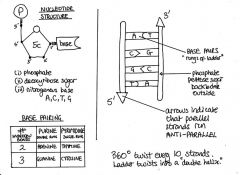
Function of DNA: guides the cell (along with RNA) in making new proteins that determine all of our biological traits
gets passed (copied) from one generation to the next. We see it in every cell. |
|
|
Draw and explain DNA replication starting at a replication fork. Be sure to label the
actions of all of the enzymes as well as include at least 2 Okazaki fragments. Do not forget to label the directions of the strands! When does DNA replication occur during the cell cycle? |
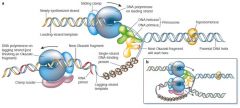
Replication happen at mid-interphase. The DNA replicates during the S phase of interphase, after G1 and before G2, the two growth phases. Throughout interphase, the DNA is extended, and free nucleotides have access to the strands.
|
|
|
What is the significance of telomerase? What happens if a cell has no active telomerase?
What happens if a cell has too much telomerase? |
It contains an internal RNA that the enzyme uses as a template to extend the DNA of the chromosome end.
If a cell has no active telomerase a gradual shortening of the ends of chromosomes occurs. (aging and cancer) |
|
|
List and explain some causes of DNA damage? Explain any mechanisms to repair this damage
|
Radiation, UV light and X-rays can damage DNA (mutagens).
DNA repair restores damaged DNA, without repair mechanisms, cells would accumulate mutations until inviability occurred. |

