![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Solution |
Homogenous mix of solvent and one or more solute. |
|
|
|
Unsaturated Solution |

Solution that contains less solute than the solvent. Has the capacity to dissolve at a specific temperature. |
|
|
|
Saturated Solution |

One that contains the max amount of solute that will dissolve in solvent at a specific temperature. |
|
|
|
Super Saturated Solution |

Contain more dissolved solute than is present in a saturated Solution and are generally unstable. |
|
|
|
Solvation |
Occurs when solute molecules are separated from one another and surrounded by solvent molecules. |
Depends on 3 type of reactions. 1.) Solute-solute interactions 2.) Solvent-Solvent interactions 3.) Solute-solvent interactions |
|
|
Ion-Dipole |

The charge of an ion is attracted to the partial charge on a polar molecule. (NaCl or Ki in water) |
Intermolecular interaction |
|
|
Dipole-Induced Dipole |
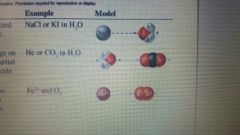
The partial charge on a polar molecule induces a temporary partial charge on a neighboring Nonpolar molecule or atom. (He or CO2 in water) |
Intermolecular Force |
|
|
Ion-Induced Dipole |

The charge of an ion induces a temporary partial charge on a neighboring Nonpolar molecule or atom. (Fe II and O2.) |
Intermolecular Force |
|
|
Entropy |
A measure of how the dispersed or spread out its energy is. |
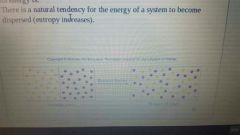
There is a natural tendency for the energy of the system to become dispersed. |
|
|
Miscible |

When 2 liquids are completely soluble in each other in all proportions. |

|
|
|
Molarity |
The amount of solute relative to the volume of a solution or to the amount of solvent in a solution. (called concentration). |
Molarity= Moles of solute/Liters of solution. |
|
|
Mole Fraction |
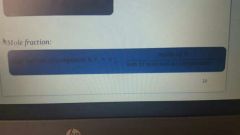
Moles of A/Sum of moles of all components. |
Concentration unit. |
|
|
Molality |
Moles of Solute/Kg of solvent |

Concentration Unit |
|
|
Percent by Mass |
Independent of temperature. |

|
|
|
Solubility |

Temperature affects solubility of most substances. |
|
|
|
Henry's Law |

States that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is proportional to the pressure of the gas over the solution. |
|
|
|
Colligative Properties |
Properties that depend on the number of solute particles in solution. Do not depend on the nature of the solute particles. |

|
|
|
Raoults Law |

states that the partial pressure of a solvent over solution is given by the vapor pressure of the pure solvent X the mole fraction of the solvent in the solution. |
Ideal solutions obey Raoults Law |
|
|
Volatile |
The vapor pressure of the solution is the sum of the individual partial pressures. |
|
|
|
Boiling Point Elevation |

Solution boils At a higher temperature than the pure solvent. |
Colligative Property |
|
|
Freezing Point Depression |
Solution freezes at a lower temperature than the pure solvent. |
Colligative Property |
|
|
Osmosis |

Selective passage of solvent molecules through a porous membrane from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated one. |
|
|
|
Osmotic Pressure |

The pressure required to stop osmosis. |
P=MRT |
|
|
Van's Hoff Factor (i) |
Ion particles dissolved in a solution. 1 is for nonelectrolytes. 2 is for strong electrolytes 3 is for strong electrolytes. |
Usually smaller than predicted due to formation of ion pairs. |
|
|
Ion pair |

made up of one or more cations and one or more anions held together by electrostatic forces. |

|
|
|
Percent Dissasociation |

The percentage of dissolved molecules that separate into ions in a solution and this can be found using colligative properties. |

Strong Electrolytes should have complete 100% dissociation. But experimentally determined is not the case. More complete at lower concentration. |
|
|
Colloid |

A Dispersion of particles of one substance throughout another substance. Colloid particles are much larger than the normal solute molecules. |

|
|
|
Emulsification |
The process of stabilizing a colloid that would otherwise not stay dispersed. |
|

