![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How is white matter organized in the spinal cord? |
Ascending and descending tracts, grouping into columns |
|
|
Spinal cord is protected by: |
Vertebral column, spinal meninges, cerebro spinal fluid, and denticulate ligaments |
|
|
Spinal meninges |
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater |
|
|
What does the enlargement of the spinal cord in the lumbar segments of the spinal cord control? |
The lower limbs |
|
|
What does the enlargement of the spinal cord in the cervical segments of the spinal cord control? |
The upper limbs |
|
|
A strand of fibrous tissue that provides longitudinal support as a component of the coccygeal ligament |
Filum terminale
|
|
|
The tapered inferior portion of the spinal cord is called |
conus medullaris |
|
|
Spinal cord is divided into how many segments? |
31 |
|
|
When does elongation of the spinal cord cease? |
4 years old |
|
|
Why is the spinal cord shorter in relation to the spine? |
Elongation of the spine stops at 4, but vertebral column continues to grow. |
|
|
Outermost meninge of the spinal cord |
Dura mater |
|
|
Where are the blood vessels located that supply the spinal cord |
Pia mater |
|
|
Where is the pia mater bound to? |
Tightly bound to the surface of the neural tissue |
|
|
Ligaments that are thickenings of the pia mater |
Denticulate ligaments |
|
|
Subdural space separates what? |
Dura mater and the arachnoid mater |
|
|
The space of the spinal cord that contains cerebro-spinal fluid |
subarachnoid space |
|
|
Epidural space |
space between the dura mater and the wall of vertebral canal |
|
|
Space that contains connective tissue and blood vessels |
Epidural space |
|
|
There is epidural space in the meninges of the.... |
Spinal cord |
|
|
There is no epidural space in the meninges of the... |
Brain |
|
|
Epidural block primarily provides what |
Sensory anasthesia as a method of pain control during labor and delivery |
|
|
Epidural block affects what? |
Spinal nerves in the immediate area of injection |
|
|
Horns of the spinal cord |
Projections of gray matter toward outer surface of the spinal cord |
|
|
Anterior gray horn contains what |
Nerve cell bodies of motor neurons |
|
|
Polio virus affects what area of the spinal cord? |
Anterior horn in the lumbar region |
|
|
Dorsal root ganglia contains what |
cell bodies of sensory neuron |
|
|
Posterior gray horn of the spinal cord contains what? |
Nerve cell bodies of interneuron and terminal axon of the sensory neuron |
|
|
Gray commisures |
Contain axons from one side of the spinal cord to the other within gray matter
|
|
|
What structures partially divide the spinal cord into left and right sides? |
anterior and posterior median fissure sulcus |
|
|
White matter of spinal cord contains what? |
Bundles of axons that share origins, destination, and function |
|
|
White matter of the spinal cord is dominated by |
Myelinated axons |
|
|
Epineurium |
Outermost connective tissue covering of spinal nerve |
|
|
Perineurium |
Middle layer of spinal nerve |
|
|
Endoneurium |
Innermost layer of spinal nerve |
|
|
Spinal nerves are part of CNS/PNS? |
PNS |
|
|
What do spinal nerves in the CNS do? |
Sensors and effectors in all parts of the body |
|
|
How are spinal nerves named? |
According to the region of the cord from which they emerge |
|
|
Spinal nerves are "mixed" nerves which means... |
They are formed by the union of the dorsal and ventral root. |
|
|
Shingles infect what? How does the rash spread? |
Dorsal root ganglia. Causing a painful rash whose distributioncorresponds to that of the affected sensory nerves. |
|
|
Dorsal root contains what kind of neurons? |
Axons of sensory neurons |
|
|
Ventral root contains what part of neurons? |
Axons of motor neurons |
|
|
Thejoining of the VENTRAL RAMIof adjacent spinal nerves is called |
Nerve plexus |
|
|
Ventral rami of of nerves T2-T12 do not form what? |
Plexus |
|
|
Nerves T2-T12 are called what? |
Intercostal nerves |
|
|
Intercostal nerves connect where? |
Directly to the structures they supply |
|
|
Four major nerve plexus? |
Cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral |
|
|
Cervical plexus |
Ventral rami of spinal nerves C1-C5 |
|
|
Brachial plexus location |
Ventral rami of spinal nerves C5-T1 |
|
|
Lumbar plexus location |
Ventral rami of spinal nerves L1-L4 |
|
|
Sacral Plexus |
Ventral rami of spinal nerves L4-S4 |
|
|
The brachial plexus is organized into |
Trunks and cords |
|
|
Trunks in the brachial plexus is a fusion of what |
Several roots |
|
|
Ulnar, median, and radial nerves are found in what plexus? |
Brachial plexus |
|
|
Injury to the ulnar nerve may result in a condition called |
Claw hand |
|
|
Injury to the radial nerve may result in a condition called |
Wrist drop
|
|
|
What nerve is affected in carpal tunnel? |
median nerve |
|
|
Femoral nerve is found in what plexus? |
Lumbar plexus |
|
|
Longest nerve in the body |
Sciatic nerve |
|
|
What plexus is the sciatic nerve found? |
Sacral plexus |
|
|
Where does the sciatic nerve divide? |
As it approaches the knee |
|
|
The names of the two branches of the sciatic nerve? |
Tibial and fibular nerves |
|
|
Tibial nerve controls what muscles |
Hamstring muscles and muscles of the superficial and deep posterior compartment of the leg |
|
|
Fibular nerve controls what muscles |
Tibialis anterior and muscles that dorsiflex the foot |
|
|
Obturator nerves location |
Lumbar plexus |
|
|
Obturator nerves control what muscles? |
Most hip adductors and gracilis |
|
|
Largest nerve of the lumbar plexus |
femoral nerve |
|
|
Femoral nerve controls what muscles? |
Quadriceps and sartorius |
|
|
Injury to femoral nerve results in |
An inability to extend the leg andloss of sensation in the skin over anteromedial aspect of the thigh |
|
|
Phrenic nerve is found where? |
Cervical plexus |
|
|
Phrenic nerve controls what? |
Diaphragm muscle |
|
|
What happens when the phrenic nerve is damaged? |
breathing stops |
|
|
Dermatome |
specificregion of the SKIN that is innervated by a specific spinal nerve |
|
|
Reflexes can be classified according to... |
-Development of the reflex -the site of information processing -the nature of the motor response -the complexity of neural circuit involved |
|
|
Somatic reflexes involve what kinds of muscles? |
skeletal |
|
|
Visceral reflexes involve what kinds of muscles? |
Smooth |
|
|
Components of a reflex arc |
a) Sensoryreceptor b) Sensoryneuron c) Integrating center d) Motorneuron e) Effector |
|
|
Integration center |
a part of a reflex arc that receives sensoryinformation and decides how to respond to a change in the body’s condition |
|
|
a part of a reflex arc that receives sensoryinformation and decides how to respond to a change in the body’s condition |
Integration center |
|
|
Effector |
part of a nervous reflex arc that is usually a muscle or gland |
|
|
Where does a sensory neuron synapse go in a monosynaptic reflex |
directly on a motor neuron |
|
|
Where does a sensory neuron synapse go to in a polysynaptic reflex |
An interneuron (one or more) --> motor neuron |
|
|
Polysynaptic reflex is intersegmental in distribution. What does this mean?
|
Interneurons of severalsegments of the spinal cord are activated from one sensory neuron |
|
|
Polysynaptic reflex involves reciprocal innervation. What does this mean? |
contraction of one muscleand relaxation of its antagonists |
|
|
Receptor in stretch reflex (EPSP) |
Muscle spindle |
|
|
Function of stretch reflex (EPSP) |
Prevents a muscle from overstretching
|
|
|
Characteristics of stretch reflex (EPSP) |
1.) Monosynaptic 2.) Ipsilateral 3.) Regulates posture 4.) Activates when muscle elongates 5.) Involves reciprocal innervation |
|
|
Reciprical innervation |
contractionof the intended prime muscle, inhibition of the antagonists reciprocal innervation is process that interneurons inthe spinal cord prevent muscle antagonists from interfering with an intendedmovement |
|
|
A somatic spinal reflex that involves one effector muscle being stimulated while the opposing muscle is inhibited is called |
reciprocal innervation |
|
|
In response to a muscle being stretched a musclespindle initiates a |
Somatic spinal reflex |
|
|
In response to a muscle being stretched a musclespindle initiates a somatic spinal reflex (stretch reflex), that causes: ____ of the agonist muscleand ____ of the antagonist muscle. |
Contraction. Relaxation. |
|
|
In response to a tendon being stretched excessively, atendon organ initiates a somatic spinal reflex (tendon reflex), that causes: ____ of the antagonist muscleand _____ of the agonist muscle |
Contraction. Relaxation. |
|
|
Flexor reflex (EPSP) does what regarding tension? |
Prevents a muscle from exerting too much tension |
|
|
Flexor reflex characteristics
|
1.) polysynaptic 2.) ipsilateral 3.) reciprocal inhiibition 4.) Moves limbs away from a painfaul stimulus |
|
|
Reflex that moves limbs away from a painful stimulus |
Flexor reflex |
|
|
Crossed extensor reflex (EPSP) characteristics |
1.) Polysynaptic 2.) Contralateral 3.) Reciprocal innervation 4.) Complementsa withdrawal reflex by making compensatory adjustment on the opposite sideof the body receiving stimulus 5.) Reciprocal inhibition |
|
|
Tendon reflex (IPSP) characteristics |
a) Prevent tearing of muscle and tendons during contraction b) Polysynaptic c) Ipsilateral d) Reciprocal inhibition e) Sensory receptors are called Golgi tendon organ |
|
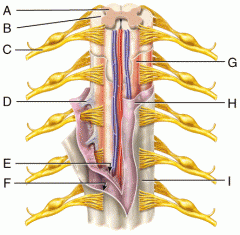
A |
Gray Matter |
|
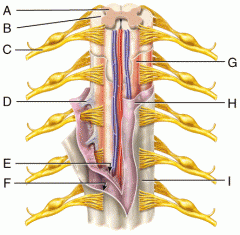
B |
White Matter |
|
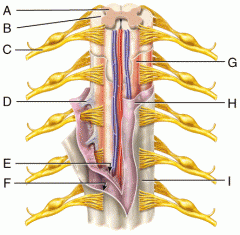
C |
Spinal Nerve |
|
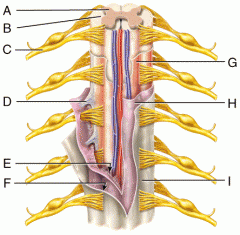
D |
Denticulate Ligament |
|
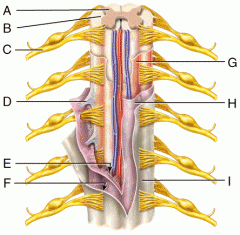
E |
Subarachnoid Space |
|
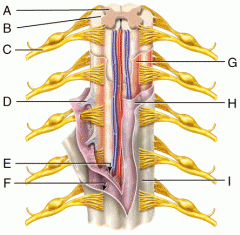
F |
Subdural Space |
|
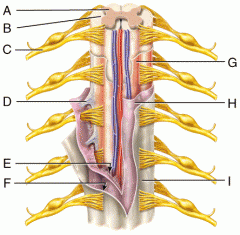
G |
Pia Mater |
|
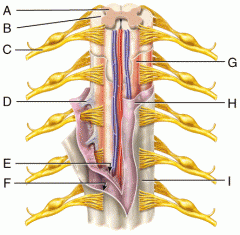
H |
Arachnoid Mater |
|
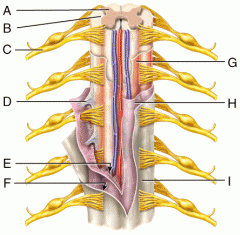
I |
Dura Mater |

