![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gravitational force between two objects is determined by their _____ and the ____ between them. |
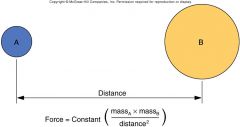
masses and distance |
|
|
Gravitational forces vary slightly at different locations on Earth's surface due to the shape of the Earth. Gravity is stronger at the ______ and weaker at the ______. |
Poles Equator |
|
|
True or False. Differences in density of materials in Earth's interior produces small differences in local gravity field. |
True |
|
|
If mass above the compensation depth is uniform (isostatically balanced) with no excess or deficiency in mass, thus ____ gravity anomalies. |
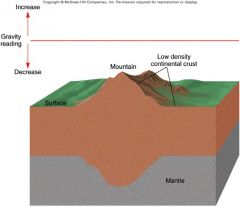
no |
|
|
If mass above the compensation depth is not uniform and there is an excess mass of dense mantle below the mountain (no crustal root) then it will generate _______ gravity and thus, a _____ gravity anomaly. |
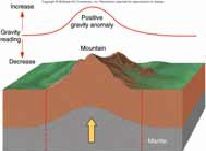
increased positive
|
|
|
If mass above the compensation depth is not uniform and there is a deficiency of mass below low area (too much crust) generates _____ gravity and a ______ gravity anomaly. |
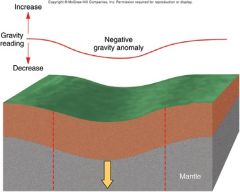
decreased negative |
|
|
Earth's magnetic field is generated in the Earth's _______ as it spins and convects and produces _______. |
liquid outer core electrical currents |
|
|
Why does Earth's magnetic field change over time? |
The rotation of the outer core. |
|
|
The Earth's magnetic field inclination is _______ at the poles and ______ near the equator. |
Steeper Horizonal |
|
|
What is "normal" polarity? |
North is north and South is South |
|
|
What is "reversed" polarity? |
South is North and North is South |
|
|
Rocks and minerals that cool through Curie temperature and stay below that temperature record magnetic field at ________. |
The time of their cooling |
|
|
the study of ancient magnetic fields in rocks and the reconstruction of past fields. |
paleomagnetism |
|
|
Magnetic alignment preserve din magnetite records ______ of Earth's magnetic field. |
orientation |
|
|
Are the lengths of magnetic periods uniform? |
No. This likely relates to turbulent flow of outer core. |
|
|
Magnetic material below the surface "add" magnetism and creates a _____ magnetic anomaly. |
positive |
|
|
What are some examples of magnetic rocks? |
iron ore, gabbro, and granite |
|
|
Removal of magnetic material from near the surface causes a _____ magnetic anomaly. (Ex. normal faulting) |
negative |
|
|
Earth's magnetic field is a self-generating and self-reversing dynamo in the _______. |
Outer Core |
|
|
What is the result of convection in the mantle? |
Warm rock rises as narrow pipe-like plumes. |
|
|
Which layer of Earth has the smallest volume? |
The Crust |
|
|
Who discovered the crust-mantle seismic discontinuity? In what year? |
Andrija Mohorovicic in 1909 |
|
|
What is the best evidence of Earth having a solidified inner core? |
P waves travel faster in the inner core than in the outer core. |
|
|
Which layer of Earth does not transmit S waves? |
Outer core |
|
|
The boundary between the crust and the mantle was discovered in 1909 using ______ and now bears he name ______ after Mohorovicic. |
Seismic waves Moho |
|
|
At the base of the crust, the velocity of P waves ________ abruptly, so Mohorovicic determined that the waves were traveling through two different layers composed of different materials. |
increases |
|
|
Who calculated the 2900 km to the core boundary depth? When? Is this value still accepted today? |
Beno Gutenberg 1914 Yes |
|
|
Who published the book "On the Origin of Continents and Oceans"? What year? |
Alfred Wegener, 1915 |
|
|
Who developed the Richter magnitude scale? When? |
Charles F. Richter, 1935 |
|
|
Which layer of the Earth includes the zone called the "asthenosphere" (the "weak sphere")? |
The Upper Mantle |
|
|
What does the upper mantle include? (Which "spheres") |
lower part of the rigid lithosphere and the weak asthenosphere. |
|
|
How much volume of the Earth is the mantle? |
82% |
|
|
How much volume of the Earth is the core? (outer + inner) |
16% |
|
|
Where does Earth's magnetic field originate? |
the outer core |
|
|
Which rock type is probably the closest in chemical composition to the upper mantle? |
Peridotite. It is an ultramafic rock composed mostly of the minerals olivine and pyroxene and is richer in iron and magnesium than rocks found in either the continental or oceanic crust. |
|
|
Which layer of Earth is very dense and solid and consists most likely of an iron-rich alloy? |
The inner core |
|
|
What structure in Earth is thought to be caused by a change in the mineral structure of olivine? |
The 660-km-depth discontinuity or transition zone |
|
|
At high latitudes, the force lines intersect Earth's surface at _____ angles. |
steep |
|
|
How was the diameter of Earth's core and the nature of the outer core discovered? |
Through analysis of he P-wave and S-wave shadow zones. |
|
|
What causes the P-wave shadow zone? |
Refraction of P waves crossing the mantle-outer core boundary. |
|
|
What causes Earth's magnetic field? |
Weak electrical currents associated with fluid motions of molten iron in the outer core. |
|
|
Which of Earth's layers is marked at its top by the Mohorovicic discontinuity? |
the Mantle |
|
|
Which sphere would be characterized as a zone of softened peridotite in the upper mantle. |
the asthenosphere |
|
|
What is the upper layer of the lithosphere called? |
Crust |
|
|
Which rocks are the closest to the average chemical composition of the oceanic crust? |
Basalt and gabbro |
|
|
______ are probably major components of Earth's inner core. |
Crystalline iron and nickel |
|
|
Which materials will transmit seismic waves most rapidly? (more or less rigid materials?) |
More rigid |
|
|
A seismic wave may change direction, without bouncing back, when crossing the boundary between two rock types. This phenomenon is called ________. |
Refraction |
|
|
Which is Earth's weakest layer? |
Asthenosphere |
|
|
Where do the rocks of the ocean crust form? |
At mid-oceanic ridges |
|
|
The seismic boundary between the crust and the mantle is referred to as the __________. |
Mohorovicic discontinuity |
|
|
The greatest change in the velocity of P waves occurs at the __________ boundary. |
mantle–outer core |
|
|
The source of heat that produces deep mantle plumes is believed to be located at the __________. |
outer core–mantle boundary or the "D" layer. |
|
|
Approximately how deep is Earth's core–mantle boundary? |
2900 kilometers |
|
|
How does the rotational speed of the inner core compare with the rest of the planet? |
Perhaps a century or more faster |
|
|
__________ is the transfer of heat by the mass movement or circulation in a substance. |
Convection |
|
|
It is thought that convection within the __________ of the rotating planet generates Earth's magnetic field. |
Outercore |
|
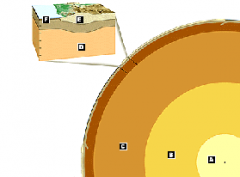
What are the physical properties of each layer? |
A. Solid iron and nickel composition B. Liquid iron and nickel composition C. Rich in the mineral perovskite D. Composed of the ultramafic rock peridotite E. Composition comparable to granodiorite F. Predominantly basalt |
|
|
What did Andrija Mohorovicic do? |
He discovered the discontinuity between the crust and the mantle in 1909. |
|
|
What did Inge Lehman do? |
Discovered the boundary between solid inner core and liquid outer core in 1936. |
|
|
What did Richard Dixon Oldham do? |
Discovered the central core of the earth in 1906 using the shadow effect of P and S waves. |
|
|
What did Beno Gutenberg do? |
Calculated the depth to core boundary at 2900 km. |
|
|
Continents lose heat faster than old oceanic seafloor because they contain higher amounts of heat-producing ___________. |
Radioactive isotopes |

