![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
3' end |
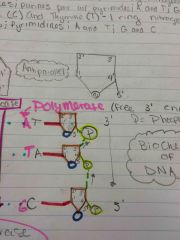
Back (Definition) |
Free 3' end |
|
|
5' end |
Where DNA polymerase begins |
DNA Polymerase |
|
|
A and P Site |
A site: where the second tRNA molecule binds
P site: where the first tRNA binds and the second moves to it |
tRNA |
|
|
Adenine |
2 ring nitrogenous base; purine; pairs with Thymine (T) |
A |
|
|
Anti-codon |
On the bottom of tRNA and allows it to bond with the codon; complementary to the codon but does not code for the amino acid |
Codons bind |
|
|
Codon |
Three consecutive nucleotides that specify a single amino acid |
Ex: AUG
Codes for methionine (met) |
|
|
Cyptoplasm |
Material inside the cell membrane but does not include the nucleus; transition takes place inside it |
Holds organelles |
|
|
Cytosine |
1 ring nitrogenous base; pyrimidines; pairs with Guanine (G) |
C |
|
|
Deletion |
Changes how codons are read |
Frame shift mutation and/or point mutation |
|
|
Deoxyribose |
Base of nucleotide; 5 carbon sugar |
DNA |
|
|
DNA |
Deoxyribose nucleic acid; codes for genes; double helix to histones to nucleosome to coils to supercoils to chromosome |
- Stores genetic info and provides instructions for protein synthesis - can be accurately copied each time it goes under mitosis - transmits genetic info from one generation to the next |
|
|
DNA helicase |
Unzips DNA at hydrogen bonds between base pairs |
Replication fork |
|
|
DNA Ligase |
Bonds lagging strand together to make a continuous chain |
Okazaki fragments |
|
|
DNA Polymerase |
Speeds up synthesis of DNA; uses DNA as a template; only synthesizes in the 5' to 3' direction; "proofreads" each DNA strand |
5' to 3' |
|
|
Duplication |
2 copies of a gene are made |
Chromosomal mutation |
|
|
Enhancer sites |
Where promoters can bind to start transcription; eukaryotic genes |
Transcription |
|
|
Frameshift mutations |
Mutations that shift the "raging frame" |
Deletions and Insertions |
|
|
Gene |
A sequence of DNA used to code for a specific protein |
Made up by DNA |
|
|
Guanine |
2 ring nitrogenous base; purines; bind to Cytosine (C) |
G |
|
|
Hox genes |
Genes that control the differentiation of cells and tissues within an embryo |
Pax6 gene- master control gene for gene development |
|
|
Insertion |
Change way codon is read; add of a nucleotide to DNA strand |
Point mutation and Frameshift mutation |
|
|
Inversion |
Changes order of genes |
Chromosomal mutation |
|
|
Lagging strand |
Made in direction opposite DNA helicase; made discontinuously |
Okazaki fragments |
|
|
Leading Strand |
Engender by DNA polymerase by adding DNA nucleotides; synthesized continuously |
Follows DNA helicase |
|
|
mRNA |
Complimentary to strand of DNA; extra oxygen; produced during transcription; Thymine (T) replaced by Uracil (U) |
Messenger RNA |
|
|
Nitrogenous base |
Base pair; A, T, G, or C |
Purines and Pyrimidines |
|
|
Nucleotide |
5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose), phosphate group, and nitrogenous base |
Backbone of DNA |
|
|
Nucleus |
Where transcription occurs; stores DNA; controls activities of the cell |
Brain of the cell |
|
|
Okazaki fragment |
Segment made on lagging strand; causes DNA to be discontinuous and DNA to take part |
Gaps in DNA |
|
|
Operon |
Groups of genes operating together |
Common in prokaryotes; lac operon |
|
|
Peptide bonds |
Between amino acids |
Holds polypeptide together |

